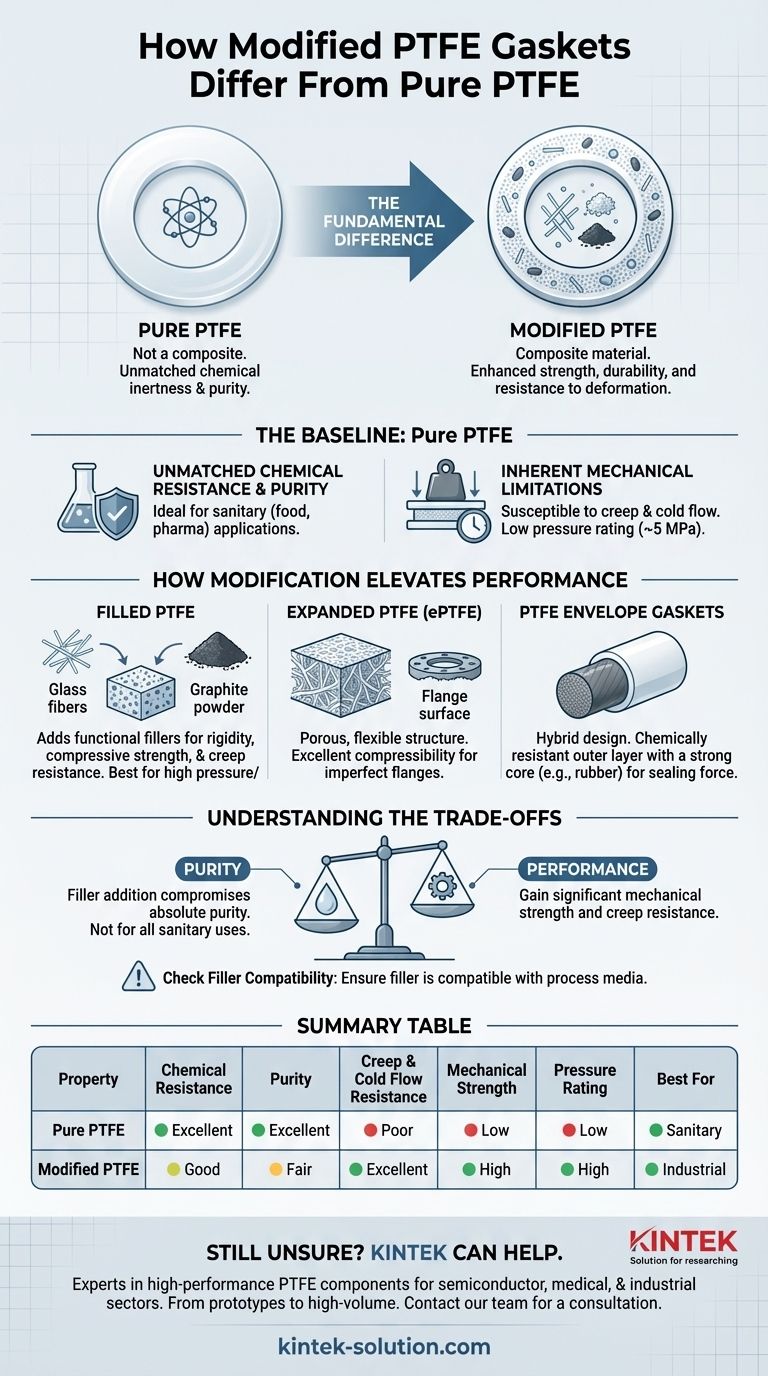
The fundamental difference is that modified PTFE gaskets are composite materials, while pure PTFE gaskets are not. Modified PTFE incorporates fillers like glass fiber, graphite, or undergoes a structural change to enhance specific mechanical properties such as strength, durability, and resistance to deformation, which are known weaknesses of pure PTFE.
The choice between pure and modified PTFE is a classic engineering trade-off. Pure PTFE offers unparalleled chemical inertness and purity, making it essential for sanitary applications. Modified PTFE, however, sacrifices some of this purity to gain significant improvements in mechanical strength and creep resistance, making it suitable for more demanding industrial conditions.

