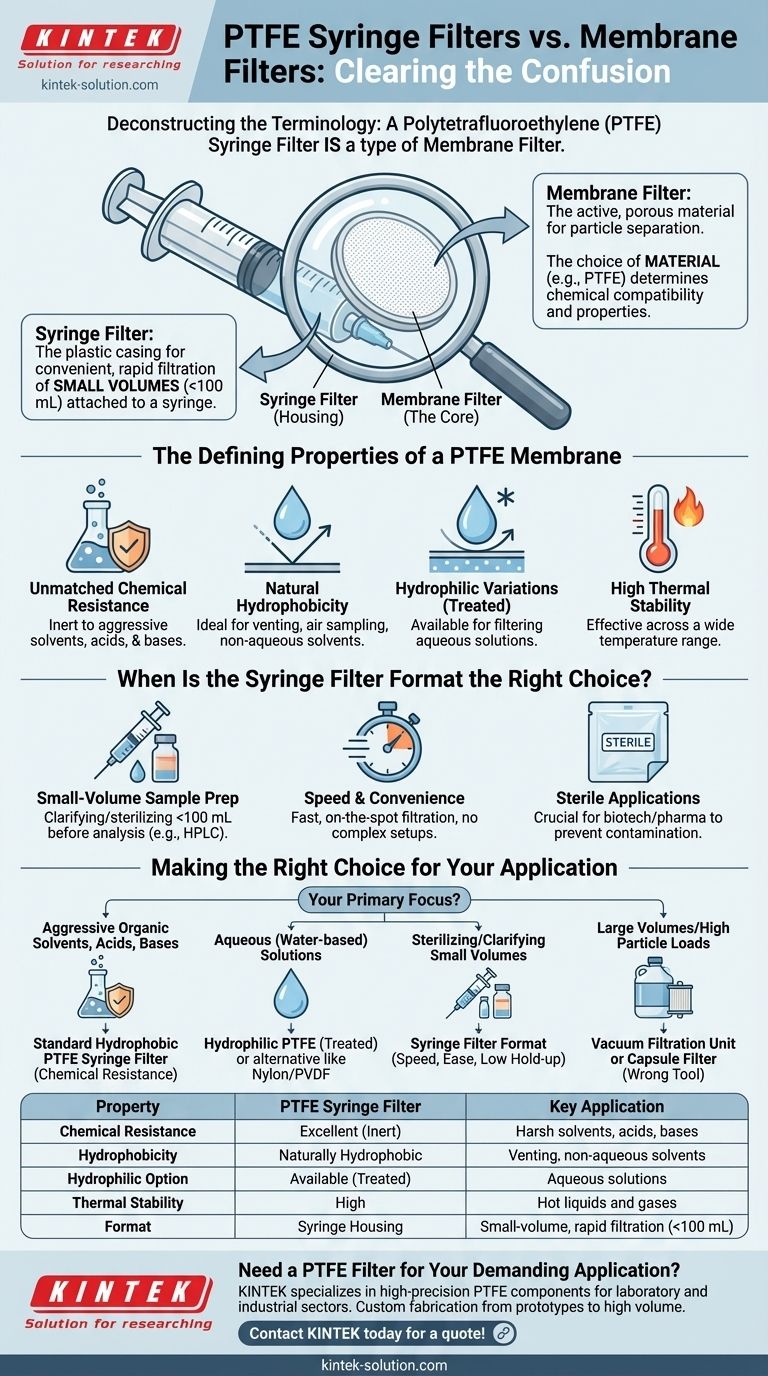
The fundamental confusion in this question is a common one: it compares a specific product to a general category. A Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) syringe filter is simply one type of membrane filter, where PTFE is the membrane material and the syringe filter is the device housing it. The real comparison is between PTFE and other membrane materials.
The core distinction is not between a "syringe filter" and a "membrane filter." Rather, it's about understanding that a syringe filter is a convenient housing for a small membrane, and the choice of the membrane material, such as PTFE, is what dictates its chemical compatibility and application.
