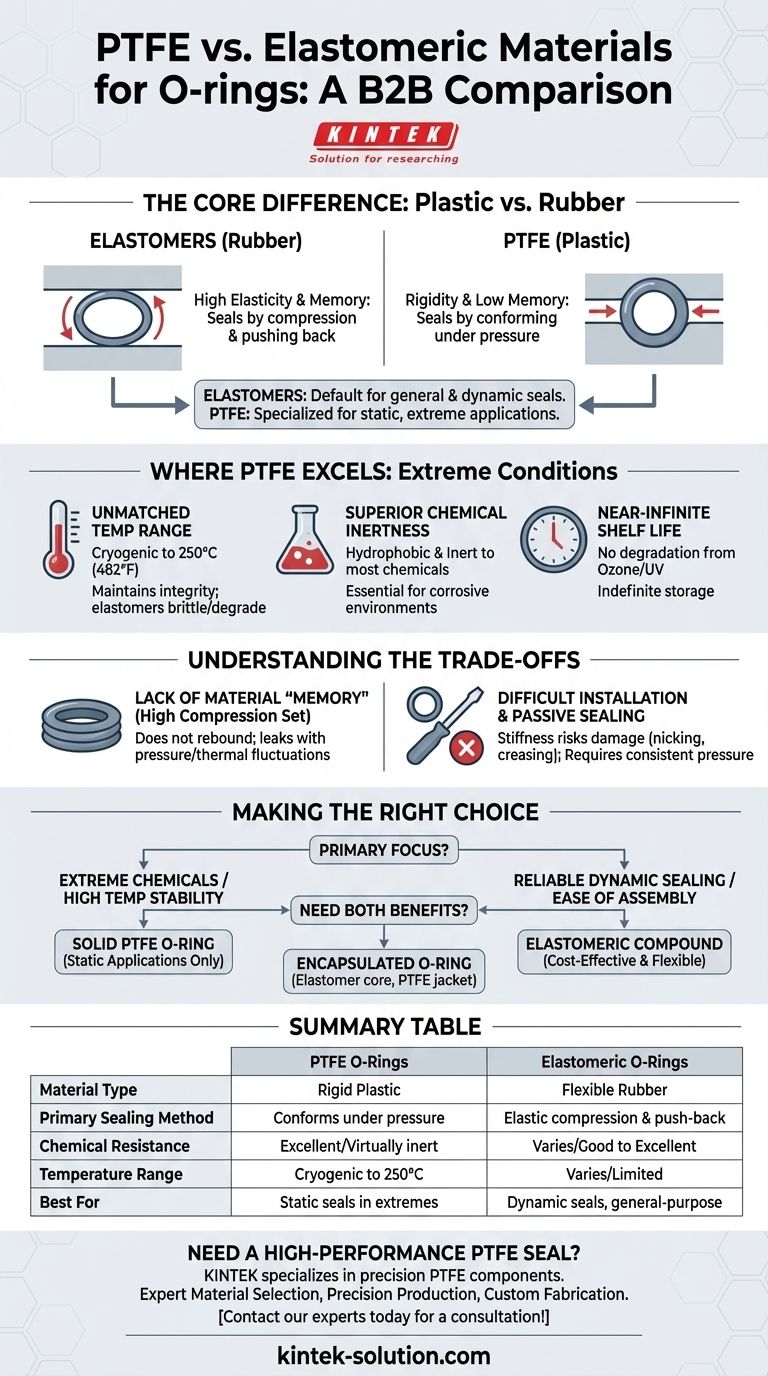
When choosing an O-ring for demanding environments, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers a level of chemical and thermal resistance that far surpasses traditional elastomeric (rubber) materials. Its unique molecular structure provides stability in conditions where rubber would quickly fail. However, PTFE is fundamentally a rigid plastic, not a flexible elastomer, which critically impacts its sealing ability and installation requirements.
The core distinction is one of physics: Elastomers seal by compressing and pushing back, while PTFE seals by being forced to conform to a surface. This makes elastomers the default for general-purpose and dynamic seals, while PTFE is a specialized solution for static applications facing extreme chemical or thermal attack.
