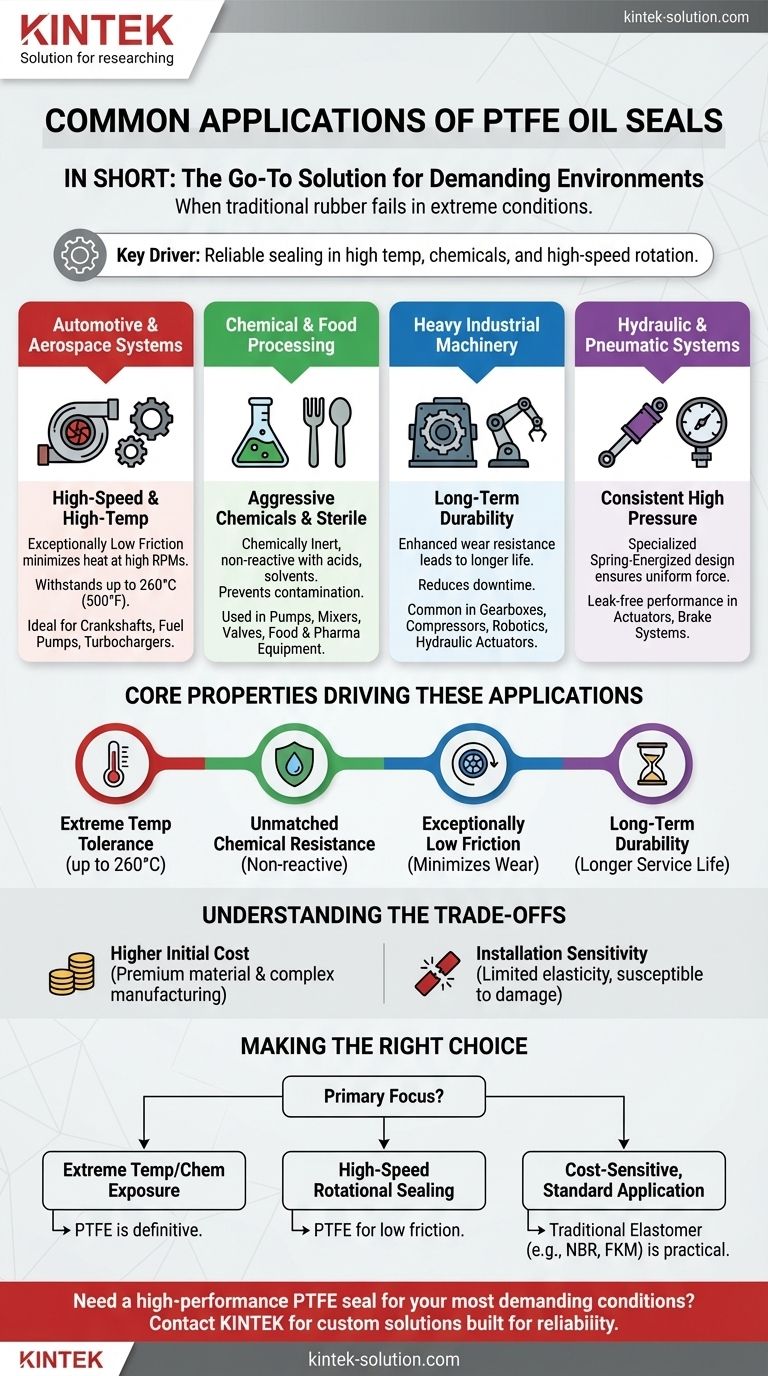
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) oil seals are the go-to solution for demanding applications where traditional rubber seals would fail. They are commonly found in high-performance automotive and aerospace systems like turbochargers and transmissions, industrial equipment such as compressors and pumps, and sterile environments within the food and pharmaceutical industries.
The core reason for choosing a PTFE seal is its ability to provide reliable sealing in extreme operating conditions—specifically, high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and high-speed rotational movement—where conventional elastomeric seals would quickly degrade and fail.

