In short, the chemical resistance of a PTFE reducing flange is its most critical feature because it allows the component to maintain its structural integrity and sealing capability when exposed to aggressive substances like acids, bases, and solvents. This prevents corrosion, degradation, and catastrophic failure within a piping system.
The decision to use PTFE is not merely about preventing a single leak. It is a strategic choice to ensure the long-term safety of personnel, the purity of the product, and the financial viability of the operation by eliminating the risks associated with material degradation.
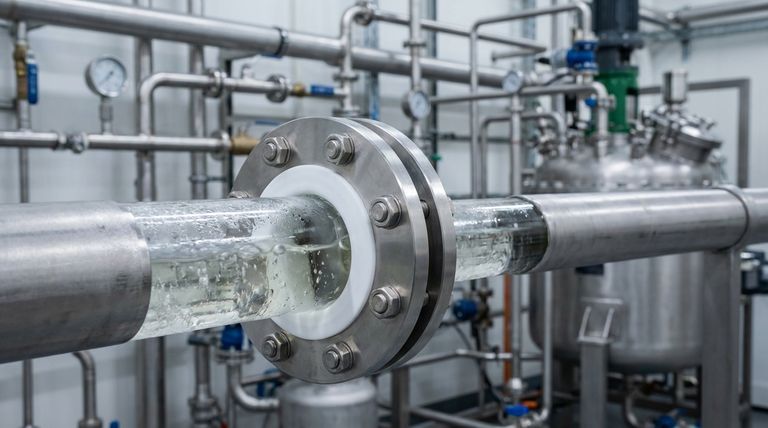

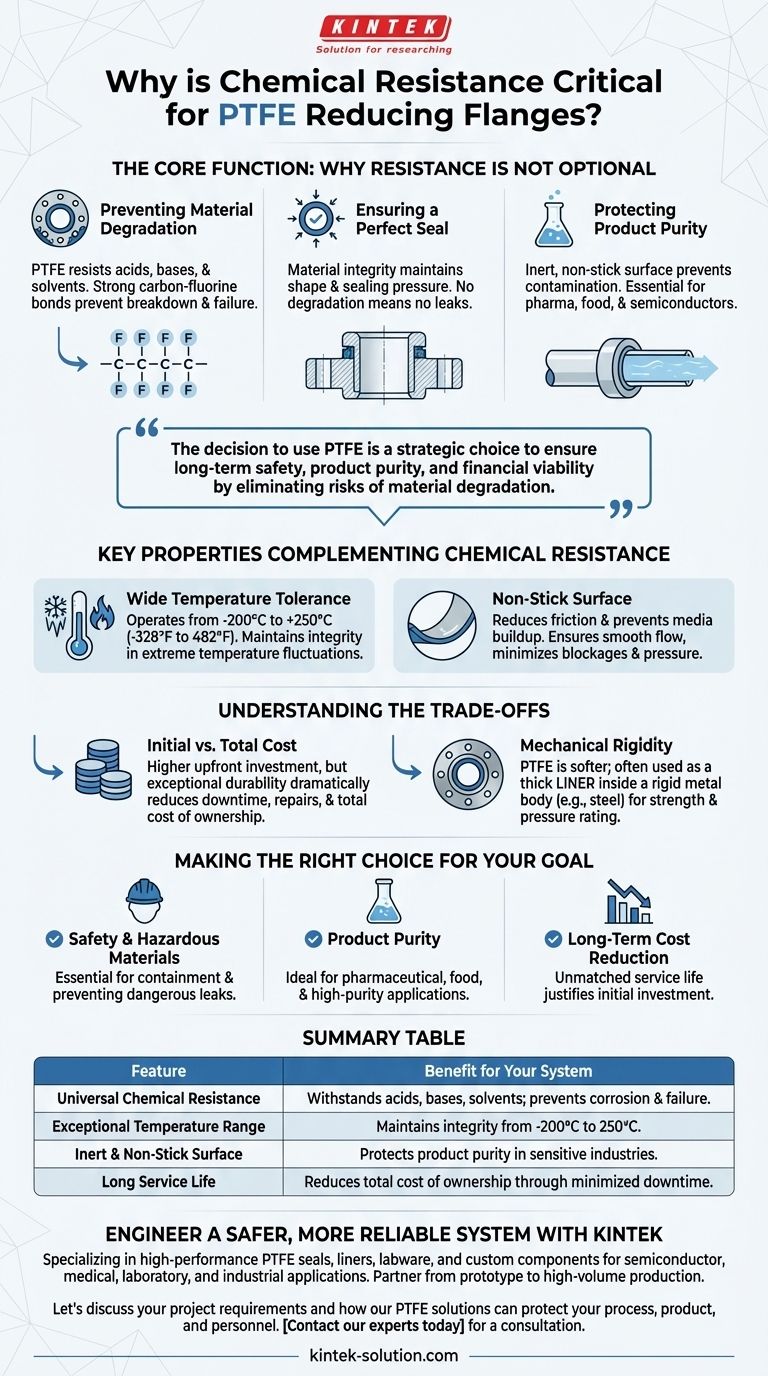
The Core Function: Why Resistance is Not Optional
A reducing flange is a point of transition, connecting a larger pipe to a smaller one. This change in diameter inherently creates turbulence and mechanical stress, making it a potential point of weakness. When the fluids being transported are corrosive, this weakness is magnified.