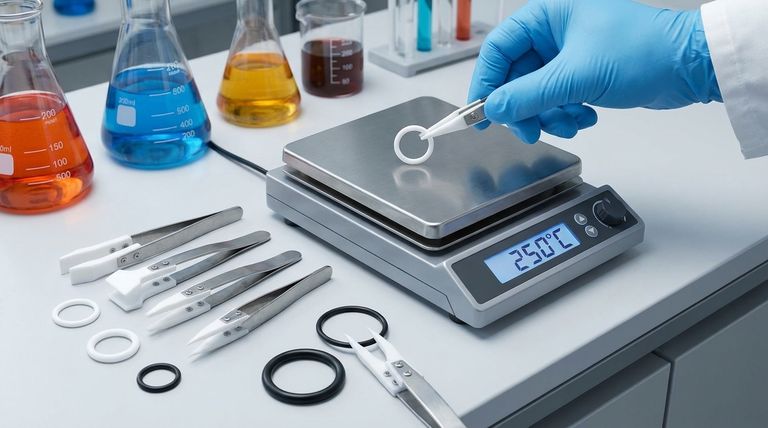

The Core Difference: Plastic vs. Rubber
To compare these materials, we must first understand their fundamental nature. This distinction is the root of all their practical differences.
Elastomers: The Power of Elasticity
Elastomers, like Nitrile (Buna-N) or Viton™ (FKM), are polymers defined by their high elasticity.
When an elastomeric O-ring is installed in a groove, it is compressed. Its material "memory" causes it to push back against the mating surfaces, creating a reliable and resilient seal that can tolerate minor surface imperfections and pressure fluctuations.
PTFE: The Strength of Rigidity
PTFE is a fluoropolymer—a type of plastic. It is dense, stiff, and has very little elasticity or "memory."
Once stretched or deformed, PTFE does not readily return to its original shape. It functions more like a high-performance gasket, relying on system pressure and extremely precise grooves to force it into place and create a seal.
Where PTFE Excels: Extreme Conditions
PTFE's unique properties make it the definitive choice when environmental conditions are the primary challenge.
Unmatched Temperature Range
Due to its high molecular weight and density, PTFE maintains its integrity and durability in a very wide temperature range, typically from cryogenic levels up to 250°C (482°F). Most elastomers will become brittle or degrade well before these limits.
Superior Chemical Inertness
PTFE is hydrophobic (water-repelling) and virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases. This makes it essential for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and other corrosive environments.
Near-Infinite Shelf Life
Unlike elastomers, which can dry out, crack, or lose their properties over time due to ozone and UV exposure, PTFE O-rings are not subject to this degradation. They can be stored indefinitely without any loss of performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sealing and Installation
The very rigidity that gives PTFE its strength also creates its primary weaknesses compared to flexible elastomers.
Lack of Material "Memory"
The most significant drawback of PTFE is its high compression set. It does not rebound after being compressed. If system pressure fluctuates or thermal cycling causes parts to expand and contract, a solid PTFE O-ring may not be able to adapt, leading to leaks.
Sealing Force and Reliability
An elastomeric O-ring actively pushes outward to maintain a seal. A PTFE O-ring is passive. This makes it less forgiving of surface irregularities and highly dependent on consistent pressure to keep it energized against the sealing surface.
Difficult Installation
The stiffness of PTFE makes O-rings challenging to install. They cannot be easily stretched over shafts or into tight grooves without a high risk of nicking, scratching, or creasing the material, which permanently damages its sealing capability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between these materials is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the engineering problem at hand.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical exposure or high-temperature stability: A solid PTFE O-ring is likely the necessary choice, but it must be used in a well-designed, static (non-moving) application.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing in a dynamic system or ease of assembly: An appropriate elastomeric compound is almost always the correct and more cost-effective solution.
- If you need the benefits of both: Consider an encapsulated O-ring, which features an elastomeric core inside a thin PTFE jacket, combining the chemical resistance of PTFE with the flexibility and sealing force of an elastomer.
By recognizing PTFE as a specialized plastic for extreme conditions, you can confidently specify the right material to ensure a durable and reliable seal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE O-Rings | Elastomeric O-Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid Plastic | Flexible Rubber |
| Primary Sealing Method | Conforms under pressure | Elastic compression & push-back |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Virtually inert) | Varies (Good to Excellent) |
| Temperature Range | Cryogenic to 250°C (482°F) | Varies (Limited by compound) |
| Flexibility & Memory | Low (High compression set) | High (Low compression set) |
| Best For | Static seals in extreme environments | Dynamic seals, general-purpose use |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal for Your Application?
Choosing the right O-ring material is critical for reliability and safety in demanding environments. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including O-rings, seals, and custom fabrications for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance on whether PTFE, an elastomer, or an encapsulated solution is best for your specific temperature, chemical, and pressure requirements.
- Precision Production: High-quality PTFE parts manufactured to exact specifications for a perfect, reliable seal.
- Custom Fabrication: From rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs, we tailor solutions to meet your unique needs.
Let us help you solve your toughest sealing challenges. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















