In the medical field, expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is a cornerstone material for implants and devices that must integrate with the human body. Its unique, mesh-like structure is ideal for applications like vascular grafts, surgical sutures, and hernia repair meshes because it encourages the body's own tissue to grow into it, creating a strong, natural bond over time.
The primary value of ePTFE in medicine stems from its unique microporous structure. This property allows it to act as a biocompatible scaffold, promoting natural tissue integration for permanent implants while its inherent low-friction nature benefits temporary devices.
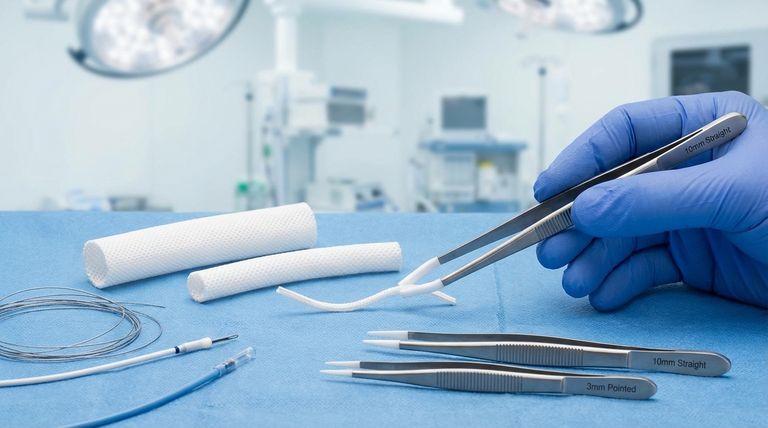
The Core Properties Driving Medical Innovation
To understand why ePTFE is so widely used, we must look at its fundamental characteristics. It is not just one property, but the combination of several, that makes it so effective for clinical applications.
The Microporous Structure
The "expansion" process creates a structure of solid PTFE nodes connected by thin fibrils, resulting in a material that is up to 70% air.
This web-like or porous nature is the key to its success in implants. It provides a scaffold that allows the body's own cells and blood vessels to grow into the material.
This process, known as tissue integration, makes the implant a seamless part of the body, reducing the risk of migration or rejection.
Biocompatibility and Inertness
Like standard PTFE, ePTFE is chemically inert and highly biocompatible. The human body does not recognize it as a foreign invader, which significantly minimizes the chance of an inflammatory or immune response.
This inertness ensures that the material will not break down or release harmful substances over its lifetime inside the body.
Strength and Flexibility
Despite its porous nature, ePTFE is remarkably strong and durable. It can withstand the dynamic forces within the body, such as the pressure of blood flow in a vascular graft.
At the same time, it is soft and flexible, allowing it to conform to the shape of anatomical structures and move with the body's tissues without causing irritation.
Key Applications in Practice
These core properties translate directly into critical, life-saving medical devices and components. Each application leverages a specific strength of the material.
Vascular Grafts and Heart Patches
ePTFE is a leading material for creating artificial blood vessels. Its porous structure allows endothelial cells to line the inner surface, creating a smooth, natural pathway for blood flow.
For patching holes in the heart, its strength prevents ruptures under pressure while its flexibility allows it to beat with the heart muscle.
Hernia Repair and Surgical Sutures
In hernia repair, ePTFE mesh acts as a durable scaffold to reinforce the weakened abdominal wall. Over time, tissue grows into the mesh, creating a permanent and robust repair.
As a suture material, ePTFE is valued for its strength and minimal tissue drag, making it easier for surgeons to work with delicate tissues.
Catheters and Guidewires
While the core of these devices may be another material, coating them with PTFE or ePTFE is common practice.
The material's exceptionally low coefficient of friction, or lubricity, allows these devices to be inserted and navigated through blood vessels with minimal trauma to the patient. This also reduces the ability of bacteria to adhere to the surface, lowering infection risk.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and ePTFE has considerations that are critical for medical device design. Objectivity requires acknowledging these realities.
The Challenge of Infection
While its surface resists bacterial adhesion, if an infection does take hold within the porous structure of an ePTFE implant, it can be very difficult to treat.
The same pores that encourage tissue ingrowth can also shield bacteria from the body's immune response and antibiotics, sometimes necessitating removal of the implant.
Not Suited for High-Load Bearing
While strong and flexible, ePTFE does not possess the compressive or shear strength required for orthopedic applications like joint or bone replacement. Its strengths lie in soft-tissue applications.
The Permanence of Integration
The excellent tissue ingrowth that makes ePTFE a superior material for permanent implants also makes it very difficult to remove. In cases where a revision surgery is needed, surgeons must carefully dissect the implant from the integrated native tissue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use ePTFE depends entirely on the specific engineering and clinical goal of the medical device.
- If your primary focus is permanent soft-tissue replacement: ePTFE is a premier choice for applications like vascular grafts and patches where long-term integration is the primary goal.
- If your primary focus is reducing surface friction on a temporary device: A PTFE or ePTFE coating is ideal for catheters, guidewires, and surgical instruments to improve patient comfort and reduce infection risk.
- If your primary focus is strong, biocompatible tissue reinforcement: ePTFE meshes provide an excellent and durable scaffold for applications like hernia repair.
Ultimately, ePTFE's distinct combination of porosity, biocompatibility, and strength has made it an indispensable tool in advancing modern medicine.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Medical Applications |
|---|---|
| Microporous Structure | Promotes natural tissue ingrowth for permanent implants like vascular grafts and hernia meshes. |
| Biocompatibility & Inertness | Minimizes inflammatory response; safe for long-term implantation. |
| Strength & Flexibility | Withstands dynamic bodily forces while conforming to anatomical structures. |
| Low Friction (Lubricity) | Ideal for coatings on temporary devices like catheters to ease insertion and reduce infection risk. |
Need High-Precision ePTFE or PTFE Components for Your Medical Device?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing custom PTFE and expanded PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. Our expertise in precision production ensures your devices meet the highest standards for biocompatibility and performance, from initial prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your next medical innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















