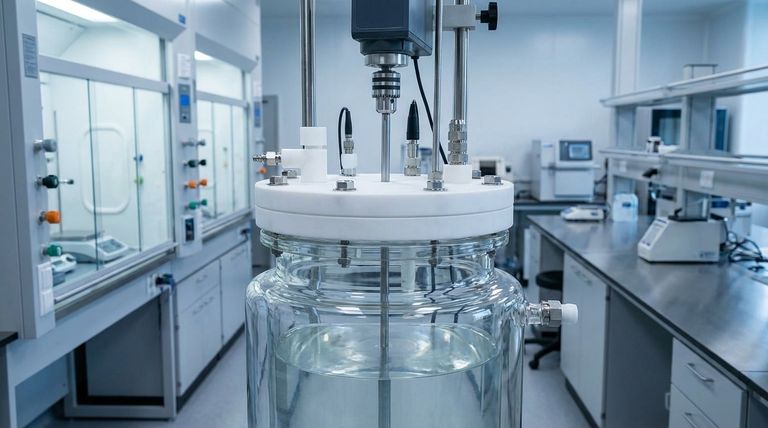
The primary advantages of PTFE lids are their superior durability and chemical resistance compared to glass. They are far less prone to breaking or chipping, especially when handling heavy analytical probes, and their inherent chemical inertness ensures they will not react with or contaminate the vessel's contents across a vast range of temperatures and chemical environments.
The choice to use a PTFE lid over a traditional glass one is a strategic shift from simple containment to an integrated, robust, and highly adaptable system. It prioritizes operational safety, chemical purity, and experimental flexibility above the single benefit of transparency offered by glass.

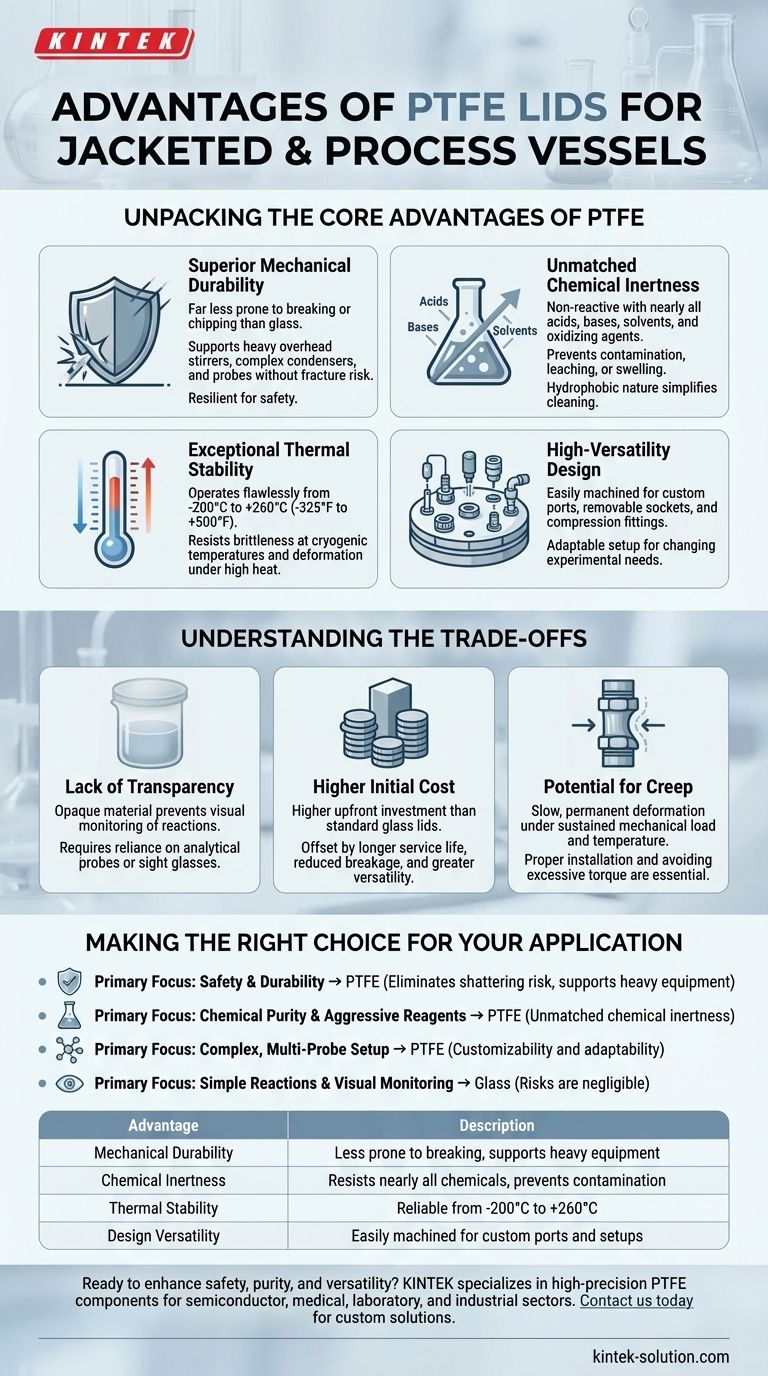
Unpacking the Core Advantages of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers a unique combination of physical and chemical properties that make it an ideal material for the demanding environment of jacketed process vessels.
