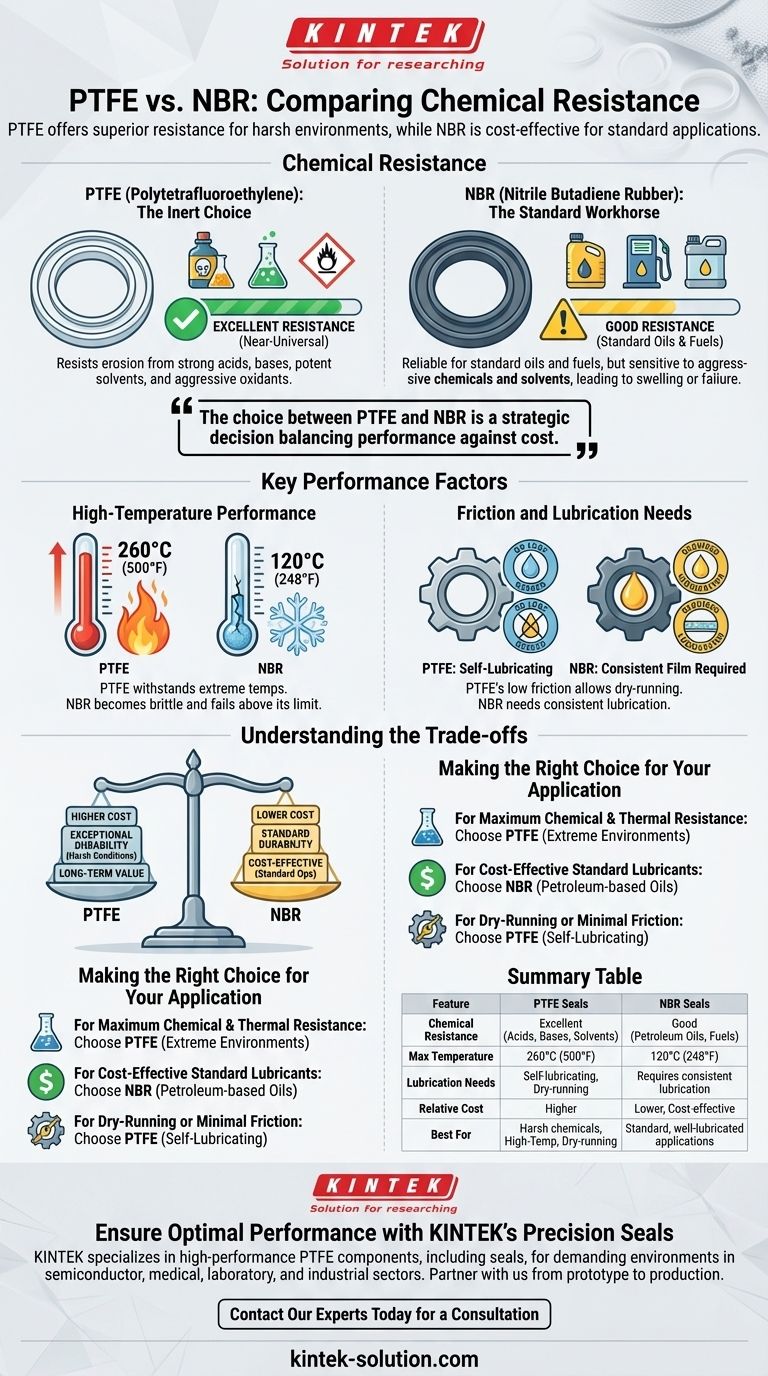
When comparing chemical resistance, PTFE oil seals are vastly superior to NBR seals. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a highly inert material, making it resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents. In contrast, Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is a reliable choice for standard oils and fuels but has limited resistance to more aggressive or corrosive substances.
The choice between PTFE and NBR is not merely about chemical resistance; it's a strategic decision balancing performance against cost. PTFE is the definitive solution for harsh chemical and high-temperature environments, while NBR is the cost-effective workhorse for standard, well-lubricated applications.

The Fundamental Difference in Material Chemistry
The core of the comparison lies in the inherent chemical stability of each material. Their molecular structures dictate how they react—or fail to react—with external substances.
PTFE: The Inert Choice
PTFE exhibits exceptional chemical stability, meaning it resists erosion from almost all chemicals. This includes strong acids, strong bases, potent solvents, and aggressive oxidants.
Its non-reactive nature makes it the ideal material for use in harsh chemical environments where other seals would quickly degrade and fail.
NBR: The Standard Workhorse
NBR is an excellent general-purpose elastomer known for its resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. It provides a reliable seal in countless standard industrial applications.
However, NBR is sensitive to certain aggressive chemicals and solvents, which can cause it to swell, harden, or dissolve over time, leading to seal failure.
Beyond Chemicals: Key Performance Factors
While chemical resistance is critical, a complete technical assessment must include other operational demands that often go hand-in-hand with aggressive media.
High-Temperature Performance
A significant advantage for PTFE is its ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It remains stable in applications up to 260°C (500°F).
NBR has a much lower temperature limit, typically around 120°C (248°F). Exceeding this limit will cause the material to become brittle and lose its sealing capability.
Friction and Lubrication Needs
PTFE is known for its extremely low coefficient of friction and self-lubricating properties. This allows it to be used in dry-running applications where consistent lubrication is not possible.
NBR seals, by contrast, require a consistent film of lubrication to function properly and prevent premature wear and failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right material requires a clear-eyed view of its practical limitations and cost implications.
The Cost Equation
There is a significant price difference between the two materials. PTFE seals are considerably more expensive due to the raw material and manufacturing process.
NBR is a much more affordable and widely available material, making it the default choice for budget-conscious projects with standard operating conditions.
Durability in Context
PTFE provides exceptional long-term durability in harsh conditions, justifying its higher initial cost by preventing frequent replacements and costly downtime.
NBR offers excellent durability and service life within its intended operational window—standard lubricants and moderate temperatures—making it a highly cost-effective and reliable choice for the vast majority of applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical and thermal resistance: Choose PTFE for its near-universal compatibility and ability to perform reliably in extreme environments.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for standard lubricants: NBR is the reliable and economical choice for applications involving petroleum-based oils and moderate temperatures.
- If your application involves dry-running or requires minimal friction: PTFE is the only suitable option due to its inherent self-lubricating properties.
By understanding these core differences, you can select a seal that ensures both reliability and cost-effectiveness for your specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Seals | NBR Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Resists acids, bases, solvents) | Good (Resists petroleum oils, fuels) |
| Max Temperature | 260°C (500°F) | 120°C (248°F) |
| Lubrication Needs | Self-lubricating, suitable for dry-running | Requires consistent lubrication |
| Relative Cost | Higher | Lower, cost-effective |
| Best For | Harsh chemical, high-temperature, or dry-running applications | Standard, well-lubricated applications with moderate temperatures |
Ensure Optimal Performance and Reliability with KINTEK's Precision Seals
Choosing the right seal material is critical to the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. The wrong choice can lead to premature failure, costly downtime, and product contamination.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the most demanding environments. Whether you operate in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, we provide the chemical and thermal resistance your applications require.
We partner with you from prototype to high-volume production, ensuring every seal meets your exact specifications for precision and durability.
Don't compromise on performance. Contact our experts today for a consultation on the ideal sealing solution for your specific chemical and operational needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















