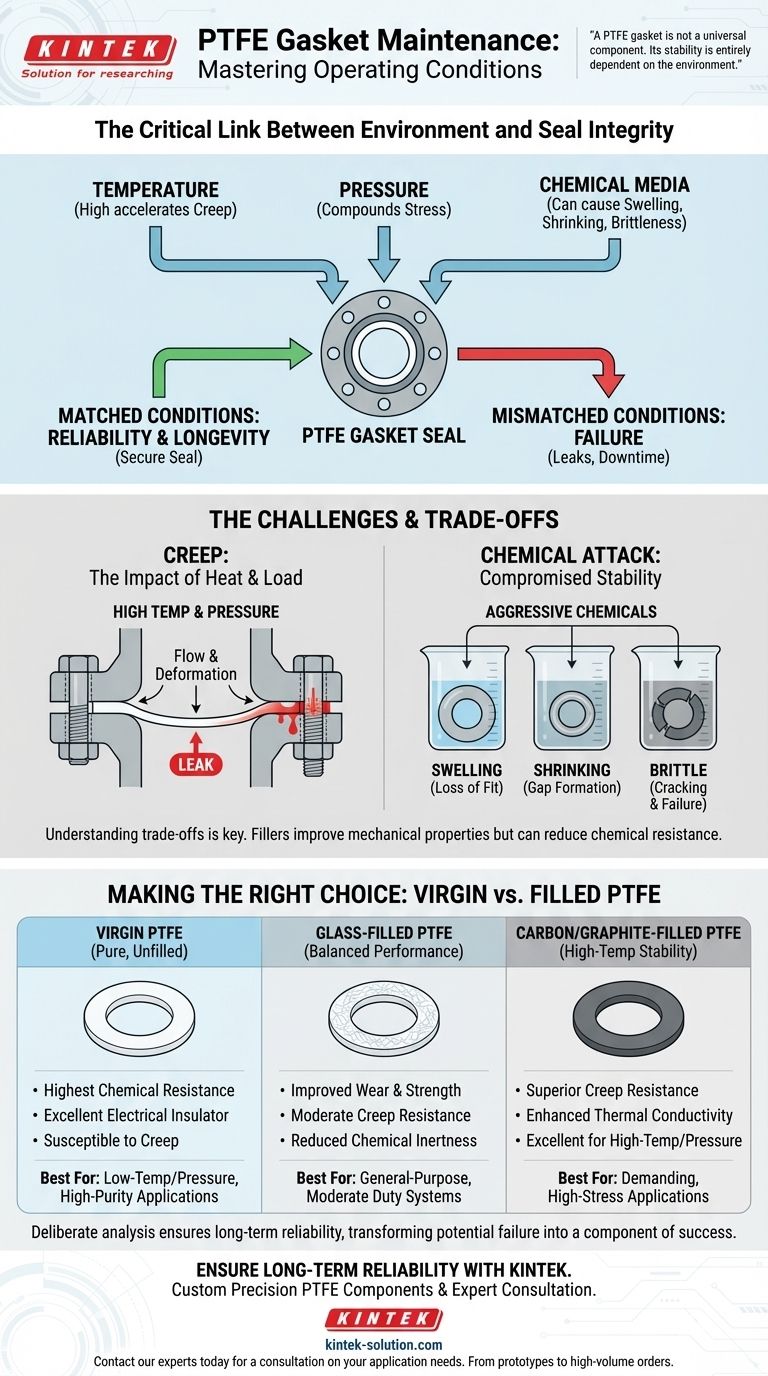
Understanding your operating conditions is the most critical factor in ensuring the reliability and longevity of a PTFE gasket. The specific temperature, pressure, and chemical media of your application directly dictate whether a gasket will maintain its seal or fail prematurely. Failing to match the gasket to its environment can lead to material degradation, leaks, and costly downtime.
A PTFE gasket is not a universal component. Its physical and chemical stability is entirely dependent on the environment. The core challenge is selecting the right PTFE formulation—virgin or filled—to counteract the degrading effects of temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure, thereby preventing seal failure.

The Critical Link Between Environment and Seal Integrity
A gasket creates a seal by conforming to the imperfections of two flange surfaces and maintaining that compressive force over time. The success of this function depends entirely on the stability of the gasket material itself.
