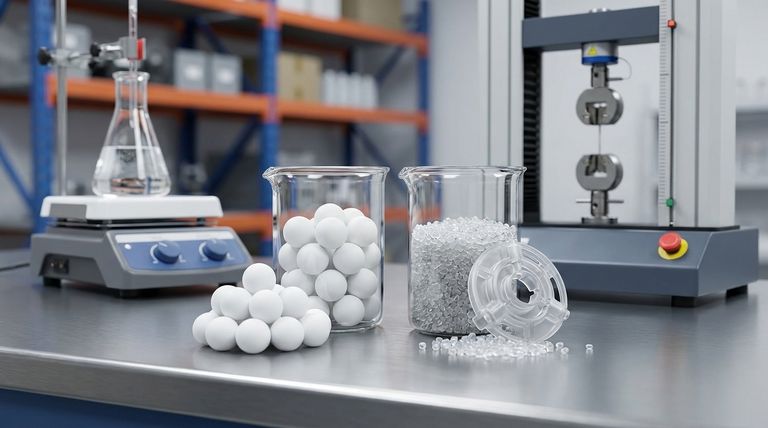
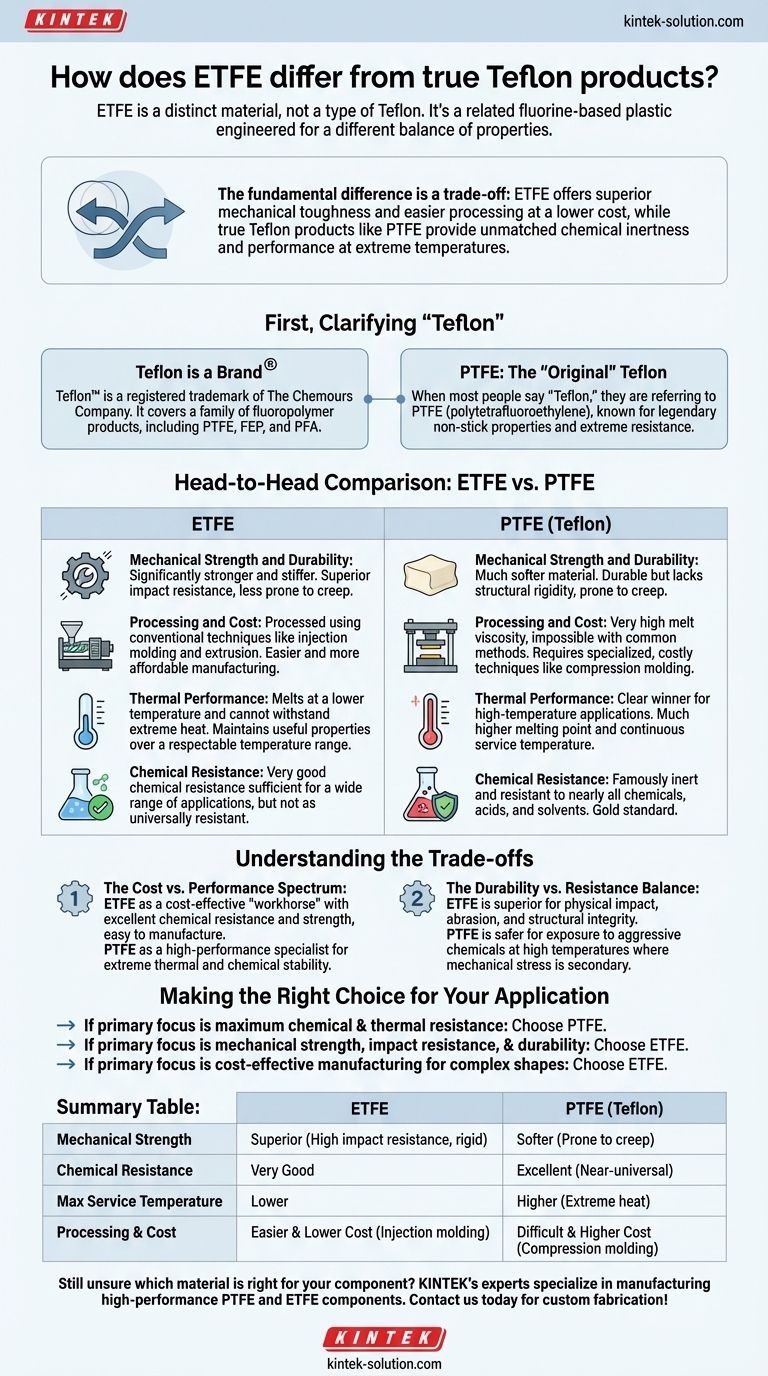
While often compared, ETFE is a distinct material, not a type of Teflon. Teflon is a brand name for a family of fluoropolymers, most famously PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene). ETFE (ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene) is a related fluorine-based plastic specifically engineered for a different balance of properties, prioritizing mechanical strength and easier manufacturing over the absolute thermal and chemical resistance of PTFE.