The Baseline: Understanding Pure PTFE
Pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a remarkable material, but its unique properties come with distinct limitations. Understanding this baseline is key to appreciating why modified versions were developed.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Purity
Pure PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, making it an exceptional choice for corrosive environments.
It is also prized for its non-contaminating nature. This makes it a default choice in industries like food, beverage, and pharmaceuticals where process purity is non-negotiable.
The Inherent Mechanical Limitations
The primary weakness of pure PTFE is its susceptibility to creep and cold flow. Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform and "flow" out of the flange, leading to a loss of sealing pressure.
It has a relatively low pressure rating, typically up to 5 MPa, and can struggle in applications with significant pressure or temperature fluctuations.
How Modification Elevates Performance
Modification involves altering the PTFE to overcome its mechanical weaknesses. This is typically achieved by adding fillers or by changing the physical structure of the material itself.
Filled PTFE: Adding Strength and Durability
The most common modification involves adding functional fillers, such as glass fiber or graphite powder, directly into the PTFE during production.
These fillers act as a reinforcing matrix within the PTFE, significantly increasing the gasket's rigidity, compressive strength, and resistance to creep. This makes it far more suitable for higher pressure and temperature applications than pure PTFE.
Expanded PTFE: Conforming to Imperfect Surfaces
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is not filled but is created through a special process that introduces a porous, flexible, and fibrous structure.
This structure gives ePTFE outstanding compressibility and conformability. It can easily adapt to irregular, pitted, or warped flange surfaces where a rigid gasket would fail, ensuring a tight seal with less bolt load.
PTFE Envelope Gaskets: The Best of Both Worlds
This is a hybrid design featuring a core material—like compressed non-asbestos fiber (CNAF) or rubber—encased in a thin outer layer of pure PTFE.
This construction provides the superior chemical resistance of a PTFE surface while leveraging the mechanical strength, resilience, and sealing force of the core material. It's an effective solution for combining chemical compatibility with higher pressure ratings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a modified PTFE gasket is not a simple upgrade; it involves accepting specific compromises.
Purity vs. Performance
The addition of any filler material compromises the absolute purity of the PTFE. This immediately makes many filled PTFE gaskets unsuitable for sanitary applications where contamination is a zero-tolerance issue.
Chemical Compatibility of Fillers
While the PTFE itself is chemically inert, the filler material may not be. You must ensure that the filler (e.g., glass fiber) is also compatible with the process media, as it can become a point of chemical attack that compromises the entire gasket.
Structural Integrity
Expanded PTFE, while highly conformable, has a different mechanical profile than solid or filled PTFE. In extremely high-pressure systems, a more rigid filled or envelope gasket might be required to prevent extrusion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the system's demands.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and broad chemical resistance: Pure PTFE is the only reliable choice for food, pharmaceutical, or highly sensitive laboratory applications.
- If your primary focus is sealing older, warped, or imperfect flanges: Expanded PTFE provides the best conformability to ensure a tight, reliable seal with minimal bolt torque.
- If your primary focus is durability in high-pressure or high-temperature industrial systems: Filled PTFE or PTFE envelope gaskets offer the necessary mechanical strength and creep resistance.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can select the precise gasket material that ensures both safety and operational efficiency for your specific system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Pure PTFE | Modified PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Virtually Inert) | Good (May be compromised by fillers) |
| Purity | Excellent (Non-contaminating) | Fair (Fillers can introduce contaminants) |
| Creep & Cold Flow Resistance | Poor | Excellent (Greatly improved) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low | High (Reinforced by fillers/structure) |
| Pressure Rating | Low (Up to ~5 MPa) | High |
| Best For | Sanitary, high-purity applications (Food, Pharma) | Demanding industrial applications |
Still Unsure Which PTFE Gasket is Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct gasket is critical for safety and efficiency. The experts at KINTEK can help you navigate the trade-offs.
We specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom gaskets, seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need the ultimate purity of pure PTFE or the enhanced durability of a modified formulation, we provide precision production from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you find the perfect sealing solution. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















