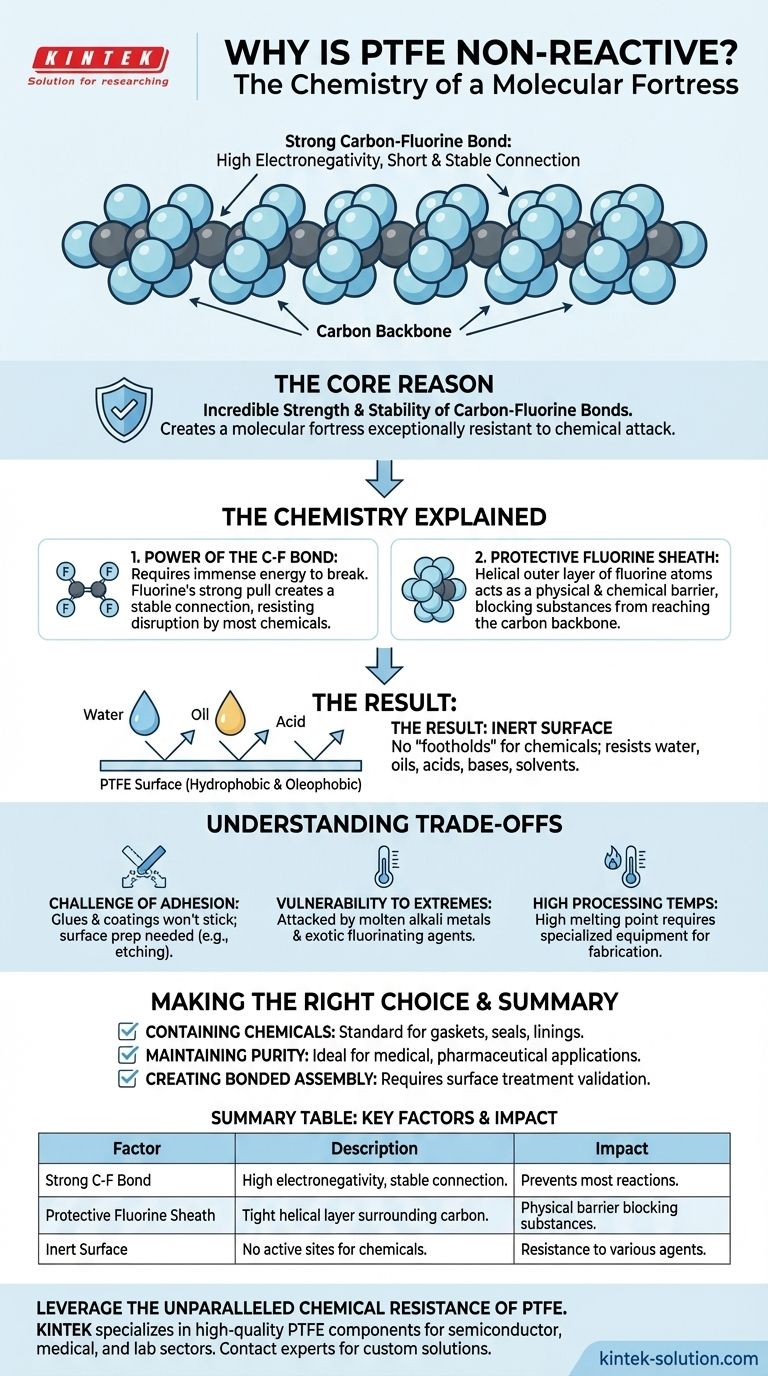
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is considered non-reactive because of the incredible strength and stability of its carbon-fluorine bonds. This simple molecular fact creates a material that is exceptionally resistant to chemical attack, making it inert when exposed to the vast majority of corrosive substances.
The non-reactivity of PTFE is not just a surface-level trait; it is a direct result of its fundamental chemistry. A protective "sheath" of fluorine atoms surrounds a carbon backbone, creating a molecular fortress that is nearly impenetrable to other chemicals.
