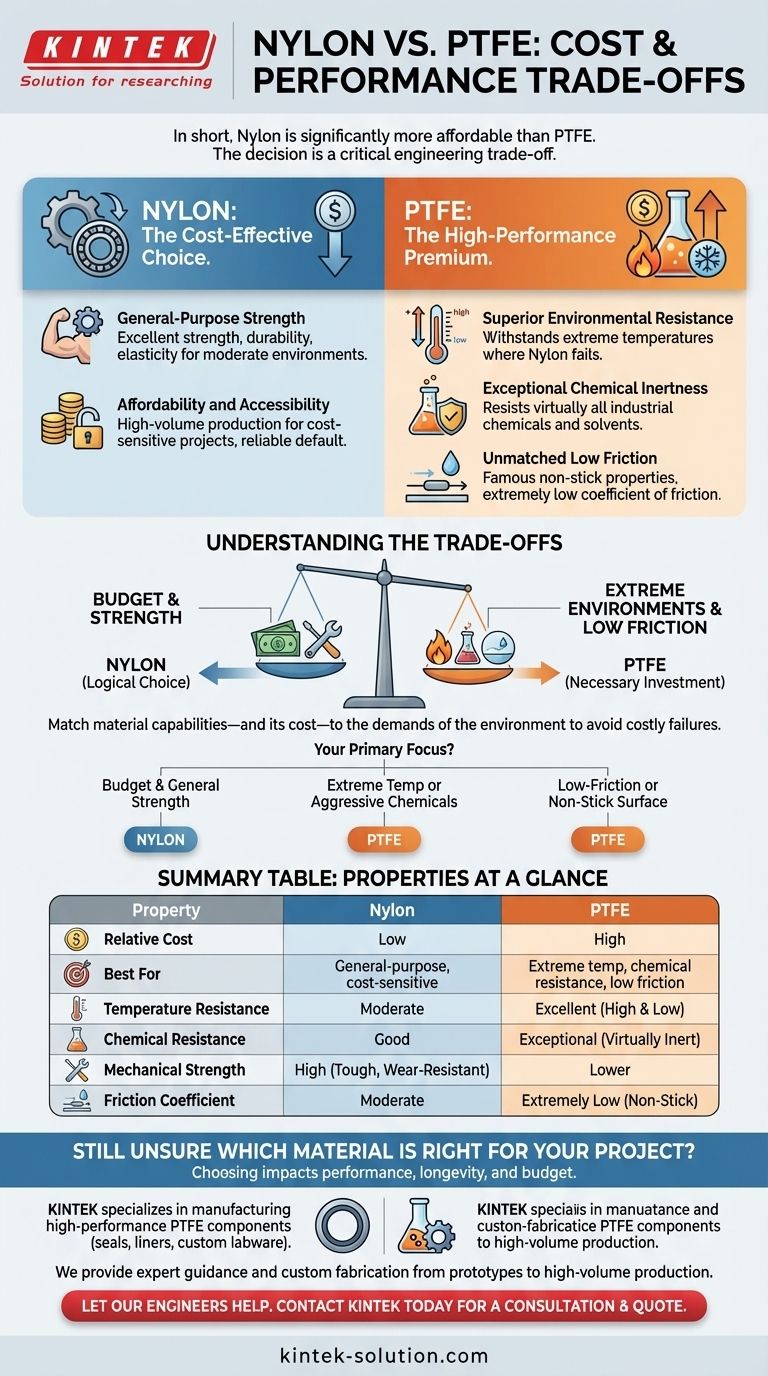
In short, Nylon is significantly more affordable than PTFE. This cost difference is a direct result of their fundamental properties and manufacturing processes. Nylon is a versatile, cost-effective polymer for general-purpose applications, while PTFE is a high-performance, premium material engineered for specialized and demanding environments.
The decision between Nylon and PTFE is rarely about cost alone. It is a critical engineering trade-off between budget constraints and the non-negotiable performance requirements of your specific application, such as temperature, chemical exposure, and friction.

Why Nylon is the Cost-Effective Choice
Nylon's lower price point is a function of its widespread use and less complex manufacturing. It serves as a reliable default for many projects where extreme conditions are not a factor.
General-Purpose Strength
Nylon is known for its excellent combination of strength, durability, and elasticity. Its chemical structure, based on amide bonds, gives it the toughness required for components like gears, bearings, and structural parts in moderate environments.
Affordability and Accessibility
Because it meets the needs of a vast range of applications without being over-engineered, Nylon is produced in high volumes, making it a go-to material for cost-sensitive projects.
Why PTFE Commands a Higher Price
PTFE's higher cost is directly tied to its specialized manufacturing and the unique, high-performance properties that result from its chemical structure.
Superior Environmental Resistance
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is engineered for survival in harsh conditions. It can withstand extreme temperatures, both high and low, where Nylon would fail.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
The fluorine-carbon bonds in PTFE's structure are incredibly strong, making it almost completely inert. It resists virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents, a property for which engineers are willing to pay a premium.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE is famous for its non-stick properties and extremely low coefficient of friction. This makes it indispensable for applications like non-stick coatings and low-friction seals where surface interaction is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong material based on price can lead to costly failures. The key is to match the material's capabilities—and its cost—to the demands of the environment.
Cost vs. Critical Performance
Using PTFE in a simple mechanical application without chemical or temperature stress is an unnecessary expense. You are paying for performance characteristics you do not need.
Strength vs. Surface Properties
Nylon offers superior tensile strength and wear resistance for mechanical loads. PTFE is mechanically weaker but provides a low-friction, non-stick surface that Nylon cannot match.
Environment as the Deciding Factor
If your component will be exposed to aggressive chemicals or operate outside of a moderate temperature range, the higher upfront cost of PTFE becomes an essential investment to prevent premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific operational demands of your project, not just the initial material cost.
- If your primary focus is budget and general mechanical strength: Nylon is the clear and logical choice for your project.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures or aggressive chemical environments: The higher cost of PTFE is a necessary and justified investment.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE is the only material that can meet these specific performance demands.
Ultimately, selecting the right polymer is about investing in the precise properties required for long-term success and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Property | Nylon | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Relative Cost | Low | High |
| Best For | General-purpose, cost-sensitive applications | Extreme temperatures, chemical resistance, low friction |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate | Excellent (High & Low) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Exceptional (Virtually Inert) |
| Mechanical Strength | High (Tough, Wear-Resistant) | Lower |
| Friction Coefficient | Moderate | Extremely Low (Non-Stick) |
Still Unsure Which Material is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between Nylon and PTFE is a critical decision that impacts performance, longevity, and budget. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide expert guidance to help you select the optimal material and offer custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume production, ensuring precision and reliability.
Let our engineers help you make the right choice. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















