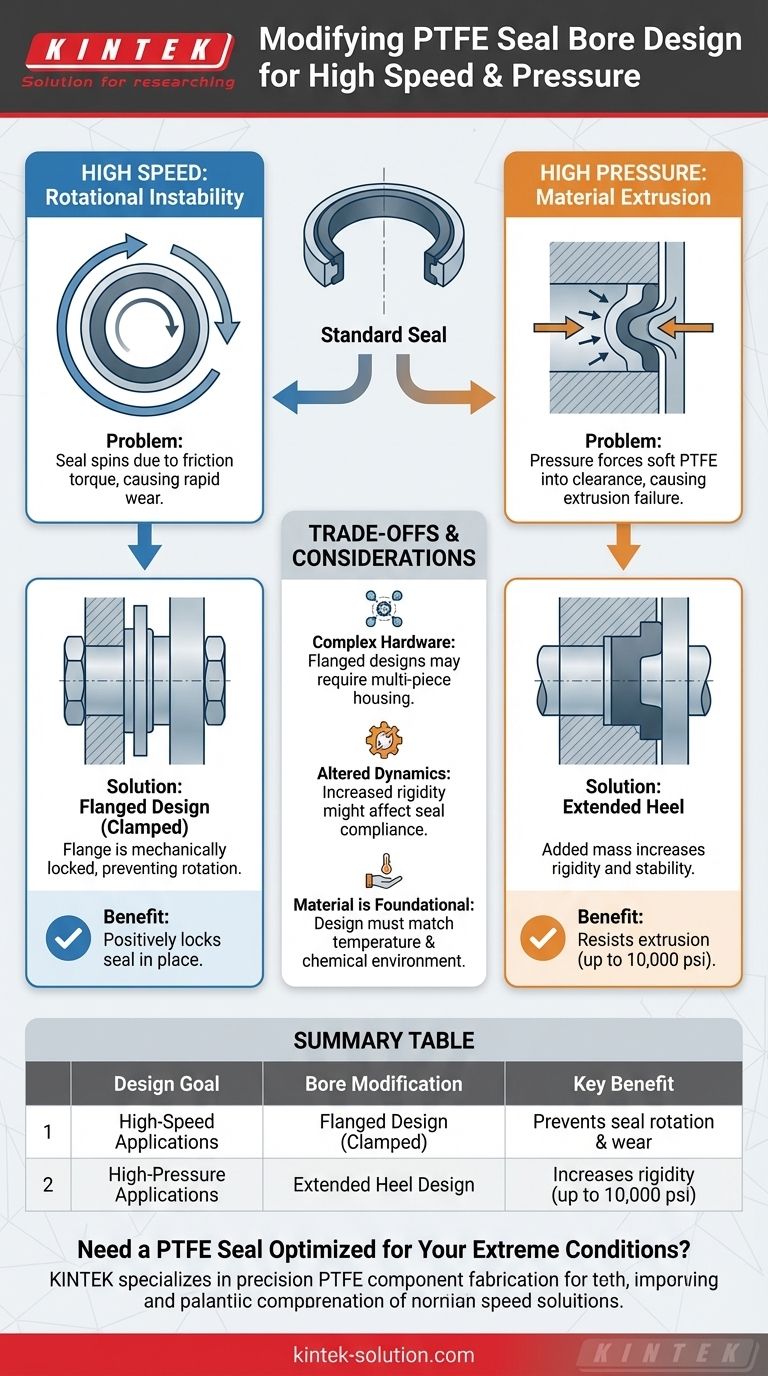
To adapt a PTFE seal for extreme conditions, the bore design must be modified to counteract specific failure modes. For high-speed applications, you must prevent the seal from rotating by using a flanged design clamped by the hardware. For high-pressure scenarios, the key is to increase the seal’s rigidity by extending its heel to resist extrusion.
The core challenge in high-performance sealing is managing physical forces. The solution lies not in changing the PTFE material itself, but in strategically modifying the seal's geometry to anchor it against rotational stress (speed) or prevent it from deforming under load (pressure).

