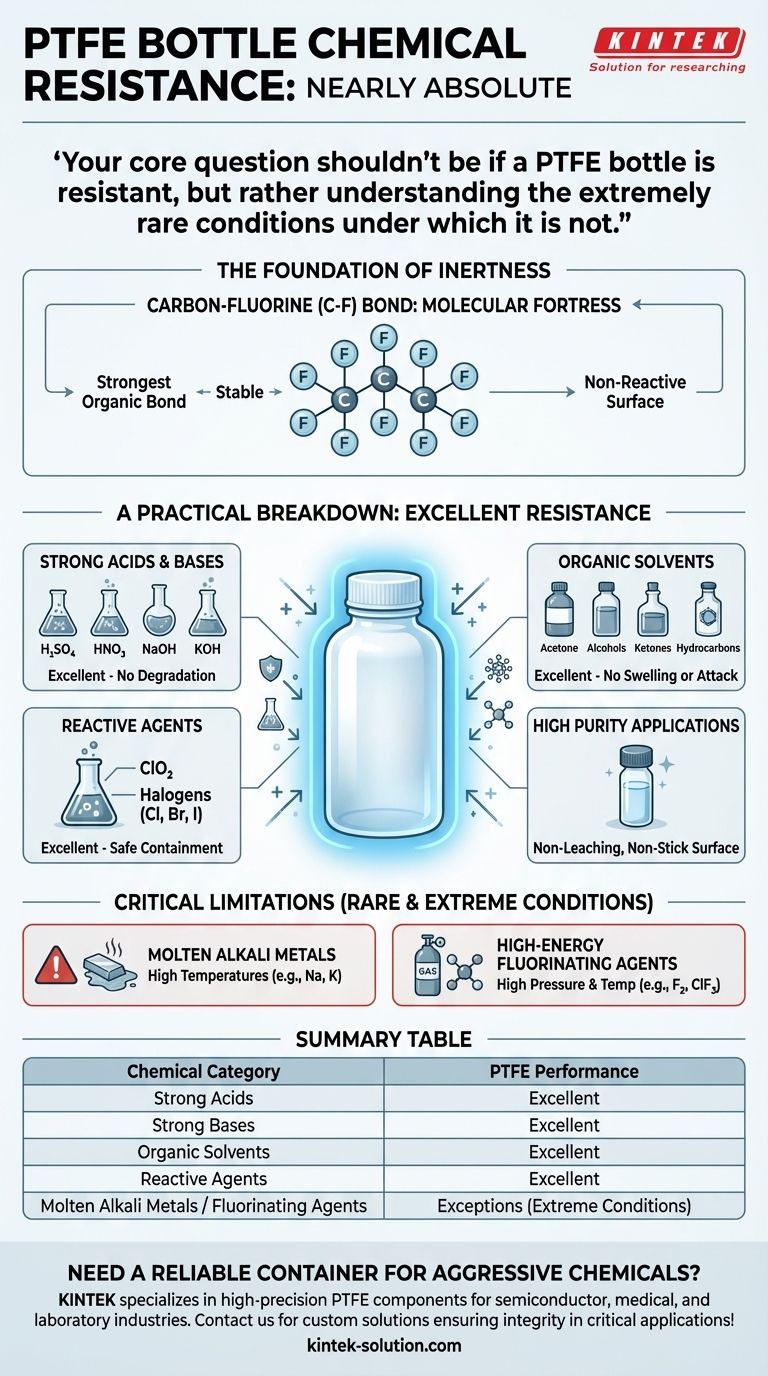
In short, the chemical resistance of a PTFE bottle is nearly absolute. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically inert materials used in laboratory and industrial settings. It is the default choice for safely handling a vast range of aggressive substances, including strong acids, bases, organic solvents, and highly reactive agents that would degrade most other materials.
Your core question shouldn't be if a PTFE bottle is resistant, but rather understanding the extremely rare conditions under which it is not. For virtually all common and corrosive chemical applications, PTFE provides complete and reliable containment.

The Foundation of PTFE's Inertness
The exceptional performance of PTFE is not a coincidence; it is a direct result of its unique molecular structure. Understanding this structure explains why it is so non-reactive.
The Unbreakable Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This molecular "fortress" is incredibly stable and requires an immense amount of energy to break, preventing other chemicals from reacting with the polymer chain.
