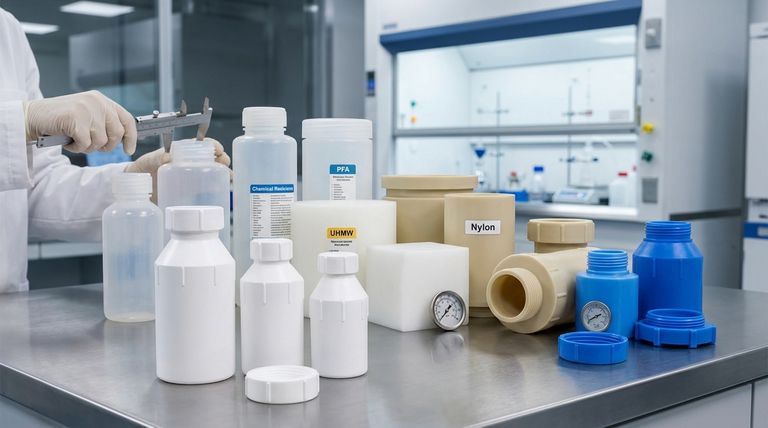
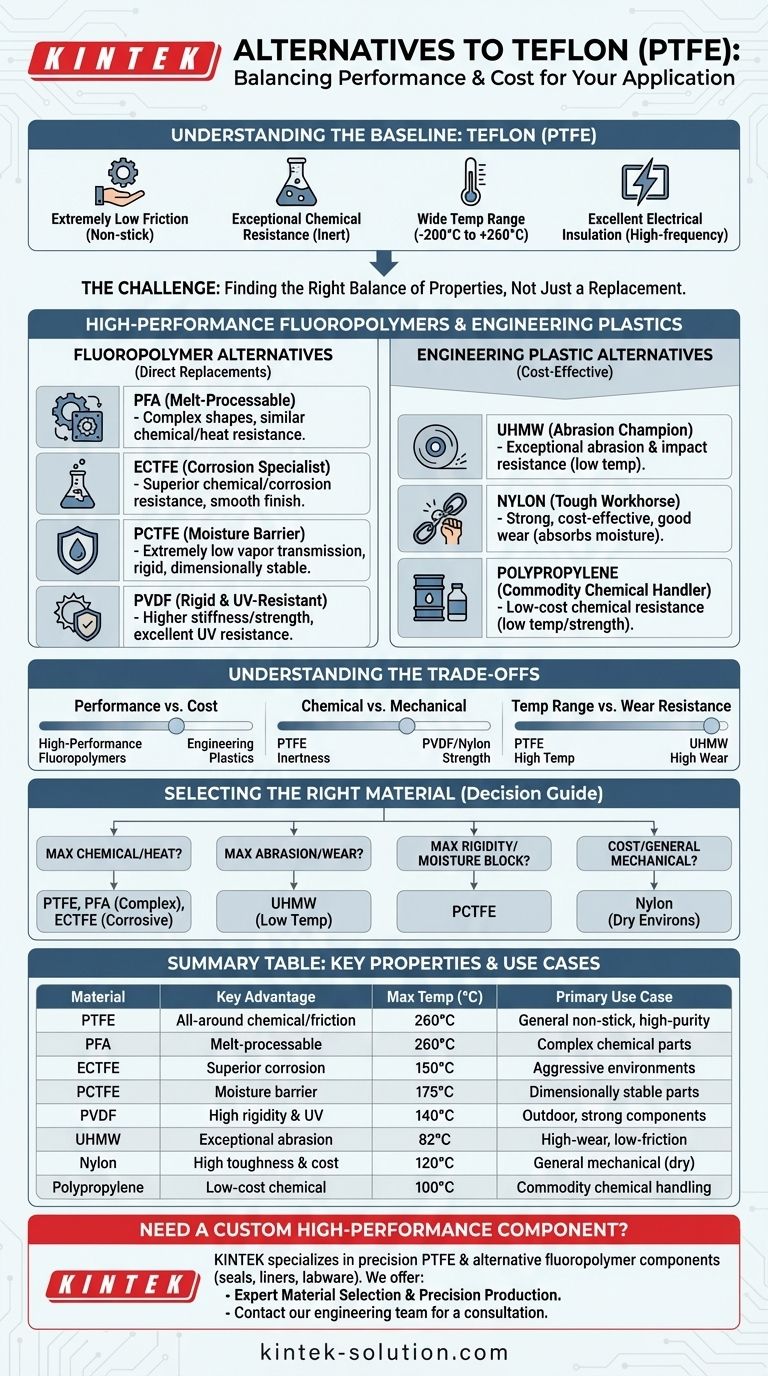
The most common alternatives to Teflon (PTFE) are other high-performance fluoropolymers like PFA, ECTFE, and PCTFE, as well as engineering plastics such as UHMW, PVDF, and Nylon. Each material offers a unique profile of chemical resistance, mechanical strength, temperature tolerance, and cost, making the best choice entirely dependent on the specific demands of your application.
The central challenge is not finding a replacement for Teflon, but rather identifying the specific properties you value most. Teflon provides an excellent all-around balance, but alternative materials often deliver superior performance in one or two key areas—such as abrasion resistance or rigidity—at a different price point.

Understanding the Baseline: Key Properties of Teflon (PTFE)
To evaluate alternatives, we must first establish the benchmark. Teflon is the brand name for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer prized for its unique combination of properties.
### An Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction values of any solid, making it exceptionally non-stick and self-lubricating. This is its most famous characteristic.
