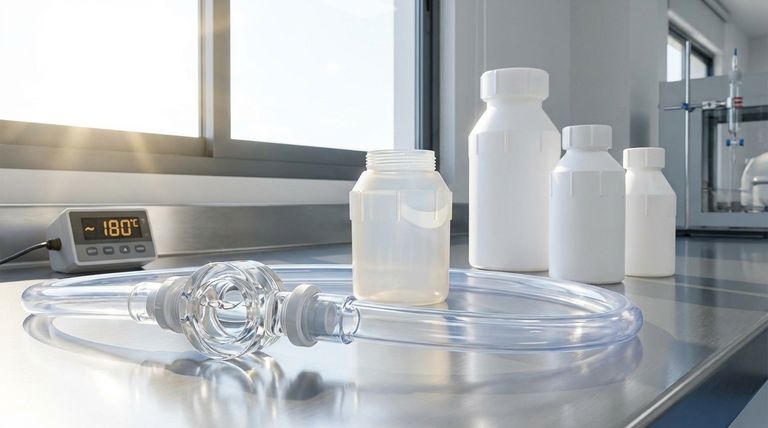
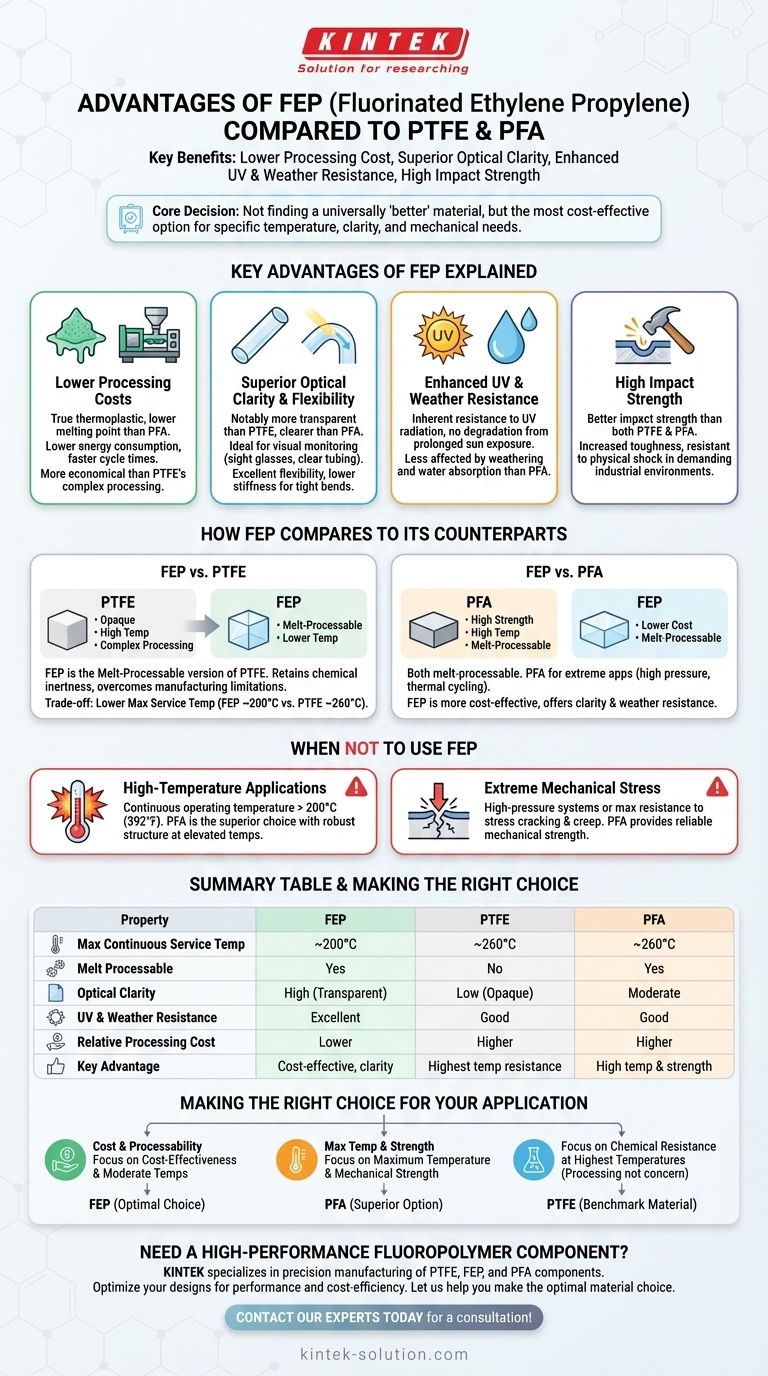
In short, FEP's primary advantages over PTFE and PFA are its lower processing cost, superior optical clarity, and enhanced resistance to UV and weathering. While it shares the excellent chemical resistance of its counterparts, FEP can be melt-processed at lower temperatures, making it a more economical choice for manufacturing methods like injection molding.
