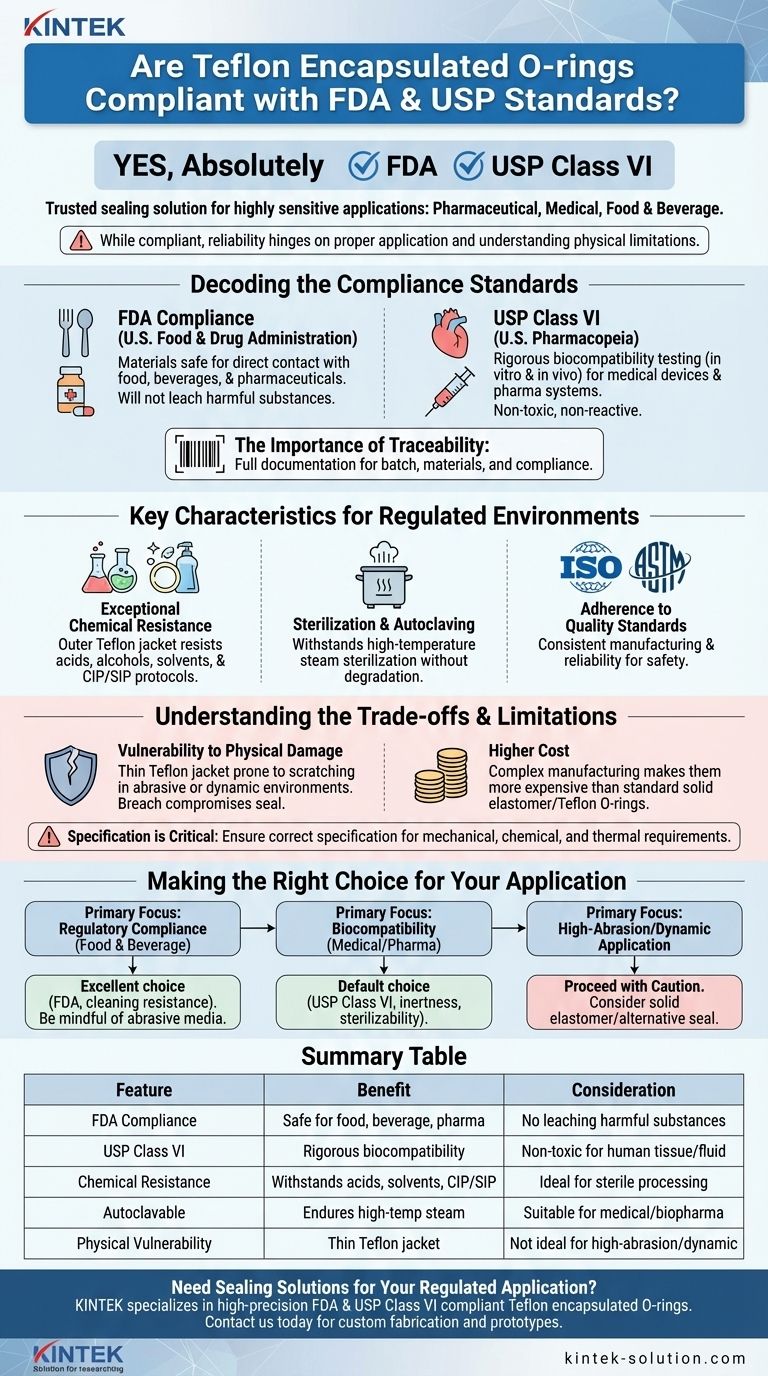
Yes, absolutely. Teflon encapsulated O-rings are specifically designed to comply with both FDA regulations and USP Class VI standards. This dual compliance makes them a trusted sealing solution for highly sensitive applications within the pharmaceutical, medical, and food and beverage industries.
While Teflon encapsulated O-rings meet the stringent material requirements for FDA and USP Class VI, their true reliability hinges on proper application. Understanding their physical limitations is just as critical as verifying their compliance documentation.

