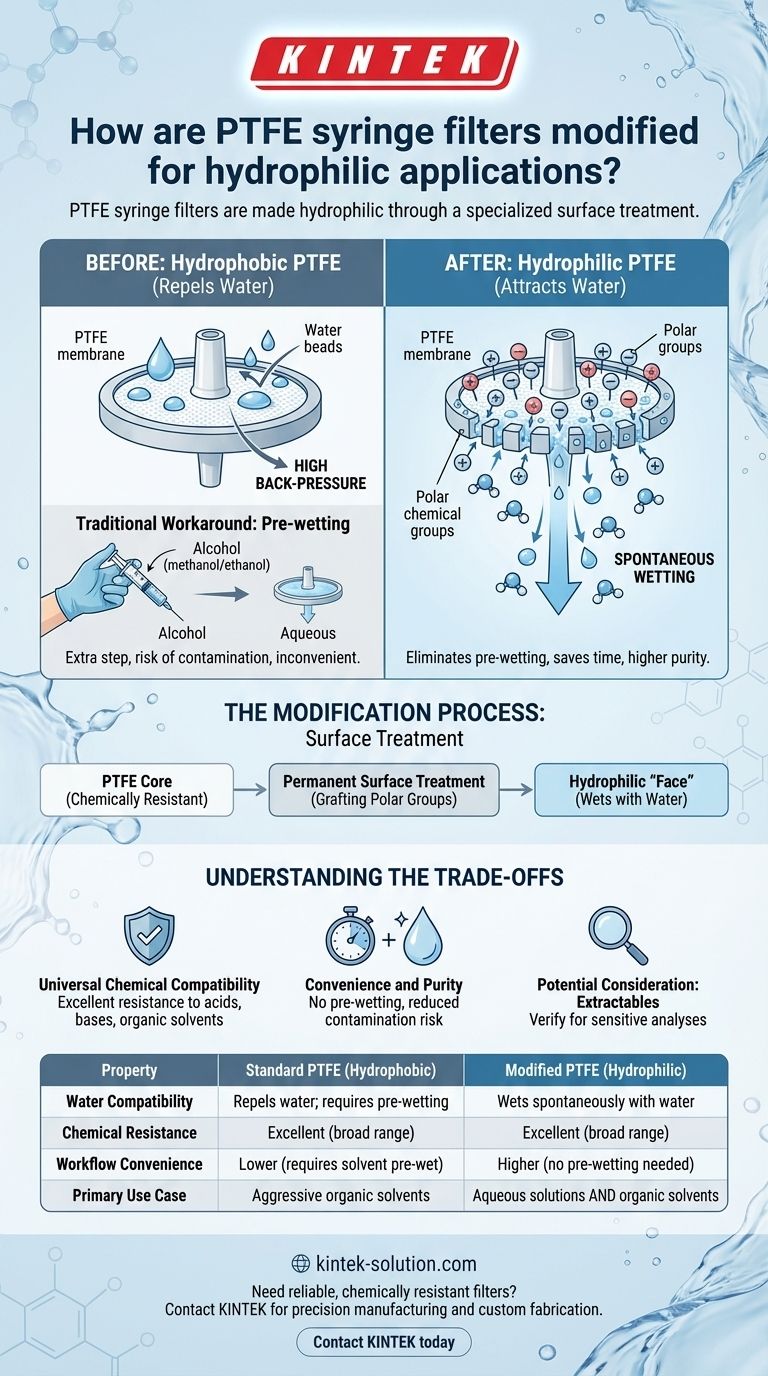
PTFE syringe filters are made hydrophilic through a specialized surface treatment. This process permanently alters the chemistry of the membrane's surface, transforming it from a material that naturally repels water (hydrophobic) to one that readily wets with water (hydrophilic). This allows the filter to be used with aqueous solutions without any pre-wetting steps.
