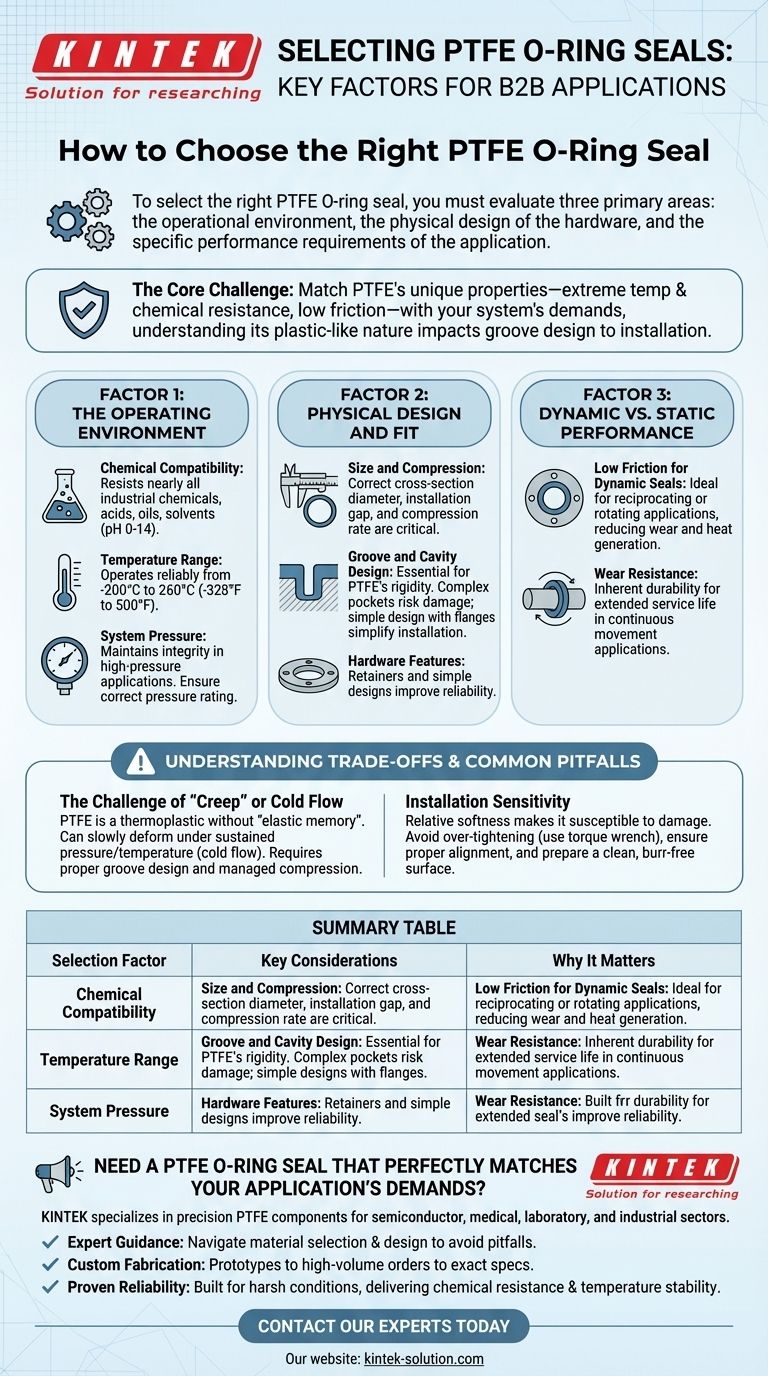
To select the right PTFE O-ring seal, you must evaluate three primary areas: the operational environment, the physical design of the hardware, and the specific performance requirements of the application. The key is to match PTFE's unique properties—its extreme temperature and chemical resistance, and low friction—with the precise demands of your system.
The core challenge is not simply choosing PTFE for its impressive capabilities, but understanding how its plastic-like nature impacts everything from groove design to installation. A successful seal depends as much on the hardware and installation process as it does on the material itself.

Deconstructing the Core Selection Criteria
A methodical evaluation of your application's demands is the foundation for choosing a reliable seal. We can break this down into three critical areas.
Factor 1: The Operating Environment
The environment is the most significant factor driving material selection. PTFE excels in harsh conditions where other materials fail.
