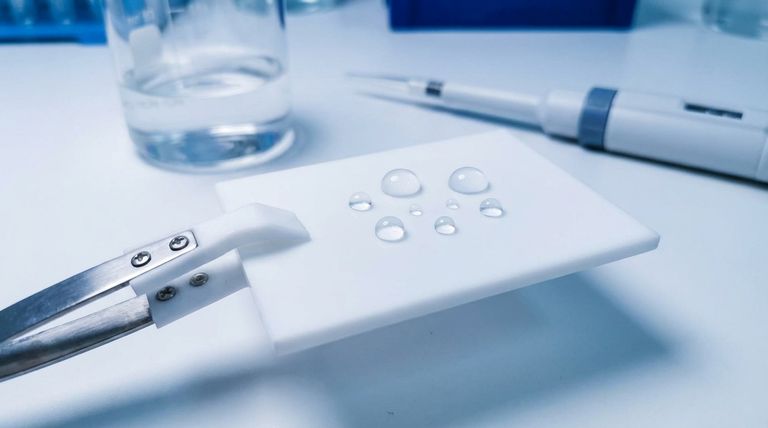
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is hydrophobic because of its chemical structure. The surface of PTFE is uniformly coated in fluorine atoms, which are highly electronegative and create an extremely stable, non-polar surface. Since water is a polar molecule, there is virtually no attraction between the two, causing water to bead up and roll off rather than wetting the surface.
The core reason for PTFE's water-repelling nature is a fundamental mismatch in chemical personality. The non-polar PTFE surface offers nothing for the highly polar water molecules to grab onto, forcing the water to stick to itself and minimize contact.
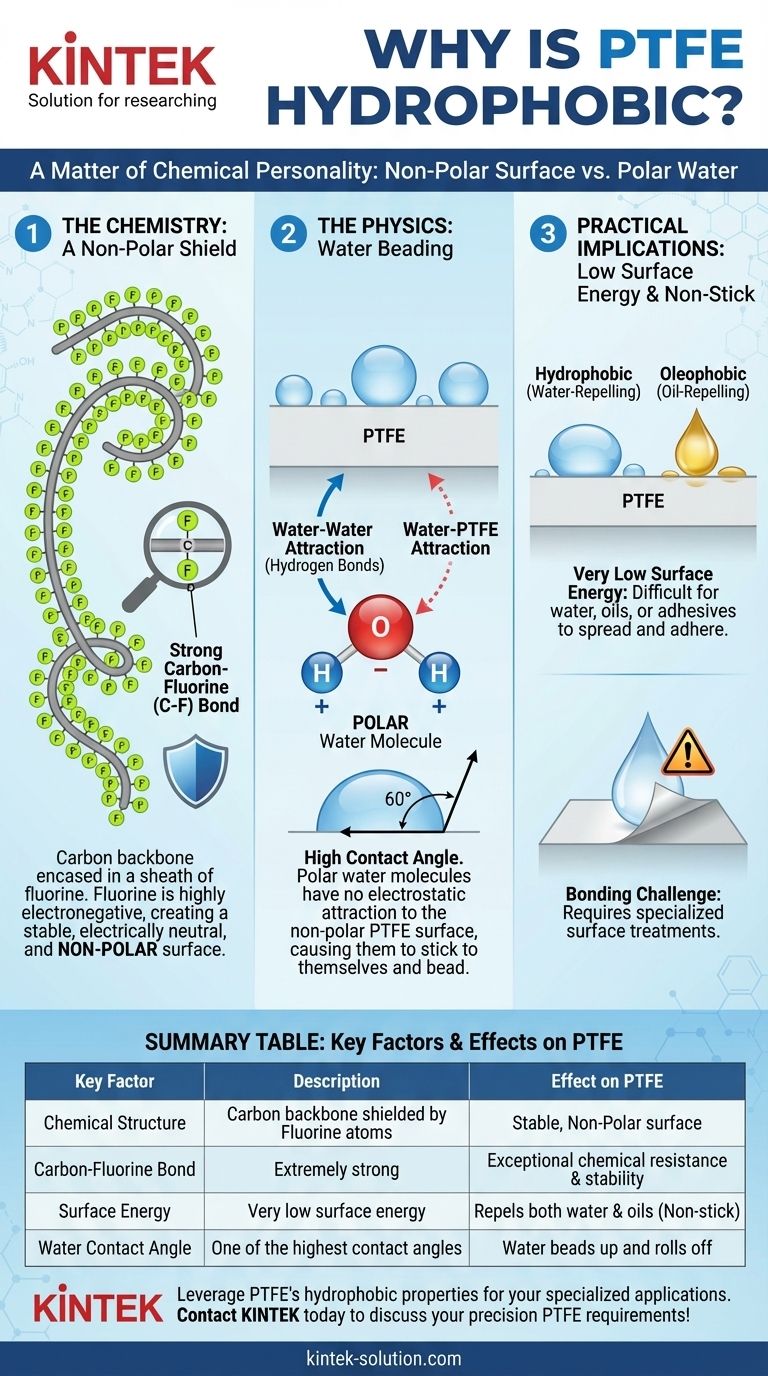
The Chemistry of the PTFE Surface
The Dominance of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE is a polymer, a long chain of carbon atoms. However, the carbon backbone is completely encased in a sheath of fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine (C-F) is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This is because fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it pulls electrons towards itself more strongly than any other element.
