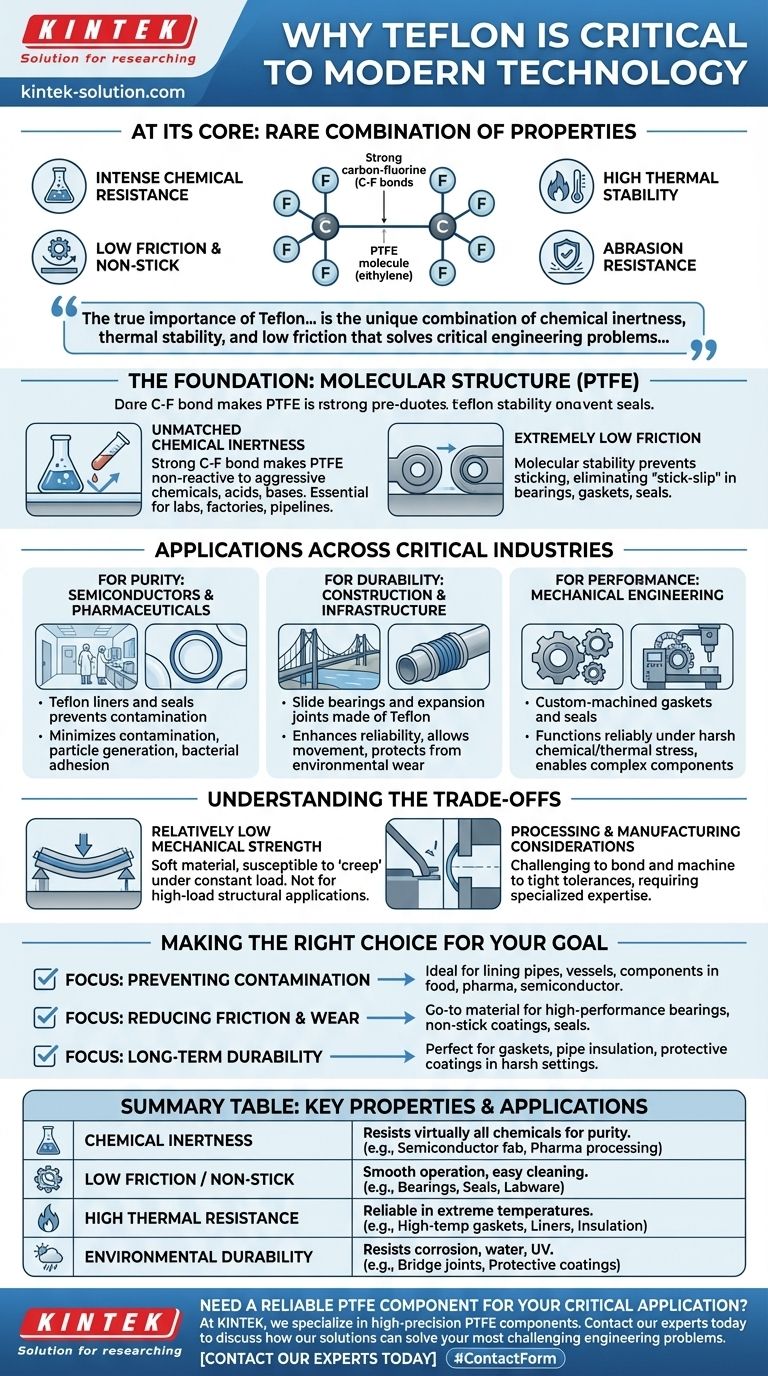
At its core, Teflon is vital to modern technology because of its exceptionally rare combination of properties. It is intensely resistant to chemicals, heat, and abrasion while also having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, making it the ultimate material for non-stick surfaces and reliable performance in extreme environments.
The true importance of Teflon isn't just one of its famous traits, like being non-stick. It's the unique combination of chemical inertness, thermal stability, and low friction that solves critical engineering problems across industries, from ensuring purity in semiconductor manufacturing to guaranteeing the durability of massive bridges.

The Foundation: A Unique Molecular Structure
Teflon, scientifically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), derives its power from its simple but incredibly stable chemical makeup. This structure is the source of all the properties that make it so indispensable.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms in PTFE is exceptionally strong. This makes the material almost completely non-reactive.