Where PTFE Seals Are the Go-To Solution
The unique properties of PTFE make it the material of choice across several critical industries. The decision to use a PTFE seal is almost always driven by a specific, challenging environmental factor that other materials cannot handle.
Automotive and Aerospace Systems
High-performance engines, transmissions, and turbochargers operate at extreme rotational speeds and temperatures.
PTFE's exceptionally low friction minimizes heat buildup and energy loss at high RPMs, while its ability to withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) prevents material degradation. This makes it ideal for sealing critical components like crankshafts and fuel injection pumps.
Chemical and Food Processing
Equipment like pumps, mixers, valves, and mechanical seals in these industries handle aggressive chemicals or require sterile, hygienic conditions.
PTFE is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with acids, solvents, or corrosive substances. This prevents seal failure and contamination, making it a safe choice for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical processing equipment.
Heavy Industrial Machinery
Components such as gearboxes, compressors, robotics, and hydraulic actuators demand long-term reliability and efficiency under constant use.
The enhanced durability and wear resistance of PTFE seals, often reinforced with fillers like graphite or glass fiber, lead to a longer service life. This significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs in critical industrial machinery.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
These systems rely on consistent pressure for operation, with components like actuators and brake systems requiring leak-free performance.
Specialized spring-energized PTFE seals provide a constant, uniform force against the sealing surface. This design ensures a reliable seal even under high pressure and compensates for minor surface imperfections or wear over time.
The Core Properties Driving These Applications
Understanding why PTFE is selected requires looking at its fundamental material characteristics. These four properties are the primary drivers for its adoption in challenging environments.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing capability in continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). This far exceeds the limits of common elastomers like Nitrile (NBR) or even Viton (FKM) in many cases.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
Often called one ofthe most non-reactive materials known, PTFE can withstand a vast range of chemicals, from aggressive acids to powerful solvents, without swelling, shrinking, or degrading.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This property is critical for reducing wear, preventing stick-slip issues in dynamic applications, and minimizing energy loss in high-speed rotating equipment.
Long-Term Durability
When properly specified for the application, PTFE seals offer a significantly longer service life than many alternatives. This is especially true for "filled" PTFE variants, which are blended with materials like glass, bronze, or carbon to enhance wear resistance and mechanical strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE seals are not a universal solution. Their unique characteristics introduce specific trade-offs that are critical to understand for successful implementation.
Higher Initial Cost
PTFE is a premium material, and the manufacturing process for these seals is more complex than for molded rubber seals. This results in a higher upfront cost compared to standard elastomeric options.
Limited Elasticity
Unlike rubber, PTFE has very little elasticity and does not rebound to its original shape if deformed. This "plastic memory" means it is far less forgiving of poor shaft finishes or installation errors.
Installation Sensitivity
The lack of elasticity makes PTFE seals highly susceptible to damage during installation. A small nick or scratch on the sealing lip, often invisible to the naked eye, can cause an immediate leak. Specialized tools and procedures are required for proper installation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct seal material is a matter of matching its properties to the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature or chemical exposure: PTFE is the definitive choice, as conventional elastomers will chemically degrade or lose their physical properties.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotational sealing: PTFE's low-friction characteristic is essential for minimizing heat generation, wear, and power loss in components like engines and turbochargers.
- If your primary focus is a cost-sensitive, standard application: For moderate temperatures, speeds, and non-aggressive fluids, a traditional elastomeric seal (like NBR or FKM) is often the more practical and sufficient solution.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE seal is an engineering decision to prioritize long-term reliability and performance in environments where other materials simply cannot survive.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key PTFE Seal Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automotive & Aerospace | Extreme temperature tolerance & low friction for high RPMs |
| Chemical & Food Processing | Chemical inertness for handling aggressive substances safely |
| Heavy Industrial Machinery | Enhanced durability & wear resistance for long service life |
| Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems | Spring-energized design for reliable, high-pressure sealing |
Need a PTFE seal that can handle your most demanding conditions?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure a perfect fit for your application's extreme temperatures, chemicals, and speeds.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing challenge and get a solution built for reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