### Exceptional Chemical Resistance
Composed of a carbon-fluorine backbone, PTFE is inert and non-reactive to the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
### Wide Temperature Range
It maintains its properties reliably across a very wide temperature spectrum, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 500°F (260°C).
### Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is a superb electrical insulator with a low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, making it ideal for high-frequency applications.
High-Performance Fluoropolymer Alternatives
These materials are in the same chemical family as PTFE and often serve as direct replacements when a specific property needs to be enhanced.
### PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy): The Melt-Processable Teflon
PFA shares PTFE's outstanding chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance.
Its primary advantage is that it is melt-processable, meaning it can be easily injection molded or extruded into complex shapes, which is very difficult with PTFE. However, it is typically softer and has lower abrasion resistance.
### ECTFE (Ethylene chlorotrifluoroethylene): The Corrosion Specialist
ECTFE is renowned for its superior chemical and corrosion resistance, often outperforming other fluoropolymers in highly aggressive environments. It also offers high impact strength and a smooth surface finish.
### PCTFE (Polychlorotrifluoroethylene): The Moisture Barrier
PCTFE’s defining feature is its extremely low water vapor transmission rate, making it one of the best materials for moisture-sensitive applications. It is also significantly more rigid and dimensionally stable than PTFE but lacks its temperature range.
### PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride): The Rigid and UV-Resistant Option
PVDF is easier to process than PTFE and offers higher stiffness, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance. It also has excellent resistance to UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor use, though its chemical and thermal limits are lower than PTFE.
Common Engineering Plastic Alternatives
For applications where the extreme performance of a fluoropolymer is unnecessary, these more common plastics offer a cost-effective solution.
### UHMW (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene): The Abrasion Champion
UHMW is a an incredibly durable and slick plastic. Its key advantage is exceptional abrasion and impact resistance, often exceeding that of PTFE in high-wear applications.
However, its maximum service temperature is significantly lower, typically around 180°F (82°C).
### Nylon: The Tough and Cost-Effective Workhorse
Nylon is a mechanically strong and tough material with good wear properties. It serves as a low-cost alternative when high chemical or temperature resistance is not a primary concern. Its main weakness is its tendency to absorb moisture, which can affect its dimensional stability.
### Polypropylene: The Commodity Chemical Handler
Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of common acids, bases, and solvents at a very low cost. It is lightweight but has low mechanical strength and a very limited temperature range compared to fluoropolymers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an alternative to Teflon is an exercise in balancing competing requirements. There is no universally "better" material, only a more appropriate one for a given task.
### Performance vs. Cost
High-performance fluoropolymers like PFA and ECTFE are typically very expensive. Engineering plastics like Polypropylene and Nylon provide a massive cost reduction but come with significant compromises in thermal stability and chemical inertness.
### Chemical Resistance vs. Mechanical Strength
PTFE's incredible chemical inertness comes from its simple, strong C-F bonds. Materials that are mechanically stronger, like PVDF or Nylon, achieve this by introducing other elements that can create points of vulnerability for chemical attack.
### Temperature Range vs. Wear Resistance
While PTFE has an exceptional operating temperature range, a material like UHMW offers far superior resistance to abrasive wear but will fail completely at temperatures where PTFE thrives.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Use your primary engineering goal to guide your decision-making process.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical and heat resistance: PTFE remains the benchmark, but consider PFA for easier fabrication or ECTFE for specific corrosive agents.
- If your primary focus is abrasion and wear resistance: UHMW is often a superior and more cost-effective choice, provided the operating temperature is low.
- If your primary focus is rigidity and moisture blocking: PCTFE offers excellent dimensional stability and the lowest water vapor transmission available in a fluoropolymer.
- If your primary focus is cost for general-purpose mechanical parts: Nylon is a strong contender, but you must carefully verify its chemical compatibility and account for moisture absorption.
Ultimately, selecting the right material requires a clear understanding of your application's unique pressures and constraints.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Advantage | Max Temp (°C) | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE (Teflon) | All-around chemical resistance & low friction | 260°C | General-purpose, non-stick, high-purity |
| PFA | Melt-processable for complex shapes | 260°C | Chemically resistant, complex parts |
| ECTFE | Superior corrosion resistance | 150°C | Highly aggressive chemical environments |
| PCTFE | Excellent moisture barrier & rigidity | 175°C | Moisture-sensitive, dimensionally stable parts |
| PVDF | High rigidity & UV resistance | 140°C | Outdoor, mechanically strong components |
| UHMW | Exceptional abrasion resistance | 82°C | High-wear, low-friction applications |
| Nylon | High toughness & cost-effective | 120°C | General mechanical parts (dry environments) |
| Polypropylene | Low-cost chemical resistance | 100°C | Commodity chemical handling |
Need a Custom High-Performance Component?
Selecting the right polymer is critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE and alternative fluoropolymer components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer:
- Expert Material Selection: Leverage our deep knowledge of fluoropolymers and engineering plastics to identify the optimal material for your specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical requirements.
- Precision Production & Custom Fabrication: From rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs, we ensure every part meets your exact specifications for performance and reliability.
Let's discuss your application requirements and find the perfect material solution. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Evaporating Dishes for Diverse Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key applications of the PTFE bottle? Ensure Chemical Safety and Sample Purity
- How does the PTFE bottle perform in terms of chemical resistance? Unmatched Protection for Harsh Chemicals
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What is the molecular structure of PTFE? The Key to Its Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the characteristics of narrow mouth PTFE laboratory bottles? Superior Chemical Resistance & Purity



















