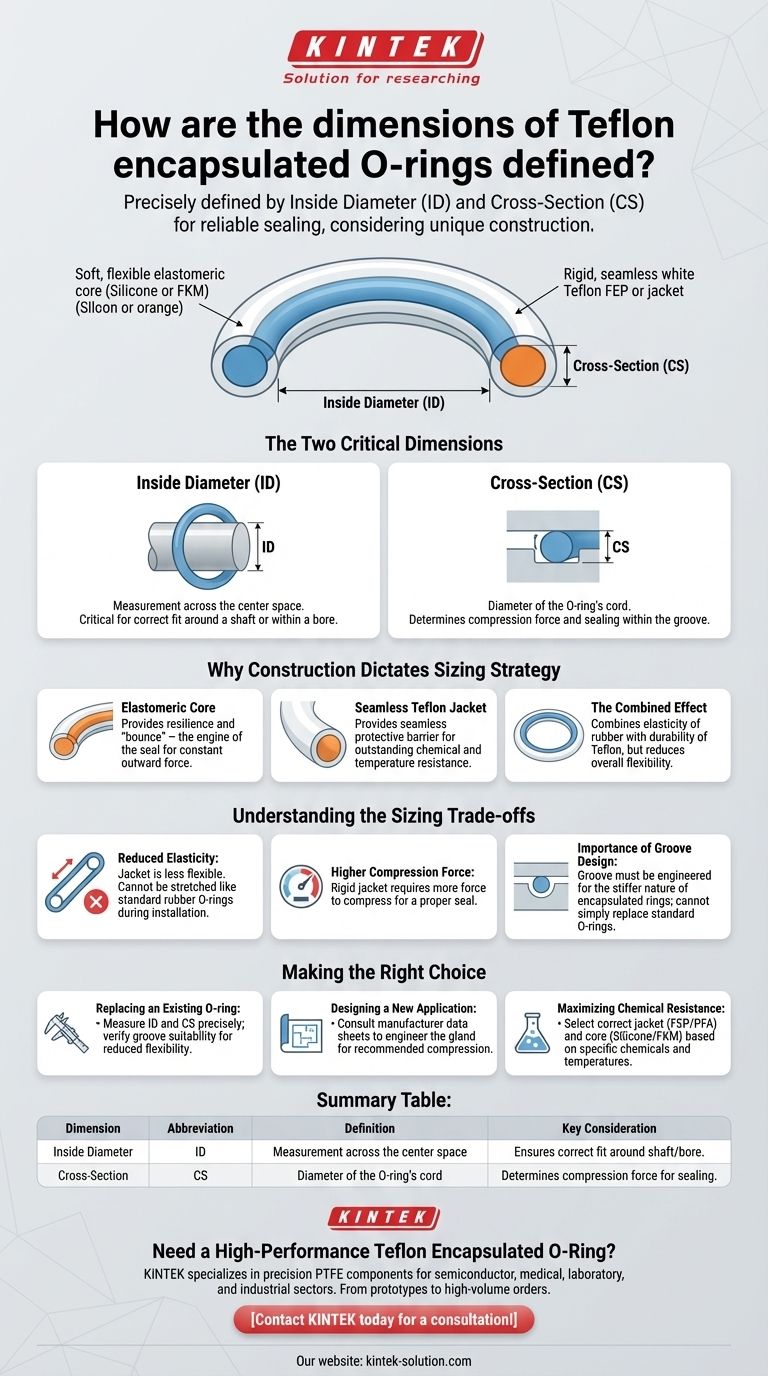
To be precise, the size of a Teflon encapsulated O-ring is defined by two fundamental measurements: its inside diameter (ID) and its cross-section (CS). These two dimensions provide the necessary information for selecting a ring that will fit correctly within a specific groove or gland to create a reliable seal.
While the dimensions are straightforward, the true challenge lies in understanding how the unique construction of an encapsulated O-ring—a rigid Teflon jacket over a soft elastomeric core—impacts sizing and installation for a successful, leak-free seal.