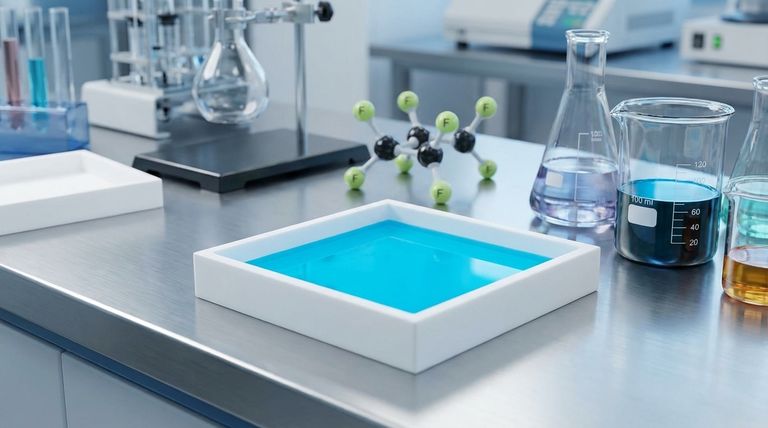

The Chemistry of a Molecular Fortress
To understand PTFE's resilience, we must look at how it is constructed at the atomic level. The entire property of non-reactivity stems from the unique relationship between carbon and fluorine.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it has an extremely strong pull on electrons. When it bonds with carbon, it forms a short, powerful, and highly stable connection.
This bond is so strong that it requires a tremendous amount of energy to break. Most chemicals simply lack the power to disrupt it, so no reaction occurs.
A Protective Fluorine Sheath
The PTFE molecule is a long chain of carbon atoms, but this carbon "backbone" is not exposed. It is completely encased by a tightly packed, helical sheath of fluorine atoms.
This outer layer of fluorine acts as a physical and chemical barrier. It effectively prevents other substances from ever getting close enough to the more vulnerable carbon chain to even attempt a reaction.
The Result: A Chemically Inert Surface
Because of these two factors—the powerful bonds and the protective sheath—the surface of PTFE presents no "footholds" for other chemicals. It does not react with water, oils, acids, bases, or aggressive solvents.
This is why PTFE is not only non-reactive but also hydrophobic (repels water) and oleophobic (repels oil), leading to its famous non-stick properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its non-reactivity is a tremendous asset, it also creates inherent challenges. This inert nature is a double-edged sword that you must consider in any application.
The Challenge of Adhesion
The same property that prevents chemicals from sticking to PTFE also prevents glues, paints, and other coatings from adhering to it. You cannot easily bond PTFE to other materials.
Specialized surface preparation, such as chemical etching, is required to create a bondable surface, adding complexity and cost to manufacturing processes.
Vulnerability to Specific, Extreme Conditions
While resistant to nearly everything, PTFE is not invincible. It can be attacked by a few highly reactive substances, such as molten alkali metals (like sodium) and some exotic fluorinating agents.
These are not common industrial chemicals, but it is critical to know that limitations exist.
High Processing Temperatures
The stability of the molecule also gives PTFE a very high melting point. This requires specialized equipment and high energy input for processes like molding or extrusion, making it more difficult to fabricate than many other plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE because it is "non-reactive" is a good start, but understanding the context is key to successful implementation.
- If your primary focus is containing aggressive chemicals: PTFE is an industry-standard choice for gaskets, seals, and linings in corrosive environments.
- If your primary focus is maintaining product purity: Its inertness prevents it from leaching into substances, making it ideal for medical, pharmaceutical, and high-purity semiconductor applications.
- If your primary focus is creating a bonded assembly: Be prepared to specify and validate a surface treatment process, as untreated PTFE will almost certainly fail to adhere.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of PTFE begins with respecting the fundamental chemistry that makes it so uniquely stable.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Description | Impact on Non-Reactivity |
|---|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bond | Fluorine's high electronegativity creates a short, powerful, and stable bond with carbon. | Requires immense energy to break, preventing most chemical reactions. |
| Protective Fluorine Sheath | A tight, helical layer of fluorine atoms completely surrounds the carbon backbone. | Acts as a physical barrier, blocking other substances from reaching the carbon chain. |
| Inert Surface | The surface presents no active sites for other chemicals to latch onto. | Results in resistance to water, oils, acids, bases, and solvents. |
Leverage the unparalleled chemical resistance of PTFE for your most demanding applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a standard part or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards of purity and durability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your critical challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties
- What is Teflon and what are its alternative names? Understanding PTFE, the Material Behind the Brand
- When was PTFE discovered and developed? The Accidental Invention That Changed Industries
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE
- What environmental resistances does PTFE offer? Unmatched Durability for Harsh Conditions



