Creating a Non-Polar Shield
This intense pull of electrons by the fluorine atoms creates a very dense, stable, and electrically neutral surface.
Because the fluorine atoms are arranged symmetrically around the carbon chain, they create a uniform surface with no positive or negative charges. This makes the PTFE surface non-polar.
The Physics of Water Interaction
Water: A Polar Molecule
Water (H₂O) is a polar molecule. The oxygen atom pulls electrons away from the two hydrogen atoms, creating a slight negative charge on the oxygen side and slight positive charges on the hydrogen side.
This polarity makes water molecules act like tiny magnets, attracting each other and other polar substances. This is what creates surface tension.
The Standoff at the Surface
When polar water molecules encounter the non-polar PTFE surface, there is no electrostatic force to attract them. The water molecules are far more attracted to each other than they are to the PTFE.
This forces the water to minimize its contact with the surface by forming beads. This phenomenon is measured as a high contact angle, which is the primary indicator of a hydrophobic surface. PTFE has one of the highest contact angles of any solid.
The Practical Implications
Understanding Low Surface Energy
The weak attraction between PTFE and other substances is described as having low surface energy. This is the key to its famous "non-stick" properties.
Because nothing is attracted to the surface, it’s difficult for water, oils, or other materials to spread out and adhere. This is why PTFE is not only hydrophobic (water-repelling) but also oleophobic (oil-repelling).
The Bonding Challenge
This same low surface energy property makes PTFE notoriously difficult to glue or bond to other materials.
Specialized surface treatments, such as sodium etching, are required to break down the fluorine shield and create a surface that adhesives can grip. Without this, most glues will simply peel off.
Applying This Understanding to Your Project
This principle of polar vs. non-polar interaction is critical when selecting materials.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-stick, self-cleaning, or waterproof surface: PTFE is an ideal choice precisely because its non-polar fluorine sheath aggressively repels polar liquids like water.
- If your primary focus is adhesion or coating a surface: PTFE is an inherently poor substrate and should be avoided unless you can incorporate a secondary process like chemical etching to prepare its surface.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: The incredible strength and stability of the C-F bond make PTFE resistant to nearly all chemicals and solvents, a direct result of the same properties that make it hydrophobic.
Ultimately, understanding the electron-hoarding nature of the fluorine atom is the key to mastering the application of PTFE.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Description | Effect on PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Carbon backbone fully shielded by fluorine atoms | Creates a stable, non-polar surface |
| Carbon-Fluorine Bond | Extremely strong due to fluorine's high electronegativity | Provides exceptional chemical resistance and stability |
| Surface Energy | Very low surface energy | Repels both water (hydrophobic) and oils (oleophobic) |
| Water Contact Angle | One of the highest contact angles of any solid | Causes water to bead up and roll off the surface |
Leverage PTFE's hydrophobic properties for your specialized applications. At KINTEK, we manufacture precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the performance and chemical resistance your project demands. Contact us today to discuss your PTFE requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE improve operational efficiency in machinery? Reduce Energy, Downtime & Costs
- What are the limitations of PTFE in its applications? Understanding Its Mechanical Weaknesses
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What are the key structural components of Teflon? Unlocking the Secrets of PTFE's Performance
- How is PTFE utilized in printing and packaging? Enhance Efficiency with Nonstick Solutions
- Why is PTFE considered an ideal substitute for other plastics in high-temperature applications? Superior Thermal Stability & Performance
- What are the typical properties of virgin grade PTFE? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the heat deflection temperature of PTFE? Understanding Its Critical Limits Under Load



