The Two Critical Dimensions Explained
Properly identifying the inside diameter and cross-section is the first step in any O-ring specification. These standard measurements dictate how the O-ring will physically interact with your hardware.
Inside Diameter (ID)
The inside diameter is the measurement across the empty space within the center of the O-ring. This dimension is critical for ensuring the O-ring fits correctly around a shaft or within the bore of a housing.
Cross-Section (CS)
The cross-section is the diameter of the O-ring's cord or tube itself. This measurement determines how much the O-ring will be squeezed, or compressed, within its designated groove to generate the sealing force.
Why Construction Dictates Sizing Strategy
Unlike a standard rubber O-ring, an encapsulated O-ring is a composite part. Understanding its two components is essential to grasping why sizing is so critical.
The Elastomeric Core
The inner core, typically made of Silicone or FKM (Viton®), provides the resilience and "bounce." This is the engine of the seal, supplying the constant outward force needed to maintain contact with the sealing surfaces.
The Seamless Teflon Jacket
The outer jacket, made of Teflon FEP or PFA, provides a seamless, protective barrier. Its primary role is to deliver outstanding chemical and temperature resistance, protecting the more vulnerable elastomeric core from harsh media.
The Combined Effect
The result is an O-ring that combines the elasticity of rubber with the durability of Teflon. However, the rigid Teflon jacket significantly reduces the O-ring's overall flexibility compared to a standard elastomer O-ring.
Understanding the Sizing Trade-offs
The unique two-part construction introduces specific mechanical limitations that directly influence how you must approach sizing and installation. Ignoring these can lead to immediate seal failure.
Reduced Elasticity
The Teflon jacket is far less flexible than the core material. This means an encapsulated O-ring cannot be stretched as much during installation. Attempting to stretch it over a shaft like a standard rubber O-ring can easily crack the jacket, compromising its chemical barrier.
Higher Compression Force
Because the jacket is relatively hard, more force is required to compress the O-ring to achieve a seal. The groove it sits in must be designed to apply the correct amount of squeeze without crushing the jacket or over-compressing the core.
Importance of Groove Design
You cannot simply replace a standard O-ring with an encapsulated one and expect optimal performance. The groove dimensions must be engineered specifically for the stiffer nature of an encapsulated ring to ensure a durable, leak-free seal over the long term.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying this knowledge correctly ensures you select a seal that is not only dimensionally correct but also functionally effective for your specific environment.
- If your primary focus is replacing an existing O-ring: Measure the ID and CS of the original part precisely, but also verify that the groove dimensions in your hardware are suitable for the reduced flexibility of an encapsulated ring.
- If your primary focus is designing a new application: Consult the manufacturer's specific data sheets to engineer the gland (groove) to achieve the recommended compression percentage, which is often different from that of standard O-rings.
- If your primary focus is maximizing chemical resistance: Ensure you select the correct jacket (FEP or PFA) and core material (Silicone or FKM) based on the specific chemicals and temperatures in your system, in addition to getting the dimensions right.
By understanding how these two simple dimensions interact with the O-ring's unique construction, you can ensure a reliable, long-lasting seal in the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Dimension | Abbreviation | Definition | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inside Diameter | ID | Measurement across the center space of the O-ring. | Ensures the O-ring fits correctly around a shaft or within a housing bore. |
| Cross-Section | CS | Diameter of the O-ring's cord itself. | Determines the compression force needed to generate the seal within the groove. |
Need a High-Performance Teflon Encapsulated O-Ring?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom Teflon encapsulated O-rings with FEP or PFA jackets and Silicone or FKM cores. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let our expertise ensure your seal is dimensionally perfect and functionally reliable for your demanding application. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What are the advantages of PTFE-based seals? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What are the main chemical resistance properties of PTFE-coated O-rings? Uncover the True Role of the Coating
- What makes PTFE stand out among materials used in sealing technology? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