The core decision between FEP, PFA, and PTFE is not about finding a universally "better" material, but about identifying the most cost-effective option that meets your specific operational requirements for temperature, clarity, and mechanical stress.

Key Advantages of FEP Explained
While all three are high-performance fluoropolymers, FEP was engineered to fill a specific gap, offering a unique balance of properties that make it ideal for certain applications.
Lower Processing Costs
FEP is a true thermoplastic, meaning it can be melted and reformed. It has a lower melting point than PFA, which directly translates to lower energy consumption and faster cycle times during manufacturing processes like injection molding.
This processability is a significant advantage over PTFE, which cannot be truly melt-processed and requires more complex and costly techniques like compression molding and sintering.
Superior Optical Clarity and Flexibility
FEP is notably more transparent than PTFE and generally clearer than PFA. This makes it the material of choice for applications where visual monitoring of fluids is necessary, such as in sight glasses or clear tubing.
It also offers excellent flexibility and a lower stiffness compared to its counterparts, making it well-suited for applications requiring tight bend radii or intricate designs.
Enhanced UV and Weather Resistance
One of FEP's standout features is its inherent resistance to UV radiation. Unlike many other polymers, it does not degrade or become brittle with prolonged sun exposure.
Furthermore, sources indicate that FEP is less affected by weathering and water absorption compared to PFA, giving it a durability advantage in outdoor or humid environments.
High Impact Strength
FEP offers better impact strength than both PTFE and PFA. This increased toughness makes it more resistant to damage from physical shock or stress, which can be a critical factor in demanding industrial environments.
How FEP Compares to Its Counterparts
Understanding FEP’s advantages requires placing it in context with the materials it is most often compared against.
FEP vs. PTFE
Think of FEP as the melt-processable version of PTFE. It was developed to retain PTFE's legendary chemical inertness and non-stick properties while overcoming its difficult and expensive manufacturing limitations.
The trade-off is a lower maximum service temperature. While PTFE can operate up to 260°C (500°F), FEP is limited to around 200°C (392°F).
FEP vs. PFA
This is a more direct comparison, as both are melt-processable. PFA is often chosen for more extreme applications, offering better mechanical strength and higher temperature resistance than FEP.
PFA excels in high-pressure systems and environments with repeated thermal cycling. However, FEP is more cost-effective to process and offers the previously mentioned advantages in clarity and weather resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Not to Use FEP
Objectivity requires acknowledging limitations. FEP is an excellent material, but it is not the correct choice for every situation.
High-Temperature Applications
If your application's continuous operating temperature will exceed 200°C (392°F), PFA is the superior and necessary choice. Its molecular structure is more robust at elevated temperatures.
Extreme Mechanical Stress
For high-pressure systems or applications requiring maximum resistance to stress cracking and creep, PFA's superior mechanical strength makes it a more reliable option than FEP.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct fluoropolymer involves balancing performance needs with budget constraints. Your primary goal will dictate the best material.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and processability for moderate temperatures: FEP is almost always the optimal choice due to its lower melting point and excellent overall properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and mechanical strength: PFA is the superior option, designed specifically to handle more extreme heat and pressure than FEP.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance at the highest possible temperatures (and processing is not a concern): PTFE remains the benchmark material.
By understanding these key differences, you can select the precise fluoropolymer that meets your performance requirements without over-engineering your solution.
Summary Table:
| Property | FEP | PTFE | PFA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Continuous Service Temp | ~200°C (392°F) | ~260°C (500°F) | ~260°C (500°F) |
| Melt Processable | Yes | No | Yes |
| Optical Clarity | High (Transparent) | Low (Opaque) | Moderate |
| UV & Weather Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Relative Processing Cost | Lower | Higher | Higher |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective processability & clarity | Highest temperature resistance | High temp & mechanical strength |
Need a High-Performance Fluoropolymer Component?
Selecting the right material is critical for your application's success and budget. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE, FEP, and PFA components—including seals, liners, and custom labware.
Our expertise helps clients in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors optimize their designs for performance and cost-efficiency. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, we provide custom fabrication to meet your exact specifications.
Let us help you make the optimal material choice. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Evaporating Dishes for Diverse Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Is the PTFE bottle suitable for ultra-pure applications? Ensure Absolute Sample Integrity
- What is the molecular structure of PTFE? The Key to Its Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How does the PTFE bottle perform in terms of chemical resistance? Unmatched Protection for Harsh Chemicals
- What are the temperature limits for the PTFE bottle? Ensure Safety from -200°C to 260°C
- What are the key applications of the PTFE bottle? Ensure Chemical Safety and Sample Purity



