The core purpose of modifying a PTFE filter is to combine its exceptional chemical resistance with the ability to filter water-based solutions. This creates a versatile, nearly universal filter membrane, but it's crucial to understand how this modification compares to using inherently hydrophilic materials for your specific application.

The Challenge: Overcoming PTFE's Natural State
What "Hydrophobic" Means for Filtration
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is an inherently hydrophobic material. This means it naturally repels water due to its low surface energy.
When trying to filter an aqueous solution through a standard PTFE membrane, the water will bead up on the surface and will not easily pass through the microscopic pores. This phenomenon, known as high back-pressure, can effectively block the flow of the liquid.
The Problem with Traditional Workarounds
The standard method to overcome this is pre-wetting the filter with a low-surface-tension solvent, such as methanol or ethanol.
This alcohol first wets the membrane and fills the pores, which then allows the aqueous solution to follow. However, this adds an extra step to the workflow, increases the risk of sample contamination from the alcohol, and can be inconvenient.
The Modification Process: From Repelling to Attracting Water
The Goal of Surface Treatment
The modification process is designed to change the surface chemistry of the PTFE membrane without altering its underlying structure or superior chemical resistance.
The treatment makes the surface energetically favorable for water to interact with, eliminating the natural repulsion between the water and the filter material.
How the Surface is Modified
This is achieved by applying a permanent surface treatment to the membrane material. This treatment effectively grafts water-attracting (polar) chemical groups onto the surface of the PTFE polymer structure within the pores.
The result is a filter that is PTFE at its core but presents a hydrophilic "face" to the liquid. This allows water and aqueous solutions to spontaneously wet the membrane and flow through with minimal resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Hydrophilic PTFE
Key Advantage: Universal Chemical Compatibility
The most significant benefit of hydrophilic PTFE is its dual nature. Because the core material is still PTFE, it retains its outstanding resistance to a very broad range of chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and organic solvents.
This makes it an excellent "all-in-one" filter for complex workflows that involve filtering both aqueous and aggressive non-aqueous solutions, simplifying inventory and filter selection.
Key Advantage: Convenience and Purity
By eliminating the need for a pre-wetting step, hydrophilic PTFE filters save time and reduce the potential for sample contamination by the pre-wetting solvent. This is particularly important in sensitive analytical techniques like HPLC.
Potential Consideration: Extractables
While modern manufacturing processes are highly refined, the surface treatment itself is an additive process. For extremely sensitive analyses, it is important to verify that the filter is certified for low extractables, ensuring that nothing from the treatment process leaches into your filtered sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct membrane depends entirely on the solvents you use and the sensitivity of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is working with aggressive organic solvents AND aqueous solutions: Hydrophilic PTFE is often the ideal choice for its universal chemical compatibility and convenience.
- If your primary focus is filtering purely aqueous or biological solutions: An inherently hydrophilic membrane like PVDF or PES may be a better choice, as they often offer specific benefits like lower protein binding.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive, non-aqueous solvents only: A standard, untreated (hydrophobic) PTFE filter remains the most direct and cost-effective option.
Understanding this modification allows you to select a filter that provides both the necessary chemical resistance and the correct wetting properties for your specific workflow.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE (Hydrophobic) | Modified PTFE (Hydrophilic) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Compatibility | Repels water; requires pre-wetting | Wets spontaneously with water |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (broad range) | Excellent (broad range) |
| Workflow Convenience | Lower (requires solvent pre-wet) | Higher (no pre-wetting needed) |
| Primary Use Case | Aggressive organic solvents | Aqueous solutions AND organic solvents |
Need a reliable, chemically resistant filter for your aqueous and solvent-based workflows?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including hydrophilic syringe filters. Our modified PTFE filters combine the unmatched chemical resistance of PTFE with the convenience of spontaneous water-wetting, eliminating the need for pre-wetting solvents and reducing contamination risk for sensitive analyses in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your filtration needs and request a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















