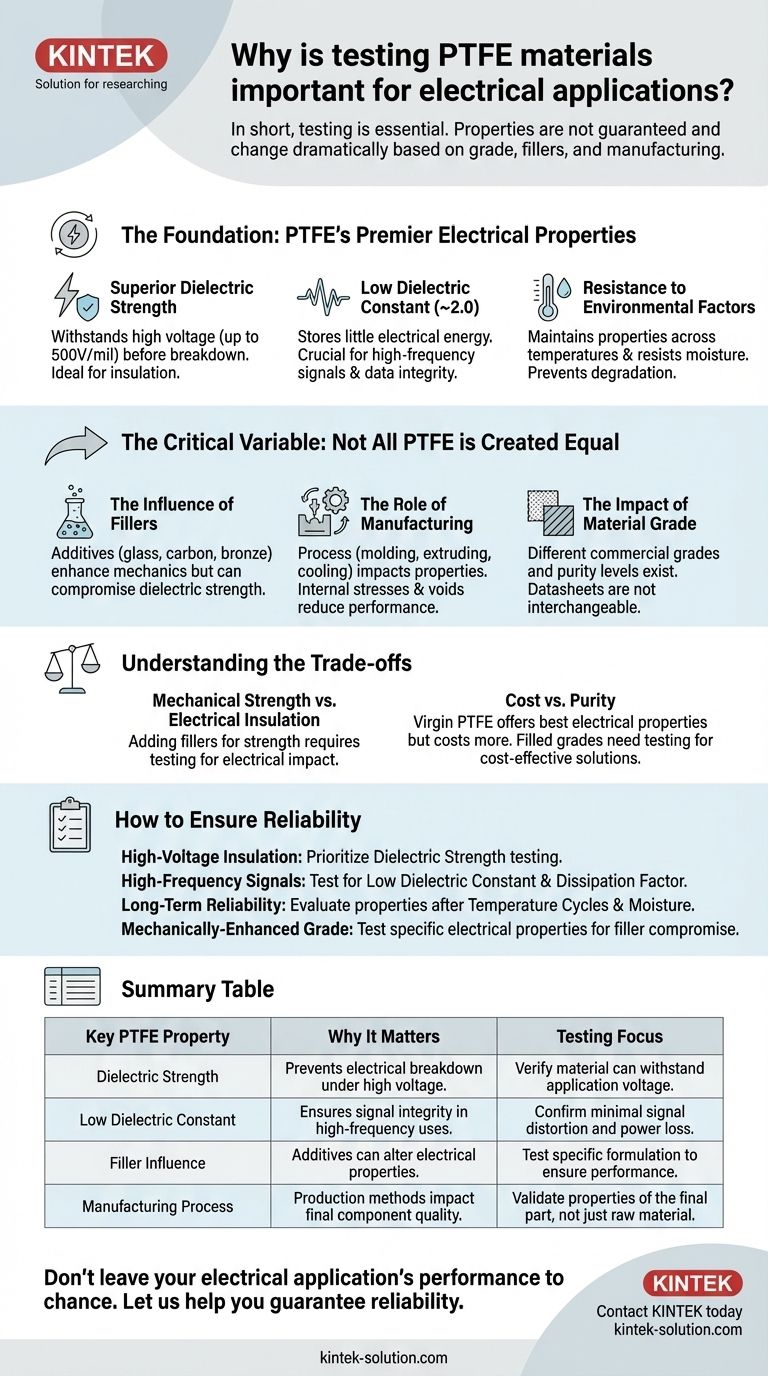
In short, testing is essential because the exceptional electrical properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are not guaranteed. These properties can change dramatically based on the specific grade, the type and amount of filler added, and the manufacturing process used to create the final component. Without testing, you are assuming—not verifying—that the material will meet your application's critical performance and safety requirements.
While pure PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators known, its real-world performance is not a fixed value. Testing is the only way to confirm that the specific formulation and form factor you are using will deliver the reliability your electrical application demands.

The Foundation: Why PTFE is a Premier Electrical Insulator
To understand the need for testing, we must first appreciate the inherent properties that make PTFE a default choice for demanding electrical applications. Its molecular structure gives it a unique combination of characteristics.
Superior Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is a measure of a material's ability to withstand a high voltage before it breaks down and allows current to pass through.
PTFE is an exceptional insulator, capable of withstanding up to 500 volts per mil in thin sections. This makes it ideal for wire insulation, high-voltage encapsulation, and separating conductive surfaces in components like capacitors.
