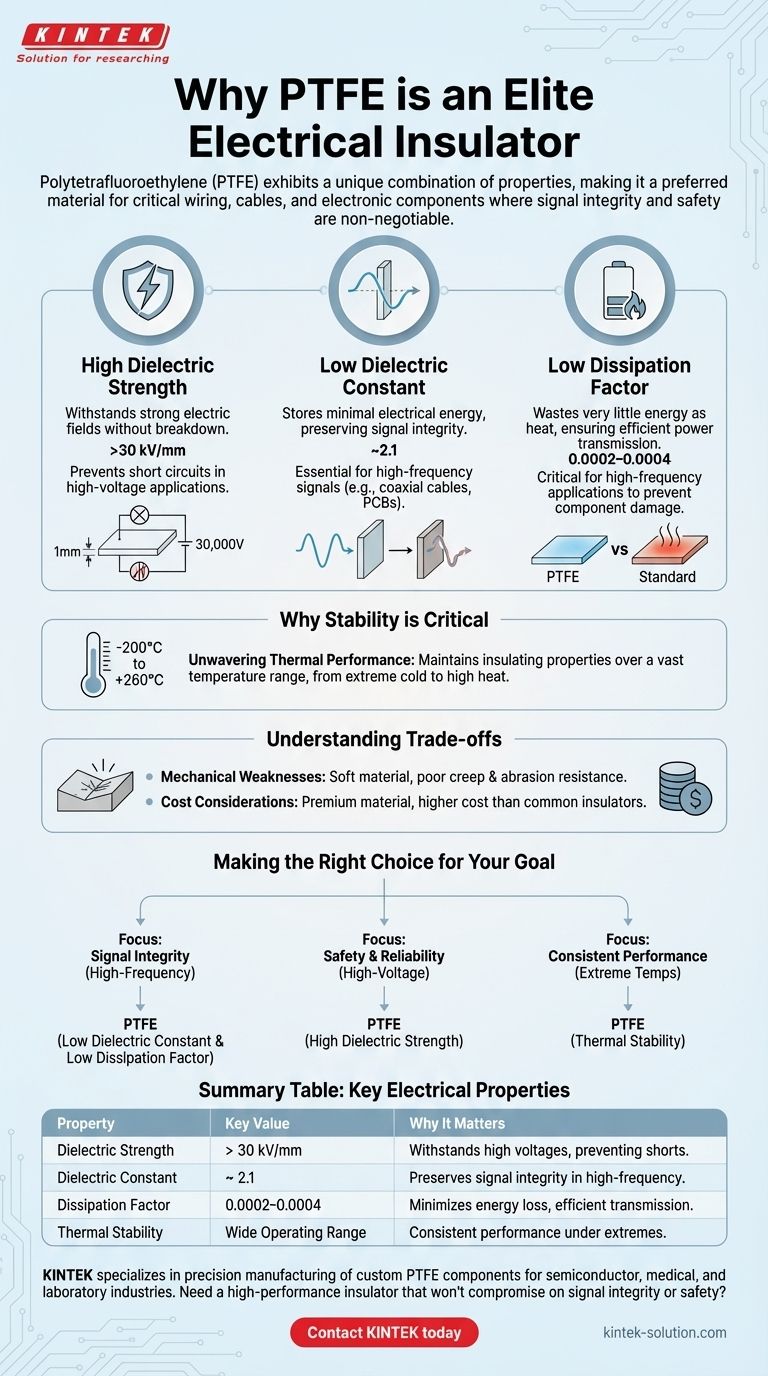
In the world of high-performance polymers, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is considered an elite electrical insulator due to a unique combination of properties. Its molecular structure results in extremely high electrical resistance, the ability to withstand high voltages without breaking down, and minimal energy loss, particularly at high frequencies. This makes it a preferred material for critical wiring, cables, and electronic components where signal integrity and safety are non-negotiable.
The core reason for PTFE's excellence is not a single attribute, but a powerful combination of three: it strongly resists the flow of electricity (high dielectric strength), it doesn't store and release electrical energy in a way that distorts signals (low dielectric constant), and it wastes very little energy as heat (low dissipation factor).

The Core Electrical Properties of PTFE
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at its specific electrical characteristics. These are the fundamental metrics that define an insulator's performance.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down and failing. PTFE exhibits an exceptionally high dielectric strength, often exceeding 30 kV/mm.
This means a 1mm thick sheet of PTFE can theoretically withstand 30,000 volts before failing, preventing dangerous short circuits in high-voltage applications.
High Electrical Resistivity
Resistivity is the fundamental property of a material to oppose the flow of electric current. PTFE has a very high electrical resistance, meaning it is a very poor conductor.
This non-conductive nature is critical for preventing current leakage, protecting sensitive electronic components, and ensuring electricity flows only along its intended path.
Low Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant indicates how much electrical energy a material can store when placed in an electric field. PTFE has a very low dielectric constant of around 2.1.
For applications involving high-frequency signals, such as in coaxial cables or printed circuit boards (PCBs), this is crucial. A low value ensures the insulator does not absorb and distort the signal, preserving signal integrity.
Low Dissipation Factor
The dissipation factor, or loss tangent, measures the inefficiency of an insulator, specifically how much energy is lost as heat. PTFE has a remarkably low dissipation factor (around 0.0002–0.0004).
This minimal energy loss is vital for high-frequency applications, ensuring that the power of the signal is transmitted efficiently without being wasted as heat, which could otherwise damage components.
Why Stability is Just as Critical
PTFE's elite electrical properties would be less useful if they weren't consistent. Its stability across a wide range of operating conditions is what makes it so reliable.
Unwavering Thermal Performance
PTFE maintains its excellent insulating properties over a vast range of temperatures. It has a high melting point and does not become brittle at very low temperatures.
This thermal stability ensures that its performance as an insulator remains predictable and reliable, whether in a hot server room or a cold aerospace application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE's electrical and thermal properties are exceptional, no material is perfect for every situation. Its primary limitations are mechanical.
Mechanical Weaknesses
PTFE is a relatively soft material with poor resistance to "creep" (deformation under load) and low abrasion resistance. It is not as physically robust as some other insulators.
Cost Considerations
PTFE is also a premium material, and its cost can be higher than that of more common insulators like PVC or polyethylene. This often reserves its use for applications where its specific high-performance benefits are a necessity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE depends entirely on whether your application demands its unique set of elite properties.
- If your primary focus is signal integrity in high-frequency systems (e.g., data cables, PCBs): PTFE is an ideal choice due to its low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor.
- If your primary focus is safety and reliability in high-voltage environments: PTFE's exceptionally high dielectric strength makes it a top-tier candidate for insulation.
- If your primary focus is consistent performance across extreme temperatures: PTFE's thermal stability ensures its electrical properties will not degrade under demanding conditions.
Ultimately, PTFE is the definitive choice when electrical performance and reliability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Value | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | > 30 kV/mm | Withstands high voltages, preventing short circuits. |
| Dielectric Constant | ~ 2.1 | Preserves signal integrity in high-frequency applications. |
| Dissipation Factor | 0.0002–0.0004 | Minimizes energy loss as heat, ensuring efficient signal transmission. |
| Thermal Stability | Wide operating range | Consistent performance from extreme cold to high heat. |
Need a high-performance insulator that won't compromise on signal integrity or safety?
PTFE's elite electrical properties make it the definitive choice for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—ensuring your designs benefit from superior insulation and reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















