In a laboratory setting, the non-wetting property of Teflon coatings is critically important because it prevents liquids from sticking to the surface of glassware. This ensures that samples are transferred completely and, most importantly, minimizes the risk of cross-contamination between different experiments, safeguarding the integrity of your results.
The core value of Teflon's non-wetting surface in a lab is not just about being "non-stick"—it's a fundamental feature that ensures experimental purity. It guarantees that the substance you are working with remains uncontaminated and is fully accounted for.
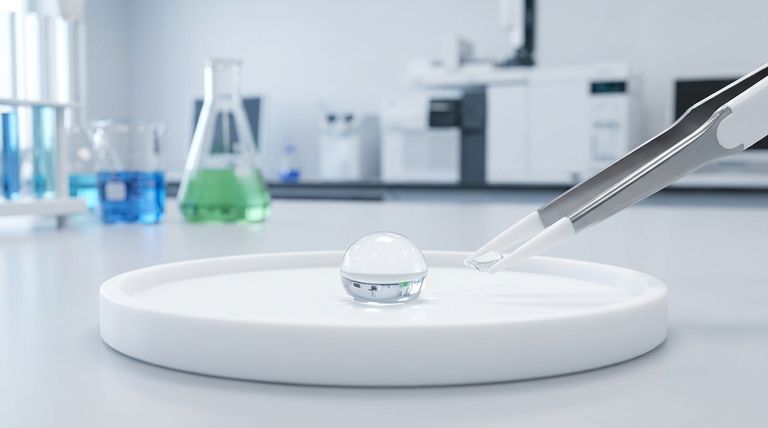

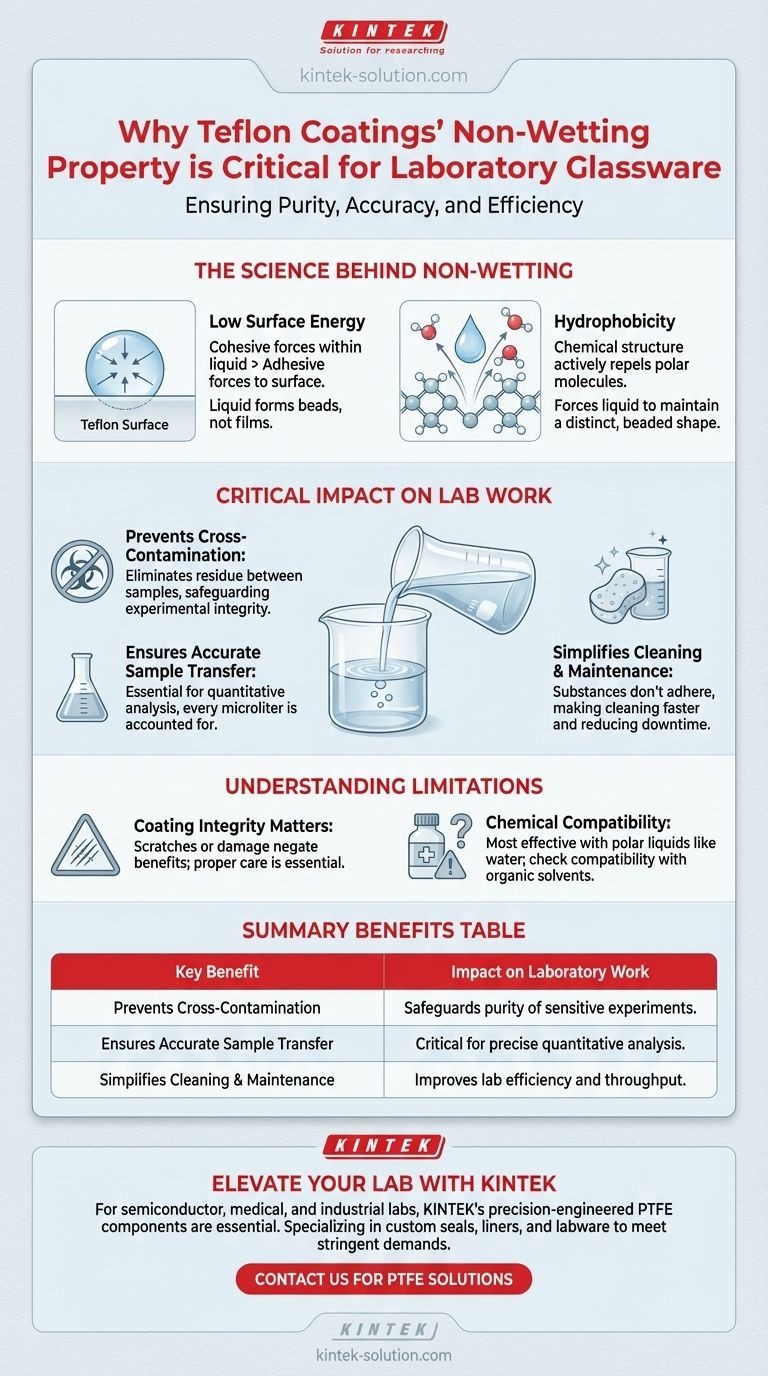
The Science Behind "Non-Wetting"
To understand why this property is so vital, we first need to look at the physics involved. The term "non-wetting" describes a specific interaction between a liquid and a solid surface, driven by a few key principles.