It can withstand exposure to a vast range of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases without degrading. This is why it is essential for handling corrosive materials in labs, factories, and pipelines.
Extremely Low Friction
The same molecular stability that prevents chemical reactions also keeps other materials from sticking to Teflon's surface. This results in its famous non-stick quality.
This property is critical in mechanical applications like bearings, gaskets, and seals, where it eliminates "stick-slip" motion, ensuring smooth, predictable, and efficient operation.
High Thermal and Environmental Resistance
Teflon maintains its structural integrity across a wide range of temperatures. It can perform reliably in environments where lesser materials would melt or become brittle.
Furthermore, it repels both water and oil and resists corrosion, making it a powerful material for protecting components from environmental wear and degradation.
Applications Across Critical Industries
Teflon’s unique profile allows it to solve problems in fields that have vastly different requirements, demonstrating its incredible versatility.
For Purity: Semiconductors and Pharmaceuticals
In industries where even microscopic contamination can be catastrophic, Teflon's inertness is paramount. Its non-reactive and smooth surface prevents materials from sticking to it.
This minimizes particle generation and bacterial adhesion, ensuring the purity of products in semiconductor fabrication, pharmaceutical production, and food processing.
For Durability: Construction and Infrastructure
Teflon enhances the reliability and lifespan of major infrastructure like bridges, pipelines, and buildings.
It is used in slide bearings and expansion joints to allow massive structures to move safely without generating destructive friction. Its corrosion resistance also protects components, extending their service life significantly.
For Performance: Mechanical Engineering
Custom-machined Teflon parts are indispensable in environments that demand high performance under stress.
Its properties are leveraged to create complex components like gaskets, sealing rings, and custom bearings that must function reliably under harsh chemical or thermal conditions where other plastics or metals would fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and being a trusted advisor means acknowledging limitations. While Teflon is revolutionary, it has specific trade-offs that engineers must consider.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or high-strength engineering plastics, Teflon is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep"—deforming slowly over time when under a constant load.
This means it is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own and is best used for its surface and chemical properties.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
The same properties that make Teflon useful can also make it challenging to process. Bonding it to other materials can be difficult, often requiring specialized surface treatments. Machining it to extremely tight tolerances also requires specific expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material is about matching its strengths to your primary objective. Teflon is often the definitive choice when performance in specific conditions is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination: Teflon's chemical inertness makes it the ideal choice for lining pipes, vessels, and components in the food, pharmaceutical, or semiconductor industries.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Teflon is the go-to material for high-performance bearings, non-stick coatings, and seals where smooth, reliable movement is essential.
- If your primary focus is long-term environmental durability: Teflon's resistance to corrosion, water, and chemicals makes it perfect for gaskets, pipe insulation, and protective coatings in harsh industrial or outdoor settings.
Ultimately, Teflon's role in technology is to provide stability and reliability in environments where other materials would quickly fail.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters | Primary Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all chemicals, ensuring purity. | Semiconductor fabrication, pharmaceutical processing. |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Provides smooth, reliable operation and easy cleaning. | Bearings, seals, non-stick coatings for labware. |
| High Thermal Resistance | Performs reliably in extreme temperatures. | High-temperature gaskets, liners, and insulation. |
| Environmental Durability | Resists corrosion, water, and UV degradation. | Expansion joints in bridges, protective coatings. |
Need a reliable PTFE component for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get a solution that delivers unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and performance, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your most challenging engineering problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of PTFE in its applications? Understanding Its Mechanical Weaknesses
- What are some common fillers used with PTFE and their benefits? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What types of plating solutions are compatible with PTFE? A Guide to Maximizing Chemical Resistance
- What is Glass-Filled PTFE and what are its properties? A Guide to Enhanced PTFE Performance
- What are the different types of Teflon available? A Guide to PTFE, FEP, PFA, and More
- How does PTFE perform as an electrical insulator? Unmatched Signal Integrity & High-Voltage Reliability
- Why is PTFE widely used in the medical device industry? Its Biocompatibility & Low-Friction Drive Safety
- What are the two main polymerization methods for producing PTFE? Choose the Right Form for Your Application



