Low Dielectric Constant
A low dielectric constant means a material stores very little electrical energy when subjected to an electric field.
PTFE's low constant (around 2.0) is crucial for high-frequency applications like data cables and printed circuit boards (PCBs). It ensures minimal signal distortion and power loss, preserving the integrity of the data being transmitted.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
PTFE maintains its excellent insulating properties across a very wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
Furthermore, it resists moisture penetration far better than other plastics like nylon or PVC. This prevents degradation of its electrical performance over time, especially in humid or harsh environments.
The Critical Variable: Not All PTFE is Created Equal
The ideal properties of pure, virgin PTFE are just a baseline. In practice, the material you specify or purchase has been modified, and these modifications are the primary reason testing becomes non-negotiable.
The Influence of Fillers
Fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze are often added to PTFE to enhance mechanical properties such as wear resistance or compressive strength.
However, these additives can significantly alter the material's electrical characteristics. A filler might improve mechanical durability but compromise dielectric strength, making the component unsuitable for its intended electrical purpose.
The Role of Manufacturing
The final form of the component dramatically impacts its properties. The electrical performance of a thin, molded PTFE sheet will differ from that of a thick-walled, extruded tube.
The manufacturing process itself—including temperatures, pressures, and cooling rates—can introduce internal stresses and voids that create weak points, reducing the material's effective dielectric strength.
The Impact of Material Grade
Different commercial grades of PTFE exist, each with a slightly different formulation. The purity of the base resin and the consistency of the processing determine the final quality.
Assuming one grade's datasheet applies to another is a common and costly mistake. Only by testing the specific material you intend to use can you guarantee it aligns with your design specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a PTFE material is rarely about finding a single "best" option. It involves balancing competing requirements, and testing is how you validate that you've made the right compromise.
Mechanical Strength vs. Electrical Insulation
This is the most common trade-off. You may need a component that is both a great insulator and highly resistant to physical wear.
Adding a filler to achieve the required mechanical strength necessitates testing to confirm that the electrical insulation properties remain within your acceptable limits.
Cost vs. Purity
Virgin, high-purity PTFE generally offers the best and most consistent electrical properties. However, it may be more expensive or lack the structural characteristics of a filled grade.
Testing allows you to evaluate if a more cost-effective, filled grade can meet the minimum electrical requirements of a less critical application, optimizing your design for both performance and budget.
How to Ensure Reliability in Your Application
Your testing protocol should be directly linked to the most critical function of the component in your design.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: Your testing must prioritize dielectric strength to prevent catastrophic electrical breakdown.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity: You must test for a low dielectric constant and dissipation factor to ensure clean, low-loss signal transmission.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability in harsh environments: Your testing should include evaluating electrical properties after exposure to temperature cycles and moisture.
- If you are using a mechanically-enhanced filled grade: You must test its specific electrical properties to verify it has not been compromised by the additives.
Ultimately, rigorous testing transforms PTFE from a promising material choice into a predictable and reliable engineering component.
Summary Table:
| Key PTFE Property | Why It Matters for Electrical Applications | Testing Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | Prevents electrical breakdown under high voltage. | Verify material can withstand application voltage. |
| Low Dielectric Constant | Ensures signal integrity in high-frequency uses. | Confirm minimal signal distortion and power loss. |
| Filler Influence | Additives can alter electrical properties. | Test specific formulation to ensure performance. |
| Manufacturing Process | Production methods impact final component quality. | Validate properties of the final part, not just raw material. |
Don't leave your electrical application's performance to chance.
At KINTEK, we understand that the exceptional properties of PTFE are only reliable when verified. We manufacture precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures that your PTFE parts, whether prototypes or high-volume orders, are fabricated to meet your exact electrical and mechanical requirements.
Let us help you guarantee reliability. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and how our custom PTFE solutions can deliver the performance and safety your application demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How is Teflon used in the textile industry? Creating Stain-Resistant, Water-Repellent Fabrics
- What is PTFE's biocompatibility and its medical applications? A Guide to Safe, Non-Reactive Medical Devices
- What are the chemical properties of Teflon? The Science Behind Its Extreme Inertness
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What industrial advantages does PTFE offer? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What are the medical applications of PTFE? Critical Uses in Implants and Instruments
- How does Teflon perform in harsh chemical environments? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications



