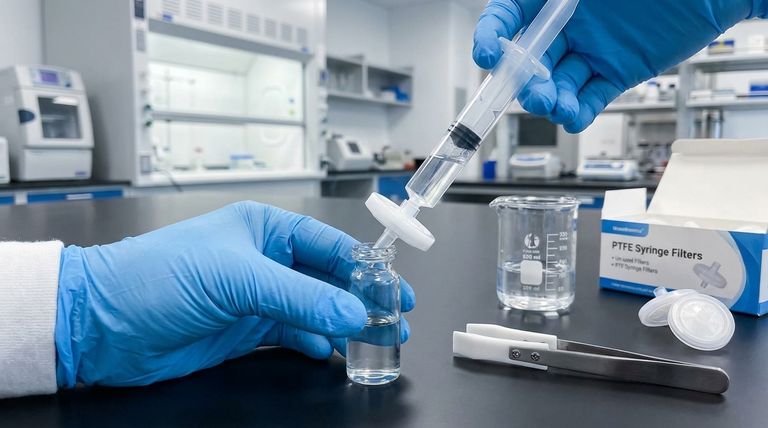

Deconstructing the Terminology: Material vs. Housing
To make an informed choice, you must first understand the two parts of the product: the functional membrane and the physical device that holds it.
What is a Membrane Filter?
A membrane filter is the thin, porous material that performs the actual particle separation. These membranes are made from various polymers, each with distinct properties.
The key is the membrane material, such as PTFE, Nylon, PVDF, or Polypropylene. This material choice determines chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and whether the filter is naturally water-attracting (hydrophilic) or water-repelling (hydrophobic).
What is a Syringe Filter?
A syringe filter is simply the plastic housing that encases the membrane filter. It's designed to be attached to the tip of a syringe.
This format is specifically for the convenient, rapid filtration of small liquid volumes, typically for sample preparation before analysis in instruments like an HPLC.
The Defining Properties of a PTFE Membrane
When you choose a PTFE syringe filter, you are choosing it for the unique characteristics of the PTFE material itself.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is renowned for its strong chemical inertness. It can withstand a vast range of aggressive and corrosive solvents, acids, and bases without degrading.
This makes it the default choice for filtering harsh organic solvents that would dissolve other membrane types.
Natural Hydrophobicity
Standard PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. This property makes it ideal for applications like venting, air sampling, and filtering non-aqueous solvents.
A laminated PTFE membrane, often supported by polypropylene, enhances strength and is excellent for phase separations.
Hydrophilic Variations
While naturally hydrophobic, PTFE membranes can be surface-treated to become hydrophilic (water-attracting).
This allows you to leverage PTFE's broad chemical and thermal stability for filtering aqueous solutions, combining the best of both worlds. It is critical to select this specific type for water-based samples.
High Thermal Stability
PTFE operates effectively across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for processes that involve filtering hot liquids or gases where other materials might fail.
When Is the Syringe Filter Format the Right Choice?
The syringe filter housing is designed for specific tasks where convenience and small volumes are key.
Small-Volume Sample Preparation
The primary use is for clarifying or sterilizing small liquid samples, typically less than 100 mL, before injection into an analytical instrument.
Speed and Convenience
This format allows for extremely fast, on-the-spot filtration directly from a syringe, eliminating the need for complex vacuum filtration setups for small jobs.
Sterile Applications
PTFE syringe filters are available in sterile, individually-packaged formats, making them essential for tasks in biotechnology and pharmaceutical labs where preventing microbial contamination is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct filter requires matching the material and format to your specific scientific goal.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive organic solvents, acids, or bases: A standard (hydrophobic) PTFE syringe filter is the most reliable choice due to its chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is filtering aqueous (water-based) solutions: You must use a specifically labeled hydrophilic PTFE filter or consider alternative materials like Nylon or PVDF.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing or clarifying small sample volumes: The syringe filter format is ideal for its speed, low hold-up volume, and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is filtering large volumes or solutions with high particle loads: The syringe filter is the wrong tool; you should use a vacuum filtration unit or a larger capsule filter instead.
Ultimately, understanding that the housing provides convenience while the membrane provides chemical compatibility is the key to selecting the right filter every time.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Syringe Filter | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Inert) | Harsh solvents, acids, bases |
| Hydrophobicity | Naturally Hydrophobic | Venting, non-aqueous solvents |
| Hydrophilic Option | Available (Surface-treated) | Aqueous solutions |
| Thermal Stability | High | Hot liquids and gases |
| Format | Syringe Housing | Small-volume, rapid filtration (<100 mL) |
Need a PTFE Filter for Your Demanding Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom syringe filters and membranes. Whether you are in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide the chemical resistance and reliability your processes demand.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get the exact filter solution for your unique needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















