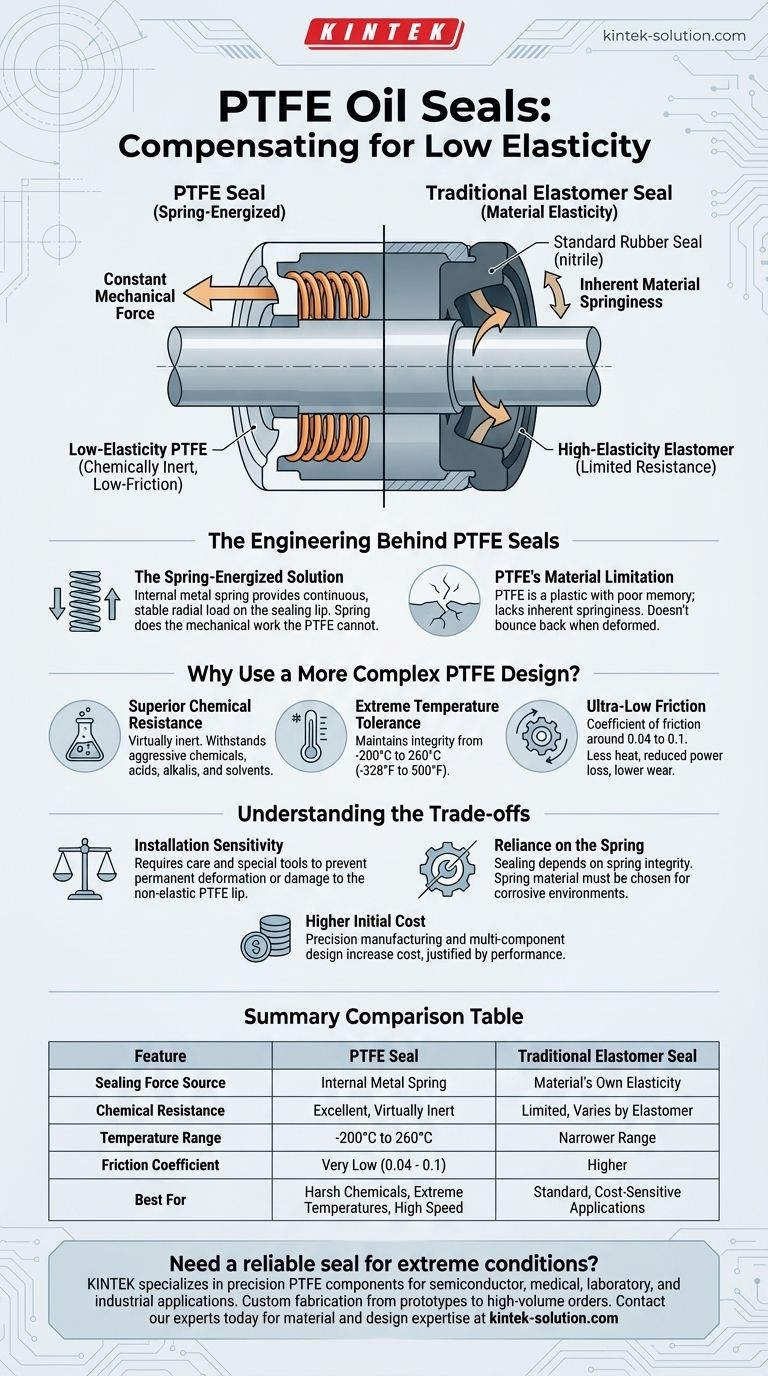
The short answer is: PTFE oil seals compensate for the material's low elasticity by incorporating a mechanical spring, typically made of stainless steel. This spring provides the constant radial force needed to press the sealing lip against the shaft, a job that the material's own elasticity would perform in a traditional rubber seal.
A PTFE seal cleverly separates the sealing material from the sealing force. It uses the chemically inert, low-friction PTFE for the contact surface and a dedicated internal spring to generate the consistent mechanical pressure required for a reliable seal.

The Engineering Behind PTFE Seals
To understand the design of a PTFE seal, it's helpful to first consider how a standard rubber seal works.
The Role of Elasticity in Traditional Seals
A traditional seal made from an elastomer like nitrile rubber relies on its own material elasticity. When installed, the seal is stretched or compressed, and its desire to return to its original shape creates the sealing force against the shaft. The material itself provides both the barrier and the pressure.
PTFE's Material Limitation
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance plastic, not an elastomer. It has very poor "memory" and lacks the inherent springiness of rubber. If you deform it, it does not readily bounce back to its original shape. This property makes it fundamentally unsuitable for a traditional seal design.
The Spring-Energized Solution
Engineers overcome this limitation with a two-part system. A precision-machined jacket is created from a PTFE compound, and a metal spring energizer is fitted inside it.
This stainless steel spring provides a continuous, stable radial load on the sealing lip. The spring does the mechanical work that the PTFE material cannot, ensuring the seal remains in constant, uniform contact with the shaft surface, even with minor imperfections or wear over time.
Why Use a More Complex PTFE Design?
This spring-energized design is intentionally more complex, but it unlocks the exceptional material properties of PTFE for sealing applications.
Superior Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert. It can withstand aggressive chemicals, strong acids, alkalis, and solvents that would quickly degrade standard rubber seals.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
The material maintains its integrity across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from approximately -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This makes it suitable for applications where elastomers would become brittle or break down.
Ultra-Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material (around 0.04 to 0.1). This translates to less heat generation, reduced power loss, and lower wear on both the seal and the shaft, which is critical in high-speed rotary applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PTFE seal design is not without its considerations.
Installation Sensitivity
Because PTFE is not elastic, the seal can be damaged during installation if not handled with care. Unlike a rubber seal that can be stretched over a shaft, a PTFE seal often requires special tools or procedures to prevent the lip from being permanently deformed or cut.
Reliance on the Spring
The entire sealing performance depends on the integrity of the internal spring. In highly corrosive environments, the spring material itself (even stainless steel) must be carefully selected to avoid failure, which would cause a complete loss of sealing pressure.
Higher Initial Cost
The multi-component design and precision manufacturing involved make spring-energized PTFE seals more expensive than simple molded elastomeric seals. This cost is justified by their performance and lifespan in demanding conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct seal requires matching the design to the operational demands.
- If your primary focus is a harsh chemical environment or extreme temperatures: A spring-energized PTFE seal is often the only reliable option, as its material properties vastly outperform standard elastomers.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, low-friction operation: The low friction of PTFE reduces wear and heat, making it the superior choice for demanding dynamic applications.
- If your primary focus is a standard, cost-sensitive application: A traditional elastomeric seal is likely the more practical and economical choice, as its simple design is sufficient for moderate conditions.
By understanding this principle of mechanical compensation, you can confidently specify PTFE seals for the challenging applications they were designed to solve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Seal | Traditional Elastomer Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Force Source | Internal Metal Spring | Material's Own Elasticity |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Virtually Inert) | Limited (Varies by Elastomer) |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Narrower Range |
| Friction Coefficient | Very Low (0.04 - 0.1) | Higher |
| Best For | Harsh Chemicals, Extreme Temperatures, High Speed | Standard, Cost-Sensitive Applications |
Need a reliable seal for extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a seal engineered for your specific challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and benefit from our material and design expertise!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















