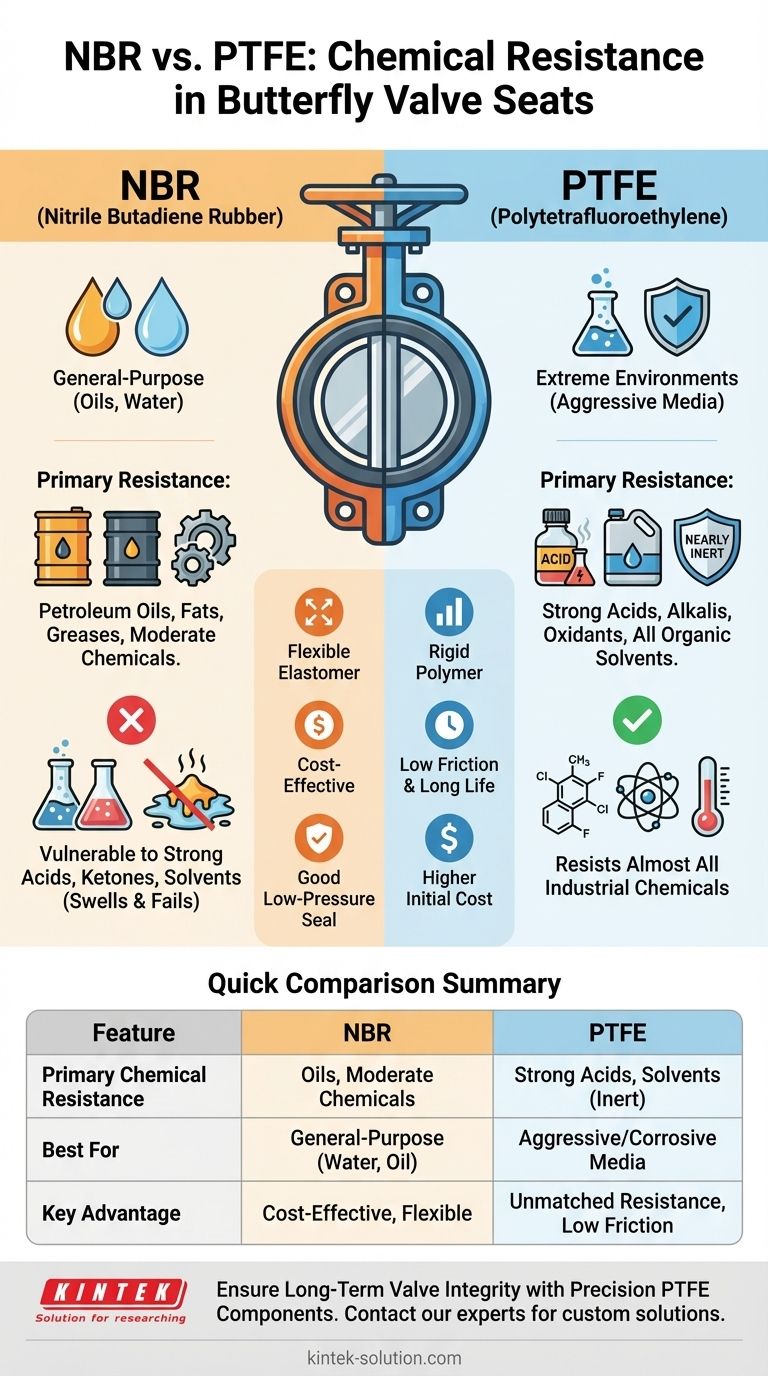
For butterfly valve seats, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) offers vastly superior chemical resistance compared to NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber). PTFE is nearly chemically inert and is the standard choice for highly corrosive and aggressive media. NBR provides good resistance to oils and moderate chemicals but will degrade quickly when exposed to the strong acids, solvents, or oxidants that PTFE handles with ease.
The choice between NBR and PTFE is not a simple question of which is "better," but a critical decision based on your specific operational environment. PTFE is the definitive choice for aggressive chemical applications, while NBR is a cost-effective and practical solution for general-purpose media like water and oils.