The Impact of Temperature and Pressure
PTFE, like all polymers, is susceptible to a phenomenon called creep. This is the tendency of the material to slowly deform or "flow" over time when subjected to constant stress, such as the pressure from tightened bolts.
High temperatures dramatically accelerate creep. As the gasket thins out from this flow, the bolt load decreases, the seal loosens, and a leak becomes inevitable. High pressure further compounds this issue by increasing the mechanical stress on the material.
The Challenge of Chemical Media
While PTFE is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance, it is not completely inert to all substances under all conditions.
Certain aggressive chemicals or high-purity applications can cause the material to swell, shrink, or become brittle. Any change to the gasket's dimensional stability compromises its ability to fill the flange space and maintain a seal.
Why Not All PTFE Gaskets Are Created Equal
To combat these environmental challenges, PTFE is often modified with filler materials. This is why understanding your operating conditions is essential—it guides you to the correct formulation.
Virgin PTFE
This is pure, unfilled PTFE. It offers the highest degree of chemical resistance and is an excellent electrical insulator. However, it is the most susceptible to creep, making it suitable primarily for low-pressure and moderate-temperature applications where chemical purity is paramount.
Filled PTFE
Fillers are added to the PTFE matrix to enhance specific mechanical properties, primarily to combat creep and improve dimensional stability at higher temperatures and pressures.
Common fillers include glass, which improves wear and general mechanical strength, and carbon or graphite, which significantly enhance creep resistance and thermal conductivity. These fillers make the gasket stronger and less likely to deform under load.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filled PTFE gasket is not without its compromises. This decision requires a careful balancing of priorities based on your specific application.
Fillers Can Reduce Chemical Resistance
The primary trade-off is that fillers can reduce the gasket's overall chemical inertness. For example, a glass-filled PTFE gasket will have inferior resistance to hydrofluoric acid or strong alkalis compared to virgin PTFE, as those chemicals can attack the glass filler itself.
Cost vs. Performance
Virgin PTFE is often less expensive than its filled counterparts. However, selecting it for a high-temperature or high-pressure service to save on initial cost is a false economy. The resulting premature failure, downtime, and potential for equipment damage will far outweigh the initial savings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection process must be a deliberate analysis of your system's demands against the properties of the gasket material.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and resistance: Virgin PTFE is the correct choice, provided your temperature and pressure are moderate.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or high-pressure stability: A filled PTFE, such as one with carbon or graphite, is essential to prevent creep and maintain seal integrity.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose seal in a moderately demanding system: A glass-filled PTFE often provides a balanced improvement in mechanical performance over virgin PTFE.
By deliberately matching the PTFE gasket to its operating environment, you transform it from a potential point of failure into a component of long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Operating Condition | Impact on PTFE Gasket | Recommended Material |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperature / Pressure | Accelerates creep, leading to seal loosening | Filled PTFE (e.g., Carbon/Graphite) |
| Aggressive Chemicals | Can cause swelling, shrinkage, or brittleness | Virgin PTFE (for maximum chemical resistance) |
| Moderate, General-Purpose | Requires balanced mechanical & chemical performance | Glass-Filled PTFE |
Ensure Long-Term Reliability for Your Critical Seals
Don't let gasket failure cause costly downtime or compromise your process. The right PTFE formulation is critical for your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical environment.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We help you select or fabricate the perfect seal—from virgin PTFE for chemical purity to filled compounds for superior creep resistance—ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your application needs. We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, delivering the precision and reliability your operations demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of glass-filled PTFE? Enhanced Strength & Wear Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What are the conditions that necessitate the use of PTFE rotary seals? Achieve Peak Performance in Extreme Environments
- What is the coefficient of friction for Pure Teflon? Unlock Superior Low-Friction Performance
- How do PTFE valves and components support high-purity liquid transfer? Ensure Product Integrity with Inert Materials
- Why are PTFE-based materials preferred for RF PCB designs? Achieve Superior Signal Integrity at High Frequencies
- What are some examples of specialty PTFE formulations and their benefits? Enhance Performance with Filled PTFE
- What role does the PTFE lining play in these valves? Achieve Superior Chemical Resistance and Purity
- What are the limitations of PTFE O-rings' media resistance? Avoid Common Application Traps



