- Chemical Compatibility: PTFE is famously inert, resisting nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, oils, and solvents. It is a safe choice for media with a pH range from 0 to 14.
- Temperature Range: Standard PTFE seals operate reliably across an exceptionally wide temperature spectrum, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
- System Pressure: PTFE maintains its integrity in high-pressure applications. You must ensure the specific seal you choose is rated to withstand your system's maximum operational and spike pressures.
Factor 2: Physical Design and Fit
How the seal interacts with your hardware is just as important as its material properties. PTFE is not a simple drop-in replacement for a standard rubber O-ring.
- Size and Compression: Key dimensions like cross-section diameter and installation gap are critical. The correct compression rate ensures a tight seal without over-stressing the material.
- Groove and Cavity Design: Because PTFE is a relatively rigid plastic, the design of the sealing pocket or groove is crucial. Complex machined pockets that require twisting the seal can make installation difficult and risk damaging the ring.
- Hardware Features: Simple designs incorporating flanges or retainers can significantly simplify installation and improve the reliability of the seal.
Factor 3: Dynamic vs. Static Performance
You must consider if the seal will be stationary (static) or moving (dynamic), as this dictates which properties are most important.
- Low Friction for Dynamic Seals: PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction. This makes it ideal for reciprocating or rotating applications, as it reduces wear, minimizes heat generation, and extends the service life of both the seal and the hardware.
- Wear Resistance: The inherent durability of PTFE reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacement, especially in applications with continuous movement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While powerful, PTFE is not without its unique challenges. Understanding its limitations is key to avoiding seal failure.
The Challenge of "Creep" or Cold Flow
PTFE is a thermoplastic, not an elastomer like rubber. Under sustained pressure and temperature, it can slowly deform over time in a process known as creep or cold flow.
This lack of "elastic memory" means it won't spring back to its original shape as readily as a rubber O-ring. This is why proper groove design and managing the compression rate are absolutely critical for long-term sealing.
Installation Sensitivity
The relative softness of PTFE makes it susceptible to damage during installation. This is the single most common point of failure.
- Avoid Over-tightening: Using a torque wrench is recommended to apply even, correct pressure. Over-tightening can permanently deform the seal and compromise its effectiveness.
- Ensure Proper Alignment: A misaligned seal will experience uneven wear and will almost certainly leak.
- Prepare the Surface: The sealing surface must be perfectly clean and free of dirt, dust, or burrs that could scratch or damage the O-ring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your final selection and design considerations.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: PTFE is one of the safest and most reliable choices available, capable of handling nearly any fluid.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Ensure your operating temperatures fall within PTFE's wide functional range to guarantee performance.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic application (moving parts): Capitalize on PTFE's low friction, but pay close attention to the hardware's surface finish to maximize seal life.
- If you are designing new hardware: Design the seal groove to simplify installation and provide optimal compression, accounting for PTFE's limited elasticity.
Ultimately, a successful PTFE seal is the result of a holistic approach that considers the material, the hardware design, and the installation process as interconnected parts of a single system.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | Key Considerations | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Environment | Chemical compatibility (pH 0-14), temperature range (-200°C to 260°C), system pressure. | Ensures the seal material can withstand the specific conditions without degrading. |
| Physical Design & Fit | Cross-section diameter, compression rate, groove design, and hardware features. | A proper fit is critical as PTFE lacks the elasticity of rubber and is sensitive to installation. |
| Performance Type | Static sealing vs. dynamic (moving) applications requiring low friction and wear resistance. | Determines the most critical material properties for your application's success and longevity. |
Need a PTFE O-ring seal that perfectly matches your application's demands?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom O-ring seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between material properties, hardware design, and installation.
We offer:
- Expert Guidance: Our team will help you navigate material selection and design considerations to avoid common pitfalls like creep and installation damage.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we manufacture seals to your exact specifications, ensuring optimal fit and performance.
- Proven Reliability: Our components are built for the harsh conditions of specialized industries, delivering the chemical resistance and temperature stability you require.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sealing challenge and receive a custom solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the five outstanding characteristics of PTFE seals? Engineered for Extreme Performance
- What are the two temperature extremes discussed for PTFE seals? Maximize Performance from Cryogenic to High-Heat
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance



















