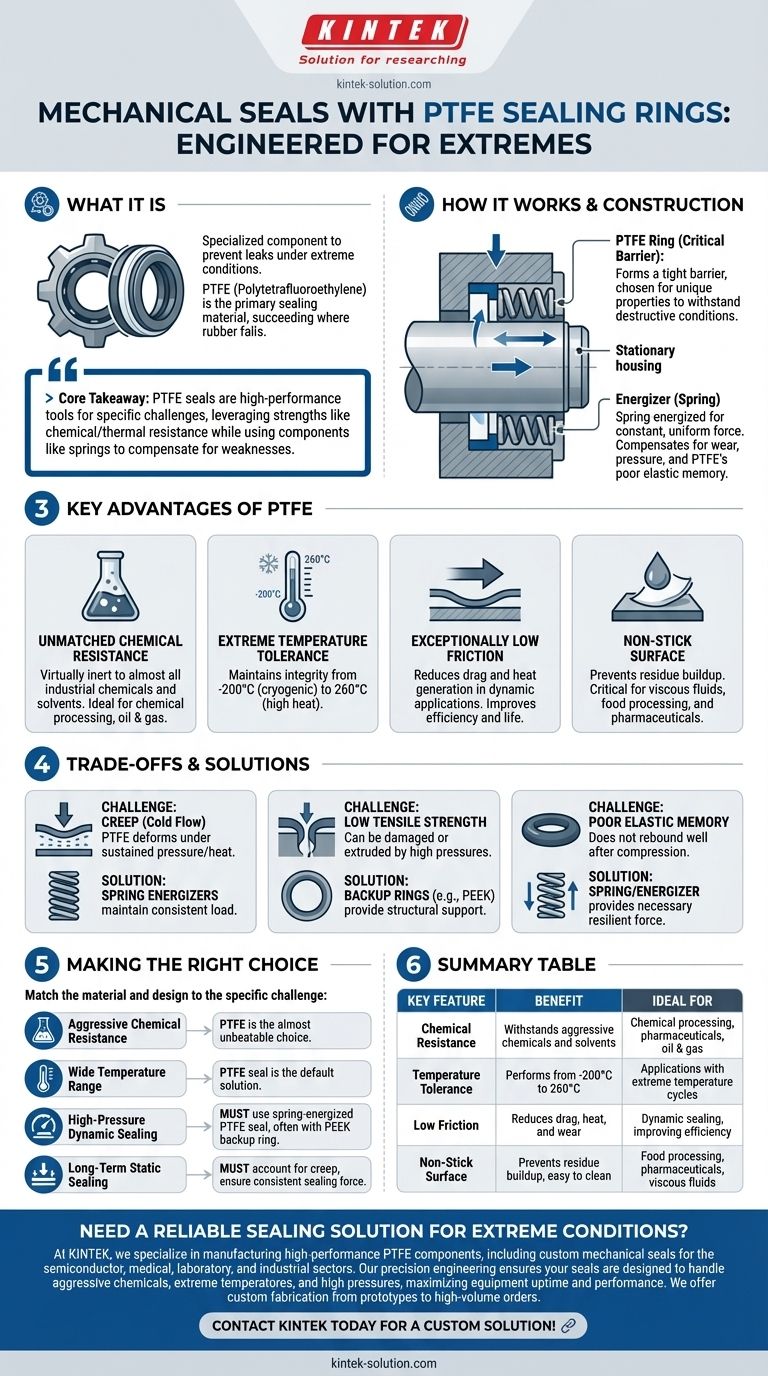
To put it simply, a mechanical seal with a PTFE sealing ring is a specialized component used to prevent leaks between moving parts in machinery operating under extreme conditions. These seals use Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as the primary sealing material because its unique properties allow it to succeed where traditional rubber or elastomer seals would quickly fail due to aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, or excessive friction.
The core takeaway is that PTFE seals are not a general-purpose solution but a high-performance tool for specific challenges. Their effectiveness relies on a design that leverages PTFE's strengths—like chemical and thermal resistance—while using components like metal springs to compensate for its inherent weaknesses, such as its tendency to deform under pressure.

How These Seals Are Constructed and Work
A standard mechanical seal creates a barrier between a rotating shaft and stationary housing. The addition of PTFE elevates this function for demanding environments.
The Role of the PTFE Ring
The PTFE component is the critical sealing surface. It is chosen for its unique combination of properties, forming a tight barrier that can withstand conditions that would destroy other materials.
The Importance of the Energizer
Many high-performance PTFE seals are spring-energized. A metal spring (often made of stainless steel or another corrosion-resistant alloy) is embedded within a PTFE jacket.
The PTFE provides the chemically-inert, low-friction sealing surface, while the spring provides a constant, uniform force. This force ensures the seal remains engaged with the mating surfaces, compensating for wear, pressure fluctuations, and PTFE's poor elastic memory.
The Key Advantages of Using PTFE
Engineers specify PTFE when other materials are not viable. Its benefits are significant in the right context.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it essential for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and oil and gas.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing characteristics across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from cryogenic lows (-200°C) to high heat (260°C).
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This reduces drag and heat generation in dynamic (moving) applications, which improves efficiency and extends the operational life of the seal and the equipment.
Non-Stick Surface
The non-stick properties of PTFE prevent residue from building up on the seal face. This is critical in applications involving viscous fluids, food processing, or pharmaceuticals where cleanliness is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Trustworthy engineering requires acknowledging the limitations of PTFE to ensure a reliable seal design.
The Challenge of "Creep"
PTFE is susceptible to creep, or cold flow. Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform over time. This can lead to a loss of sealing force and potential leaks, which is why spring energizers are so critical to maintaining a consistent load.
Low Tensile Strength
On its own, pure PTFE has relatively low strength and can be damaged by high pressures. It can be forced, or "extruded," into the clearance gap between two components, causing seal failure.
To counteract this, seals for high-pressure applications often incorporate backup rings made from a stronger material like PEEK (polyetheretherketone). The backup ring provides structural support and prevents the PTFE from extruding.
Poor Elastic Memory
Unlike a rubber O-ring that springs back to its original shape, PTFE has very poor elasticity. Once compressed, it does not rebound well. This is the primary reason why designs must incorporate a spring or other energizer to provide the force needed for a resilient seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct seal requires matching the material and design to the specific operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical resistance: PTFE is an almost unbeatable choice due to its nearly universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is a wide temperature range: A PTFE seal is the default solution for applications that cycle between cryogenic cold and high heat.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure dynamic sealing: You must use a spring-energized PTFE seal, often paired with a PEEK backup ring to prevent extrusion.
- If your primary focus is long-term static sealing under a constant load: You must account for PTFE's tendency to creep and ensure the design maintains a consistent sealing force over time.
By understanding both its unique strengths and its specific limitations, you can leverage PTFE to create a highly reliable sealing system for the most challenging environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands aggressive chemicals and solvents | Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, oil & gas |
| Temperature Tolerance | Performs from -200°C to 260°C | Applications with extreme temperature cycles |
| Low Friction | Reduces drag, heat, and wear | Dynamic sealing, improving efficiency |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents residue buildup, easy to clean | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, viscous fluids |
Need a reliable sealing solution for extreme conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom mechanical seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision engineering ensures your seals are designed to handle aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high pressures, maximizing equipment uptime and performance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let our experts help you solve your toughest sealing challenges.
Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