A Non-Stick, Non-Reactive Surface
This stable structure gives PTFE its famously non-reactive and non-stick (hydrophobic and oleophobic) surface. Chemicals have no sites to "grab onto" to initiate a reaction, and the material will not leach ions or plasticizers into a solution. This makes it ideal for applications requiring ultra-high purity.
A Practical Breakdown of PTFE's Resistance
When we say PTFE has "excellent" resistance, it means it shows no signs of degradation, swelling, or chemical attack when exposed to the vast majority of chemicals.
Strong Acids and Bases
PTFE is completely resistant to concentrated and dilute acids like sulfuric, nitric, and hydrochloric acid. It is equally unaffected by strong bases such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
Organic Solvents and Hydrocarbons
It performs flawlessly with a broad spectrum of organic compounds, including alcohols, ketones, esters, and hydrocarbons (oils, greases, fuels). Where other plastics might soften or dissolve, PTFE remains stable.
Reactive Agents and Halogens
PTFE safely contains aggressive oxidizers and disinfectants like chlorine dioxide. It is also resistant to most halogens, such as chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The key exception is elemental fluorine itself, under specific conditions.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
No material is perfect, and building trust means understanding a material's few, specific failure points. The exceptions for PTFE are rare and typically involve extreme conditions not found in most laboratories.
Molten Alkali Metals
At high temperatures, molten or dissolved alkali metals (like sodium or potassium) can react with and defluorinate the PTFE polymer. This is a highly specific and niche application.
High-Energy Fluorinating Agents
While PTFE is made from fluorine, certain highly reactive fluorine compounds can attack it. These include elemental fluorine gas (F₂) and compounds like chlorine trifluoride (ClF₃), particularly under elevated pressure and temperature.
The Role of Temperature and Pressure
It is critical to note that PTFE's chemical resistance is specified over its standard operating temperature range (typically up to 260°C / 500°F). The rare reactions mentioned above are almost always initiated or accelerated by extreme heat and pressure, conditions far outside normal storage or handling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use PTFE should be based on a clear understanding of your chemical environment and safety requirements.
- If your primary focus is storing aggressive acids, bases, or solvents: PTFE is the safest and most reliable choice, ensuring container integrity and preventing leaks.
- If your primary focus is maintaining the purity of a sample: PTFE's non-leaching and non-reactive nature makes it the gold standard for preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is working with molten alkali metals or high-pressure fluorine gas: You are in a highly specialized field and must seek alternatives, as PTFE is one of the few materials that will not withstand these specific conditions.
By understanding both its unmatched resistance and its specific, rare exceptions, you can deploy PTFE with complete confidence in your critical applications.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | PTFE Bottle Performance |
|---|---|
| Strong Acids (e.g., Sulfuric, Nitric) | Excellent - No degradation |
| Strong Bases (e.g., Sodium Hydroxide) | Excellent - No degradation |
| Organic Solvents (e.g., Acetone, Alcohols) | Excellent - No swelling or attack |
| Reactive Agents (e.g., Chlorine Dioxide) | Excellent - Safe containment |
| Exceptions | Conditions for Concern |
| Molten Alkali Metals | High temperatures can cause reaction |
| Fluorinating Agents (e.g., F₂ gas) | High pressure and temperature |
Need a reliable container for aggressive chemicals? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including bottles, seals, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our custom fabrication ensures your containers are perfectly suited to your specific chemical environment, from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss your project and ensure the integrity of your critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of PTFE shovels being autoclavable? Ensuring Absolute Sterility for Sensitive Processes
- What are the primary applications of PTFE syringe filters in laboratories? Ensure Sample Purity & Protect Sensitive Instruments
- What types of PTFE-lined bottle caps are available? Find the Perfect Seal for Your Application
- What types of PTFE liners are available for bottle caps? Choose Between Solid PTFE or Composite Liners
- What are the best practices for using PTFE syringe filters? Achieve Pure, Reliable Filtration
- Why should PTFE plugs not be used for long-term storage of liquids that attack glass? Avoid Dangerous Seal Failure
- What are PTFE ferromagnetic support discs composed of? A Dual-Material Design for Superior Grinding & Polishing
- What are the main advantages of PTFE as a material for laboratory bottles? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