The Role of Low Surface Energy
Teflon has an exceptionally low surface energy. This means that the cohesive forces within a liquid (the forces that make liquid molecules stick to each other) are much stronger than the adhesive forces between the liquid and the Teflon surface.
As a result, the liquid minimizes its contact with the glassware, pulling itself into beads rather than spreading out into a thin film.
Hydrophobicity in Action
This behavior is a clear demonstration of hydrophobicity, or water-repelling. The chemical structure of Teflon actively repels the polar molecules found in water and many aqueous solutions.
Instead of adhering to the glass, the liquid is physically pushed away at a molecular level, forcing it to maintain a distinct, beaded shape.
The Critical Impact on Laboratory Work
This non-wetting characteristic translates directly into tangible benefits that are essential for accurate and repeatable scientific work. It moves beyond a simple convenience and becomes a requirement for precision.
Preventing Cross-Contamination
The primary benefit is the prevention of cross-contamination. When a liquid "wets" a standard glass surface, a thin film of residue is inevitably left behind after the substance is poured out.
This residue can easily contaminate the next sample introduced to that beaker or test tube, invalidating experimental results. Teflon’s non-wetting surface ensures that virtually no residue remains, preserving the purity of each subsequent procedure.
Ensuring Accurate Sample Transfer
In quantitative analysis, every microliter counts. If a portion of your sample sticks to the walls of the glassware, the volume or mass you transfer is inherently inaccurate.
The non-wetting property of Teflon ensures a complete and clean transfer of substances, which is critical for experiments that rely on precise measurements.
Simplifying Cleaning and Maintenance
The non-stick nature of Teflon makes glassware significantly easier and faster to clean. Because substances do not adhere to the surface, a simple rinse is often sufficient to prepare the glassware for its next use.
This improves lab efficiency and reduces the risk of lingering contaminants that can persist even after standard cleaning protocols on other materials.
Understanding the Limitations
While highly effective, the benefits of Teflon's non-wetting property are dependent on the condition of the coating. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Importance of Coating Integrity
The non-wetting property is only as good as the coating itself. Scratches, abrasions, or chemical degradation can damage the Teflon layer.
These damaged areas can create sites where liquids can adhere, negating the benefits and potentially trapping contaminants. Proper care of coated glassware is essential to maintain its performance.
Chemical Compatibility
Teflon's non-wetting properties are most pronounced with polar liquids like water. While it is highly resistant to most chemicals, its interaction with certain non-polar organic solvents may differ.
Always ensure the coating is compatible with the specific substances being used in your experiment to guarantee optimal performance and prevent damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, using Teflon-coated glassware is a strategic decision to control variables and enhance the reliability of your work.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: The complete sample transfer enabled by a non-wetting surface is non-negotiable for accurate measurements.
- If your primary focus is preventing cross-contamination in sensitive assays: Teflon provides a physical barrier against residue, preserving the purity of each distinct experiment.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput lab efficiency: The easy-to-clean nature of non-wetting surfaces reduces downtime and minimizes the risk of cleaning-related errors.
Using Teflon-coated glassware is a direct investment in the accuracy and integrity of your scientific data.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Impact on Laboratory Work |
|---|---|
| Prevents Cross-Contamination | Eliminates residue, safeguarding the purity of sensitive experiments and assays. |
| Ensures Accurate Sample Transfer | Guarantees complete transfer of substances, critical for precise quantitative analysis. |
| Simplifies Cleaning & Maintenance | Reduces cleaning time and effort, improving lab efficiency and throughput. |
Elevate the integrity of your laboratory work with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
For semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications, the non-wetting properties of PTFE (Teflon) are essential for preventing contamination and ensuring accuracy. KINTEK specializes in the custom fabrication of high-quality PTFE seals, liners, and labware—from prototypes to high-volume orders—designed to meet the stringent demands of specialized industries.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our PTFE solutions can protect your processes and enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