The Fundamental Difference in Chemical Inertness
The primary distinction between these two materials lies in their molecular stability. This stability dictates their performance when exposed to different substances, making one suitable for general use and the other essential for hazardous or corrosive service.
PTFE: The Standard for Extreme Environments
PTFE is characterized by its near-total chemical inertness. It is non-reactive and highly insoluble in almost all industrial solvents and corrosive substances.
This exceptional stability allows PTFE seats to reliably withstand exposure to a vast range of media, including strong acids, strong alkalis, strong oxidants, and all organic solvents.
In fact, PTFE is only known to react with a few highly specialized substances like fluorine gas, chlorine trifluoride, and molten alkali metals under extreme conditions. For virtually all industrial processes, it is considered completely resistant.
NBR: A Capable General-Purpose Material
NBR is a reliable elastomer known for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fats, and greases. It also performs well in water and with many moderate or diluted chemicals.
This makes NBR a popular and cost-effective choice for applications where the media is not chemically aggressive, such as in HVAC systems, water treatment, and general industrial plumbing.
However, NBR is not suitable for applications involving strong acids, ketones, or chlorinated hydrocarbons, as these substances will cause it to swell, soften, and fail.
Why the Choice Extends Beyond Chemistry
While chemical compatibility is the primary driver, other material properties influence the valve's performance, longevity, and cost.
Flexibility and Sealing Performance
As an elastomer, NBR is inherently more flexible than the relatively rigid polymer, PTFE. This flexibility allows NBR seats to create a tight seal with less torque, which can be an advantage in low-pressure applications.
Durability and Longevity
PTFE's performance is enhanced by its extremely low coefficient of friction. This "slipperiness" reduces the torque required to operate the valve and minimizes wear and tear on the seat during actuation.
This property, combined with its chemical stability, contributes to a longer service life in demanding environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong material is a common and costly mistake. The decision requires a clear understanding of the compromises involved with each choice.
Choosing NBR: The Practical Compromise
By selecting NBR, you are prioritizing lower cost and excellent flexibility. This is the correct choice for non-corrosive media where the risk of chemical attack is negligible.
The trade-off is a limited operational window. Exposing an NBR seat to an incompatible chemical, even for a short time, can lead to catastrophic valve failure, process contamination, and safety hazards.
Choosing PTFE: The Price of Unmatched Performance
By selecting PTFE, you are prioritizing maximum chemical resistance and long-term reliability in harsh conditions. It provides a massive safety margin against chemical attack.
The trade-off is typically higher initial cost and slightly less flexibility compared to rubber seats. However, this upfront cost is often negligible compared to the cost of downtime and replacement from a chemical-induced failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process media is the definitive factor in this decision. An honest assessment of the chemicals involved, including cleaning agents and potential impurities, is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: Choose PTFE. It is the only reliable option for strong acids, solvents, alkalis, and other corrosive media.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose applications: Choose NBR. It is the cost-effective and proven solution for water, oils, hydraulic fluids, and moderate chemicals.
Ultimately, matching the seat material to your specific chemical environment is the most critical factor in ensuring valve integrity and operational safety.
Summary Table:
| Feature | NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Chemical Resistance | Oils, fats, greases, water, moderate chemicals | Strong acids, alkalis, oxidants, solvents (nearly inert) |
| Best For | General-purpose, non-corrosive media (e.g., water, oils) | Highly aggressive and corrosive media |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective, flexible for tight sealing | Unmatched chemical resistance, low friction, long service life |
| Operational Limitation | Degrades with strong acids, ketones, chlorinated hydrocarbons | Higher initial cost, less flexible than elastomers |
Ensure Long-Term Valve Integrity with Precision PTFE Components
Selecting the correct seat material is critical for valve performance and safety. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision, chemically inert PTFE components—including custom butterfly valve seats—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver reliable solutions that withstand your most aggressive media, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Don't risk valve failure. Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and get a custom PTFE solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