Superior Mechanical Durability
Unlike glass, which is brittle and can shatter from impact or thermal shock, PTFE is mechanically robust. This resilience is critical for safety, preventing catastrophic failures and loss of valuable product.
It also means the lid can easily support the weight of heavy overhead stirrers, complex condenser setups, or multiple analytical probes without risk of fracture.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is renowned for its extreme resistance to chemical attack. It is non-reactive with nearly all acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizing agents.
This property ensures that the lid will not corrode, leach impurities into the reaction, or swell, which is a common issue with lesser polymers. Its hydrophobic (water-repellent) nature also simplifies cleaning and prevents cross-contamination.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Process vessels are often subjected to extreme heating and cooling cycles. PTFE lids operate flawlessly across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-325°F to +500°F).
This thermal stability prevents the material from becoming brittle at cryogenic temperatures or deforming under high heat, ensuring a reliable seal and structural integrity at all times.
High-Versatility Design
PTFE lids are easily machined to accommodate a wide variety of ports and fittings. They can accept removable sockets and compression fittings for probes, dosing lines, and sensors.
This adaptability allows for a highly customized setup that can be modified as experimental needs change, a level of flexibility that is difficult and costly to achieve with glass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE offers significant advantages, an objective assessment must also consider its limitations compared to the traditional alternative.
Lack of Transparency
The most significant trade-off is that PTFE is opaque. Unlike a glass lid, you cannot visually monitor the reaction, observe color changes, or check for foaming directly through the top of the vessel.
This requires reliance on analytical probes or sight glasses installed on the vessel body for visual confirmation of the process.
Higher Initial Cost
A custom-machined PTFE lid often represents a higher upfront investment compared to a standard glass lid.
However, this initial cost is frequently offset by a longer service life, reduced risk of breakage and replacement, and greater experimental versatility, leading to a lower total cost of ownership.
Potential for Creep
Under sustained mechanical load (like overtightened fittings) and elevated temperatures, PTFE can be subject to "creep," a slow, permanent deformation.
While high-quality PTFE exhibits good stress recovery, proper installation and avoiding excessive torque on fittings are essential to maintain a perfect, long-lasting seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right lid material depends entirely on the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is safety and durability: PTFE is the unequivocal choice to eliminate the risk of shattering and to safely support heavy ancillary equipment.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity with aggressive reagents: PTFE's unmatched chemical inertness provides the ultimate assurance against contamination or lid failure.
- If your primary focus is building a complex, multi-probe setup: The customizability and adaptability of a PTFE lid are essential for this goal.
- If your primary focus is simple reactions requiring direct visual monitoring: A traditional glass lid may suffice, provided the risks of breakage and chemical incompatibility are negligible.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE lid is an investment in a safer, more versatile, and more reliable process environment.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Durability | Far less prone to breaking or chipping than glass; supports heavy equipment. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all acids, bases, and solvents; prevents contamination. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs reliably from -200°C to +260°C. |
| Design Versatility | Easily machined for custom ports, fittings, and probe setups. |
Ready to enhance the safety, purity, and versatility of your process vessels?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom lids, seals, and liners for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get a durable, chemically inert solution tailored to your specific application, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our PTFE components can solve your most demanding challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