The fundamental difference is a trade-off: ETFE offers superior mechanical toughness and easier processing at a lower cost, while true Teflon products like PTFE provide unmatched chemical inertness and performance at extreme temperatures.

First, Clarifying "Teflon"
To understand the comparison, we must first define the terms accurately. The name "Teflon" often causes confusion because it's used colloquially for a single material when it's actually a brand.
Teflon is a Brand, Not a Single Material
Teflon™ is a registered trademark of The Chemours Company. It covers a family of fluoropolymer products, including PTFE, FEP, and PFA.
PTFE: The "Original" Teflon
When most people say "Teflon," they are referring to PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene). This material is known for its legendary non-stick properties and extreme resistance to chemicals and heat. For a clear comparison, we will treat PTFE as the primary "Teflon" product.
Head-to-Head Comparison: ETFE vs. PTFE
Choosing between these materials requires understanding their distinct advantages in specific performance categories.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
ETFE is significantly stronger and stiffer than PTFE. It has superior impact resistance and is less prone to "creep" or deforming under a sustained load.
PTFE, by contrast, is a much softer material. While durable in its own right, it lacks the structural rigidity of ETFE.
Processing and Cost
This is a primary differentiator. ETFE can be processed using conventional thermoplastic techniques like injection molding and extrusion. This makes manufacturing complex parts easier and more affordable.
PTFE has a very high melt viscosity, making it impossible to process with these common methods. It requires more specialized and costly techniques like compression molding and sintering.
Thermal Performance
PTFE is the clear winner for high-temperature applications. It has a much higher melting point and continuous service temperature than ETFE.
ETFE melts at a lower temperature and cannot withstand the extreme heat that PTFE can handle. However, it still maintains useful properties over a respectable temperature range.
Chemical Resistance
PTFE is famously inert and resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents, making it the gold standard for harsh chemical environments.
ETFE has very good chemical resistance that is sufficient for a wide range of applications, including labware. However, it is not as universally resistant as PTFE.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between ETFE and PTFE is not about which is "better" overall, but which possesses the right characteristics for a specific job.
The Cost vs. Performance Spectrum
ETFE can be seen as a more cost-effective "workhorse" fluoropolymer. It delivers an excellent combination of chemical resistance and mechanical strength in a material that is easy to manufacture.
PTFE is a high-performance specialist. Its higher cost is justified in applications where its extreme thermal stability and near-universal chemical inertness are non-negotiable requirements.
The Durability vs. Resistance Balance
If your application will experience physical impact, abrasion, or requires structural integrity, ETFE is almost always the superior choice.
If your component must survive exposure to aggressive chemicals at high temperatures, and mechanical stress is a secondary concern, PTFE is the safer option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your project's specific demands will dictate the correct material.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical and thermal resistance: Choose PTFE for its unmatched performance in extreme environments.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength, impact resistance, and durability: Choose ETFE for its superior toughness and structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective manufacturing for complex shapes: Choose ETFE for its compatibility with conventional injection molding.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material depends on a clear-eyed assessment of your project's specific mechanical, thermal, and chemical demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | ETFE | PTFE (Teflon) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Superior (High impact resistance, rigid) | Softer (Prone to creep) |
| Chemical Resistance | Very Good | Excellent (Near-universal) |
| Max Service Temperature | Lower | Higher (Extreme heat) |
| Processing & Cost | Easier & Lower Cost (Injection molding) | Difficult & Higher Cost (Compression molding) |
Still unsure which material is right for your component? KINTEK's experts specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and ETFE components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring precision and durability for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Evaporating Dishes for Diverse Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency
- How do the chemical properties of PTFE balls influence their performance? Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
- Why are PTFE balls particularly suitable for high-performance applications? Key Properties & Selection Guide
- What temperature range can Teflon (PTFE) balls withstand? -200°C to +260°C Performance Guide
- What are the available grades of PTFE balls? Choose the Right Grade for Your Application



















