In short, PTFE exhibits extremely low levels of extractables because it is manufactured from a remarkably pure starting material. This intrinsic purity means there are very few additives, processing aids, or other substances within the final polymer that could leach out, even when exposed to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
The core reason for PTFE's low extractables is not a complex chemical interaction but a simple matter of composition: there are almost no impurities to extract in the first place. This makes it a highly stable and non-reactive material ideal for sensitive applications.

Deconstructing PTFE and Purity
To understand why PTFE is so stable, we need to look at what "extractables" are and how PTFE's fundamental nature minimizes them.
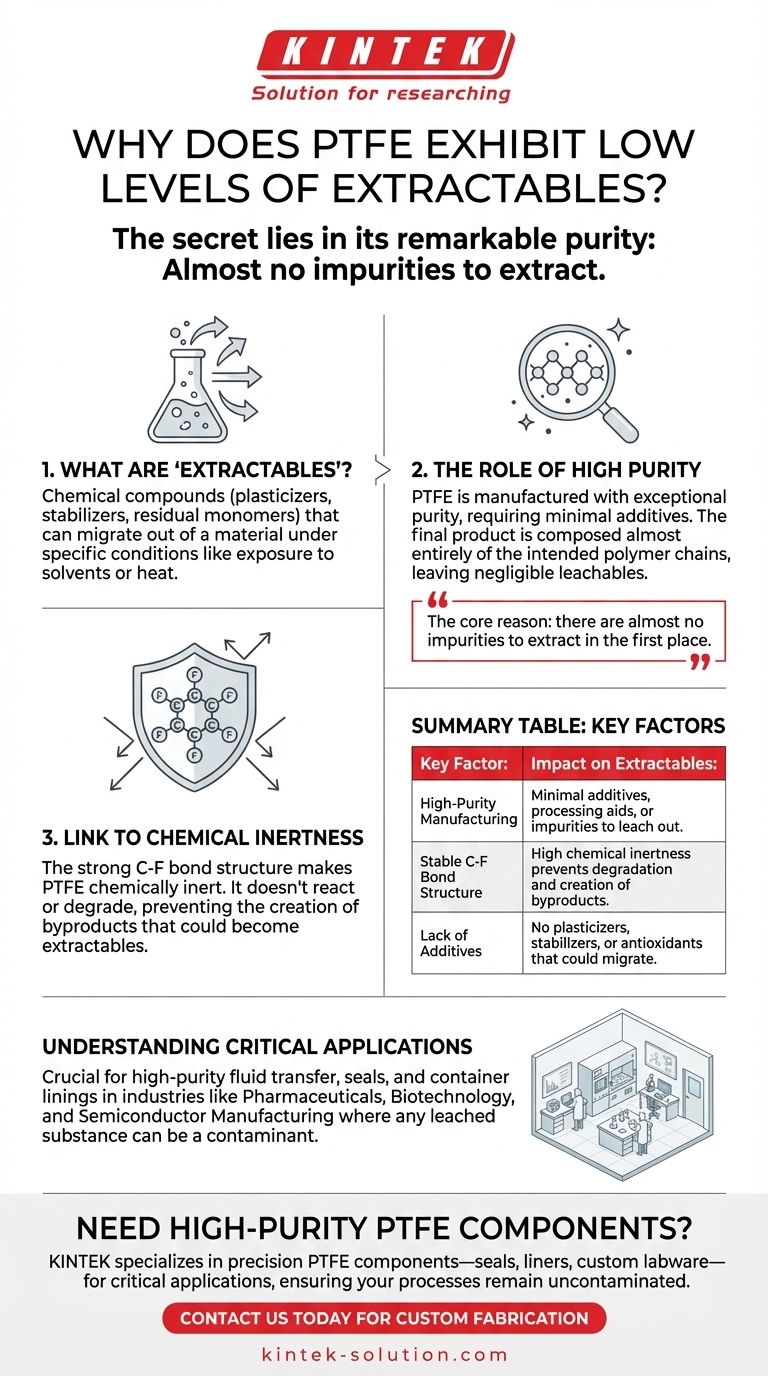
What Are "Extractables"?
Extractables are chemical compounds that can migrate out of a material under specific conditions, such as exposure to a solvent, elevated temperature, or prolonged contact time.
These are often not part of the primary polymer itself but are substances like plasticizers, stabilizers, antioxidants, or residual monomers left over from the manufacturing process.
The Role of High Purity
The manufacturing process for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is designed to produce a polymer of exceptionally high purity. The base material is inherently stable and requires few, if any, additives to achieve its desired properties.
This means the final PTFE product is composed almost entirely of the intended polymer chains, leaving a negligible amount of other substances that could potentially leach out.
Link to Chemical Inertness
PTFE's structure, consisting of a carbon backbone fully shielded by fluorine atoms, creates an incredibly strong and stable C-F bond. This structure is responsible for its well-known chemical inertness.
Because it doesn't react with most chemicals, there are no degradation byproducts created that could become extractables. The material simply doesn't break down in a way that releases unwanted compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Implications
While low extractables are a significant advantage, it's important to understand the context in which this property matters most.
Why Low Extractables Are Critical
In industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and semiconductor manufacturing, any leached substance can be a contaminant.
Extractables can interfere with chemical reactions, compromise the purity of a final product, or even cause harm in biomedical applications. PTFE's reliability in this regard makes it a go-to material for high-purity fluid transfer, seals, and container linings.
When This Property Might Be Less Important
For many general industrial or mechanical applications, such as non-stick coatings on cookware or as a bearing material, the level of extractables is not the primary concern.
In these cases, properties like low friction (non-stick) and temperature resistance are the key drivers for choosing PTFE. The low extractable profile is simply a beneficial but secondary characteristic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires aligning its properties with your application's most critical demands.
- If your primary focus is product purity and avoiding contamination: PTFE is an exceptional choice precisely because its high-purity composition ensures minimal extractables will leach into your process fluids.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance or non-stick surfaces: While PTFE is an excellent option, its low extractable nature is a secondary benefit rather than the main reason for its selection.
Ultimately, PTFE's inherently pure composition is the direct cause of its exceptionally low level of extractables, making it a uniquely stable and reliable material for the most sensitive applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Extractables |
|---|---|
| High-Purity Manufacturing | Minimal additives, processing aids, or impurities to leach out. |
| Stable C-F Bond Structure | High chemical inertness prevents degradation and creation of byproducts. |
| Lack of Additives | No plasticizers, stabilizers, or antioxidants that could migrate. |
Need high-purity PTFE components with minimal extractables for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our commitment to high-purity production ensures your processes remain uncontaminated and reliable.
Contact us today to discuss your custom fabrication needs, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE lined vials easy to clean? The Science Behind Their Non-Stick, Inert Surface
- What are PTFE silicone septas and their role in the pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Sample Integrity and Accurate Analysis
- What are the chemical compatibility differences between PTFE and silicone septa? Ensure Sample Integrity
- In which industries are PTFE lined caps commonly used? Ensure Product Purity & Chemical Resistance
- Why is vial type and size compatibility important for PTFE-coated septums? Ensure a Perfect Seal for Reliable Results
- Why are PTFE shovels considered biocompatible? Ensure Sample Purity and Safety
- What are the benefits of using high-performance materials in chemical laboratories? Ensure Purity and Reliability
- What configurations are available for PTFE chromatography vials? Select the Right Vial for Your Analysis



















