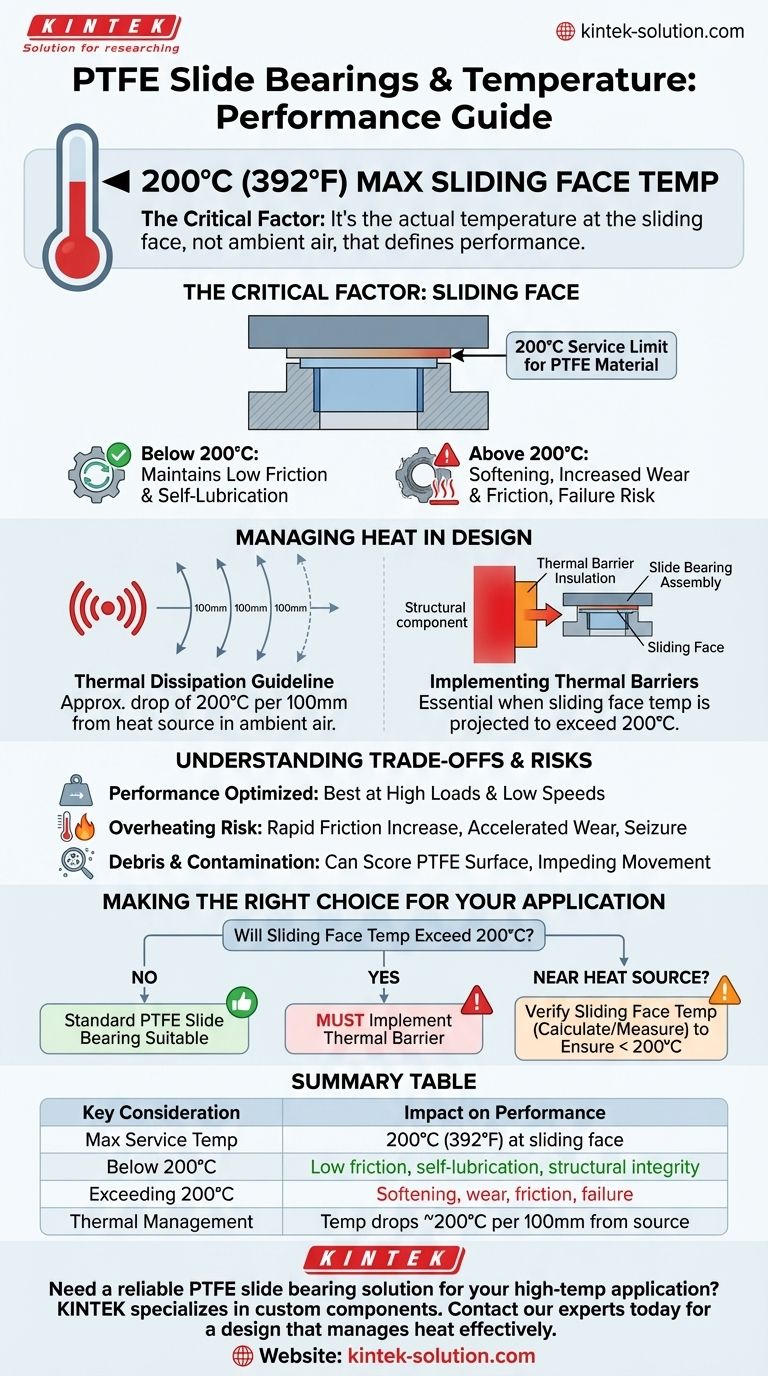
The single most important factor is the temperature at the bearing's sliding face. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) slide bearings maintain their low-friction properties and structural integrity up to a maximum continuous service temperature of 200°C (392°F). Exceeding this limit will degrade performance and can lead to premature failure.
Your primary design concern is not the ambient air temperature, but the actual temperature conducted to the PTFE surface. If this surface is expected to exceed 200°C, mitigation through design, such as adding a thermal barrier, becomes essential.

The Critical Factor: Temperature at the Sliding Face
The performance of a PTFE slide bearing is fundamentally tied to the material properties of its surface. While the overall structure might be exposed to high temperatures, it's the interface where sliding occurs that dictates the bearing's behavior.
The 200°C Service Limit
The 200°C (392°F) threshold is the established maximum service temperature for the PTFE sliding material itself. Below this temperature, the bearing will exhibit its expected low coefficient of friction and self-lubricating characteristics.
Why This Temperature Matters
When PTFE is heated beyond this service limit, its mechanical properties begin to change. The material can soften, leading to an increased rate of wear, higher friction, and a reduced load-carrying capacity, compromising the function of the entire assembly.
Managing Heat in Your Design
Successfully integrating PTFE bearings in high-temperature environments requires proactive thermal management. You must ensure the heat from the source does not elevate the sliding face temperature beyond its operational limit.
Understanding Thermal Dissipation
As a practical guideline, temperature in ambient air decreases significantly with distance. The drop is approximately 200°C for every 100mm of distance from the primary heat source.
This rule of thumb helps in initial design assessments, allowing you to estimate if the bearing's location is far enough from a heat source to operate safely without additional measures.
Implementing Thermal Barriers
When the temperature at the sliding face is projected to exceed 200°C, a thermal barrier is the standard solution.
This involves placing a layer of insulating material between the hot structural component and the slide bearing assembly. This barrier reduces the amount of heat conducted to the PTFE, keeping its surface temperature within the safe operating range.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While temperature is a critical parameter, it's essential to view it within the broader context of the bearing's operational characteristics and potential failure modes.
Performance Beyond Temperature
Remember that PTFE slide bearings are engineered for specific conditions. They perform optimally under high loads and at low speeds, where their self-lubricating properties are most effective. Mismatched applications can lead to poor performance regardless of temperature.
The Risk of Overheating
Ignoring the 200°C service limit is the most common cause of heat-related failure. The consequences include a rapid increase in friction, accelerated wear of the PTFE layer, and ultimately, a seizure of the sliding components.
Debris and Contamination
While PTFE bearings are considered maintenance-free, it's crucial to keep the sliding path clear. In high-heat environments, be mindful that surrounding materials could shed particles or degrade, creating debris that can score the PTFE surface and impede movement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use the temperature at the sliding face as your definitive guide for design and specification.
- If your sliding face temperature is consistently below 200°C: A standard PTFE slide bearing is suitable for your application without special thermal considerations.
- If a heat source is near the bearing: You must calculate or measure the temperature at the sliding face to verify it remains below the 200°C limit.
- If the sliding face temperature will exceed 200°C: Implementing a thermal barrier is not optional; it is a critical design requirement for ensuring operational reliability.
By actively managing heat transfer, you can confidently leverage the long-term, maintenance-free performance of PTFE slide bearings even in demanding thermal environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Temperature Consideration | Impact on PTFE Bearing Performance |
|---|---|
| Maximum Service Temperature | 200°C (392°F) at the sliding face |
| Below 200°C | Maintains low friction, self-lubrication, and structural integrity |
| Exceeding 200°C | Risk of softening, accelerated wear, increased friction, and failure |
| Thermal Management Guideline | Temperature drops ~200°C per 100mm from heat source in ambient air |
Need a reliable PTFE slide bearing solution for your high-temperature application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom slide bearings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production ensures your bearings meet exact thermal and mechanical requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can design a solution that manages heat effectively and ensures long-term, maintenance-free performance for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