Preventing Material Degradation and Failure
The primary job of chemical resistance is to prevent the flange material from breaking down. Unlike metals that can rust or plastics that can become brittle, PTFE remains unaffected by nearly all industrial chemicals.
This resilience is due to the incredibly strong and stable carbon-fluorine bonds that make up its molecular structure. These bonds are non-reactive, meaning they do not give up electrons to corrosive agents.
Ensuring a Perfect Seal
A flange's most important task is to create a leak-proof seal. If the material degrades from chemical attack, it will lose its shape and compressive strength.
This leads to a loss of sealing pressure, resulting in leaks that can be hazardous to personnel and the environment. Because PTFE does not degrade, it maintains its physical properties, ensuring a reliable seal over a long service life.
Protecting Product Purity
In industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and semiconductors, even microscopic contamination can ruin an entire batch.
A corroding flange can leach particles or impurities into the process fluid. PTFE is exceptionally inert and has a non-stick surface, which means it will not react with or contaminate the product flowing through the pipe.
Key Properties That Complement Chemical Resistance
While chemical resistance is the headline feature, other properties of PTFE work in concert to deliver a superior performance in demanding environments.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE components can operate effectively across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically from -200°C to over 250°C (-328°F to 482°F). This allows them to maintain their chemical resistance and physical integrity in systems with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Non-Stick Surface
The famous non-stick quality of PTFE is highly valuable in piping systems. It reduces friction and prevents media from building up on the flange surface. This ensures a smooth, consistent flow and minimizes the risk of blockages that could increase pressure and stress on the connection.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. Understanding the limitations of PTFE is key to making an informed decision.
Initial Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
PTFE-lined components often have a higher upfront cost compared to flanges made from standard metals or other plastics. This initial investment can be a significant consideration.
However, their exceptional durability dramatically reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements. When factoring in the cost of downtime, maintenance labor, and potential safety incidents, PTFE almost always provides a lower total cost of ownership in corrosive applications.
Mechanical Rigidity
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to steel or other alloys. For this reason, you will most often see it used as a thick liner inside a rigid metal flange body (such as ductile iron or stainless steel).
This design combines the mechanical strength and pressure rating of the metal housing with the superior chemical and temperature resistance of the PTFE wetted surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a reducing flange, your decision should be guided by the primary demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is safety and handling hazardous materials: PTFE's near-universal chemical resistance is essential to guarantee containment and prevent dangerous leaks.
- If your primary focus is product purity: The inert, non-leaching, and non-stick nature of PTFE makes it the ideal choice for pharmaceutical, food, and high-purity applications.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost reduction: The initial investment in PTFE is quickly justified by its unmatched service life and the elimination of maintenance costs associated with material failure.
Ultimately, choosing a flange based on its chemical compatibility is the foundation of a safe, reliable, and efficient piping system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Your System |
|---|---|
| Universal Chemical Resistance | Withstands acids, bases, and solvents to prevent corrosion and failure. |
| Exceptional Temperature Range | Maintains integrity from -200°C to 250°C (-328°F to 482°F). |
| Inert & Non-Stick Surface | Protects product purity in pharmaceuticals, food, and semiconductors. |
| Long Service Life | Reduces total cost of ownership by minimizing downtime and replacements. |
Engineer a safer, more reliable system with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
For semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications, the chemical resistance of your flanges is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components that guarantee long-term integrity against the most aggressive chemicals.
We partner with you from prototype to high-volume production, ensuring every part meets your exact specifications for precision and durability. Let's discuss your project requirements and how our PTFE solutions can protect your process, product, and personnel.
Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE's thermal expansion and contraction affect its machining and application? Master Dimensional Stability
- How do rubber bellows compare to PTFE bellows? Choose the Right Expansion Joint for Your System
- What is counter rotation in rotary seals and why is it problematic? Prevent Catastrophic Seal Failure
- Where are thick PTFE washers (2mm – 4mm) typically used? For High-Pressure Sealing & Electrical Insulation
- Why is lubrication important in PTFE machining? Master Heat Control for Precision Parts
- What is the PH range and temperature tolerance of pure PTFE gaskets? Master Extreme Chemical and Thermal Sealing
- Why are PTFE O-rings suitable for food production machinery? Ensuring Purity and Performance
- How does PTFE's low friction performance benefit industrial applications? Enable Clean, Reliable Movement Without Lubricants



