The Challenge: Why Standard Seals Fail at Extremes
Standard PTFE seals, often energized by an O-ring, are excellent for a wide range of applications. However, pushing them to the upper limits of speed or pressure exposes their mechanical weaknesses, leading to predictable failures.
The Problem with High Speed: Rotational Instability
At very high rotational speeds, the friction between the seal lip and the moving shaft can generate enough torque to overcome the static friction holding the seal body in its groove.
This causes the entire seal to spin within the bore. This uncontrolled rotation leads to rapid, uneven wear and catastrophic seal failure.
The Problem with High Pressure: Material Extrusion
Under high pressure, the relatively soft PTFE material is subjected to immense force. This force tries to push the seal material into the small clearance gap between the static and dynamic hardware components.
This process, known as extrusion, permanently damages the seal, creating a leak path and rendering it ineffective.
Bore Modifications for Demanding Applications
To overcome these limitations, the seal's geometry is modified to add mechanical stability where it's needed most. These are not exotic changes but are fundamental enhancements to the seal's core design.
The Solution for High Speed: The Flanged Design
For high-speed rotary service, the O-ring is often replaced with a flanged design. This modification adds a radial flange to the outside diameter of the seal.
This flange is then mechanically clamped between two pieces of the hardware housing during assembly. By positively locking the seal in place, it is physically impossible for it to rotate, regardless of the shaft speed or friction.
The Solution for High Pressure: The Extended Heel
To handle high pressure, the seal profile is modified with an extended heel. This adds significant material and thickness to the static, non-contacting side of the seal.
This added mass dramatically increases the seal's rigidity and stability. It acts as a buttress, preventing the pressure from deforming the seal and extruding it into the clearance gap. When combined with an O-ring energizer, this design can achieve pressure ratings up to 10,000 psi.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While these modifications are highly effective, they come with design considerations that are critical for successful implementation. Objectivity requires acknowledging these factors.
Flanged Designs Require More Complex Hardware
A simple press-in seal fits into a straightforward groove. A flanged seal, however, requires a more complex gland, often involving a two-piece housing or a bolted retaining plate to provide the necessary clamping force. This can increase manufacturing complexity and assembly time.
Extended Heels May Alter Sealing Dynamics
A more rigid seal profile is better at resisting extrusion, but it may be less compliant to hardware imperfections. The design must be carefully balanced to ensure that the increased stability doesn't compromise the seal lip's ability to maintain effective contact.
Material Properties Are Foundational
These geometric enhancements work because they leverage the inherent strengths of PTFE, such as its low friction and high-temperature resistance (up to 500°F). The best design in the world will fail if the base material is not suited for the operating temperature and chemical environment.
Making the Right Design Choice
Your final decision should be directly tied to the primary challenge you need to solve. Use the operating conditions of your system as the primary guide for seal specification.
- If your primary focus is high rotational speed: Choose a flanged seal design that is mechanically clamped in the hardware to provide a positive anti-rotation lock.
- If your primary focus is high system pressure: Specify a seal with an extended heel to provide the necessary rigidity and stability to prevent extrusion.
- If you face both high speed and high pressure: You will need an engineered solution that likely combines these principles, possibly requiring advanced PTFE filler materials to manage heat and wear.
By understanding how these specific geometric changes solve distinct mechanical problems, you can design a more robust and reliable sealing system.
Summary Table:
| Design Goal | Bore Modification | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Applications | Flanged Design (Clamped) | Prevents seal rotation and wear |
| High-Pressure Applications | Extended Heel Design | Increases rigidity to resist extrusion (up to 10,000 psi) |
Need a PTFE Seal Optimized for Your Extreme Conditions?
KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE component fabrication for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a custom flanged seal for high-speed rotary service or a high-pressure seal with an extended heel, our expertise ensures a robust, reliable solution.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your seals are engineered for peak performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