Decoding the Compliance Standards
To fully appreciate the suitability of these seals, it's important to understand what each standard signifies for your application. These are not interchangeable; they represent different levels of safety and material testing.
What FDA Compliance Means
The FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) sets regulations for materials that come into direct contact with food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
For an O-ring, FDA compliance means the constituent materials are considered safe for these applications and will not leach harmful substances into the product.
Understanding USP Class VI
The U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) Class VI standard is one of the most rigorous tests for biocompatibility of materials used in medical devices and pharmaceutical systems.
Materials must pass a series of demanding biological reactivity tests, both in vitro and in vivo. This certification provides a high degree of confidence that the material is non-toxic and will not cause a reaction when in contact with human tissue or fluids.
The Importance of Traceability
Reputable manufacturers provide full material traceability and documentation for their encapsulated O-rings. This is non-negotiable for any regulated industry.
This documentation allows you to verify the specific batch, materials used, and compliance certificates, which is essential for quality control and regulatory audits.
Key Characteristics for Regulated Environments
Beyond core compliance, the construction of Teflon encapsulated O-rings provides several advantages crucial for sterile and sanitary applications.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
The outer Teflon (FEP or PFA) jacket provides an extremely inert sealing surface. It offers excellent resistance to a broad range of corrosive chemicals, including acids, alcohols, petroleum spirits, and aromatic solvents.
This allows the seal to withstand aggressive cleaning and sterilization-in-place (CIP/SIP) protocols common in food and pharma processing.
Sterilization and Autoclaving
These O-rings are fully sterilizable and autoclavable. The ability to withstand high-temperature steam sterilization without degrading is a fundamental requirement for many medical and biopharmaceutical applications.
Adherence to Quality Standards
Manufacturing processes for these components typically adhere to international quality standards like ISO and ASTM. This ensures consistency, reliability, and safety from raw material sourcing through to the final inspection.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While compliant and chemically resistant, these O-rings are not a universal solution. Their unique two-part construction creates specific limitations that you must consider.
Vulnerability to Physical Damage
The primary weakness of an encapsulated O-ring is its thin Teflon jacket. It is prone to scratching and damage in abrasive environments or dynamic applications with sharp edges.
Any breach in the encapsulation compromises the entire seal, as the core elastomer is then exposed to the system media.
Higher Cost
The complex manufacturing process of bonding a thin jacket over an elastomeric core makes these seals more expensive than standard solid elastomer or solid Teflon O-rings.
Specification is Critical
Relying on compliance alone is a common mistake. The O-ring must be correctly specified for the application's mechanical, chemical, and thermal requirements to prevent premature failure, downtime, and costly maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires balancing regulatory needs with engineering reality. Use these guidelines to inform your decision.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance in food and beverage: These are an excellent choice due to their FDA compliance and resistance to cleaning agents, but be mindful of abrasive media like slurries.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility for medical or pharma: The USP Class VI certification makes these a default choice for many applications, especially where chemical inertness and sterilizability are required.
- If your primary focus is a high-abrasion or dynamic application: Proceed with caution. You may need to consider a more robust solid elastomer or an alternative seal design to ensure long-term reliability.
By understanding both the compliance benefits and the physical limitations, you can confidently specify the right seal for your critical application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Compliance | Safe for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical contact | Material must not leach harmful substances |
| USP Class VI Certification | Rigorous biocompatibility testing for medical use | Ensures non-toxicity for human tissue/fluid contact |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands acids, solvents, and CIP/SIP protocols | Ideal for sterile processing environments |
| Autoclavable | Can endure high-temperature steam sterilization | Suitable for medical and biopharma applications |
| Physical Vulnerability | Thin Teflon jacket prone to scratching/abrasion | Not ideal for high-abrasion or dynamic applications |
Need Sealing Solutions for Your Regulated Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including FDA and USP Class VI compliant Teflon encapsulated O-rings. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get reliable, documentable seals tailored for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and benefit from our commitment to quality and compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















