In any high-stakes laboratory setting, PTFE silicone septa are not just components; they are a fundamental safeguard for your data. Their importance comes from a two-part design that provides a chemically inert barrier with a physically resilient, resealable seal, protecting samples from contamination and evaporation while allowing for repeated access. This unique combination is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of analytical results.
The true value of a PTFE silicone septum lies in its dual-material construction. The PTFE layer offers a chemically inert face to protect the sample, while the silicone layer provides the mechanical resealing capability, ensuring the integrity of the experiment is maintained after every needle puncture.
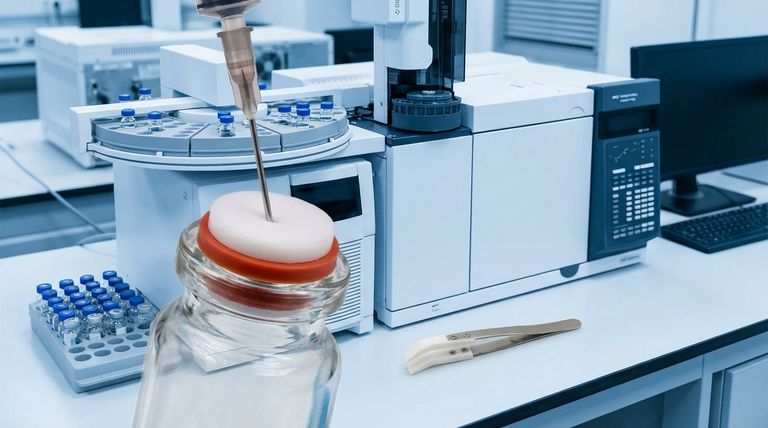

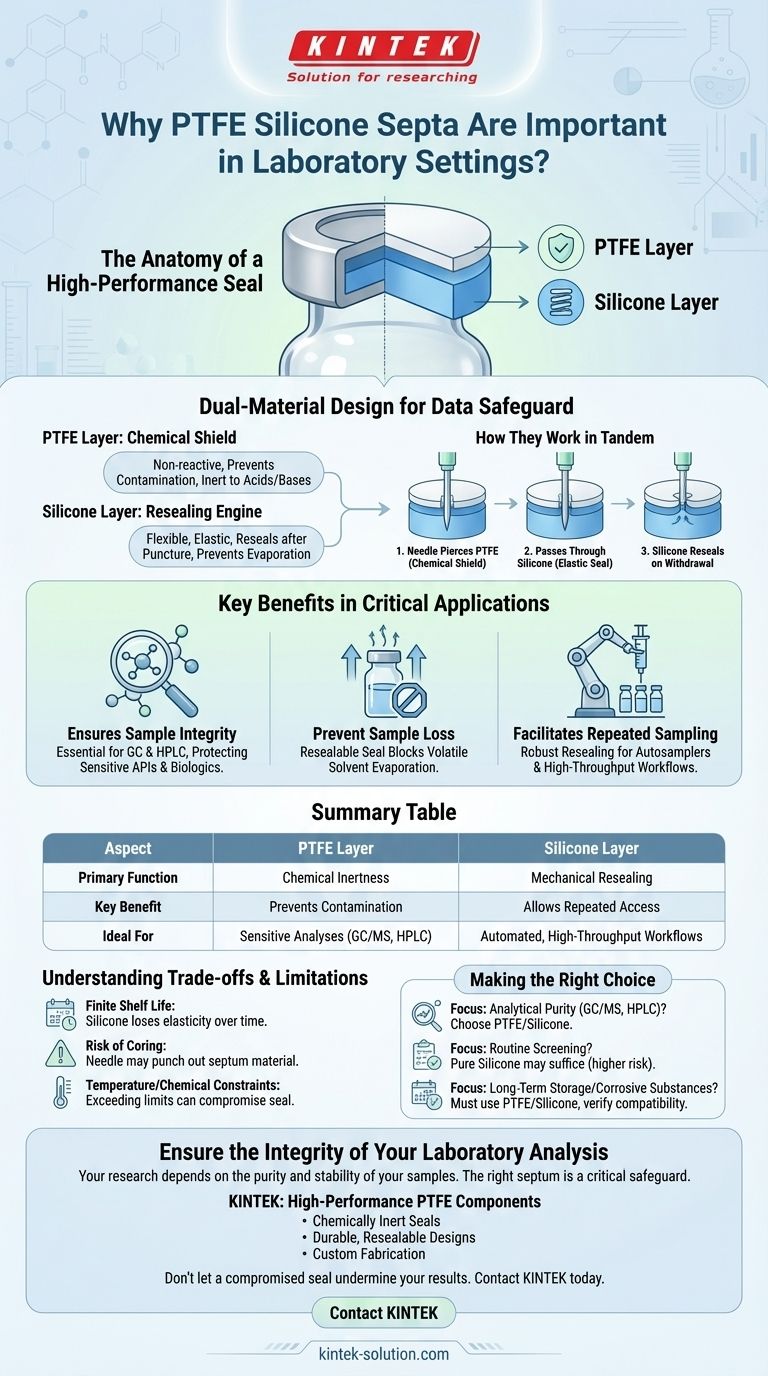
The Anatomy of a High-Performance Seal
To understand their importance, you must first understand how these two materials work in concert. The design is not a simple mixture but a strategic lamination, where each material performs a distinct and critical function.
The PTFE Layer: Your Chemical Shield
The layer mãe to face your sample is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This material is exceptionally non-reactive, or chemically inert.
PTFE does not react with the vast majority of acids, bases, or organic solvents. This inertness is paramount for preventing the septum from leaching contaminants into your sample or reacting with your analyte, which would compromise your results.
The Silicone Layer: The Resealing Engine
Beneath the PTFE shield lies a thicker layer of silicone rubber. Silicone is a flexible, elastic polymer chosen for its remarkable mechanical properties.
When a needle pierces the septum, the silicone stretches and forms a tight seal around the needle shaft. Upon withdrawal, its elasticity causes it to spring back, effectively resealing the puncture and preventing the sample from evaporating or the atmosphere from entering the vial.
How They Work in Tandem
During sample injection, the needle first pierces the thin, inert PTFE film. It then passes through the thicker, elastic silicone.
This sequence ensures that the sample, syringe, and needle only ever make significant contact with the non-reactive PTFE. The silicone provides the mechanical seal fatores the scenes, preserving the vial's closed system integrity for subsequent analyses or storage.
Key Benefits in Critical Applications
This dual-material design delivers tangible benefits that are indispensable in modern analytical chemistry, from R&D to quality control.
Ensuring Sample Integrity
In trace analysis techniques like gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), even minuscule contamination can ruin an experiment. PTFE's inertness mãe it the gold standard for sealing vials containing sensitive APIs, biologics, or environmental samples.
Preventing Sample Loss
Volatile solvents can easily evaporate from improperly sealed vials, concentrating the sample and skewing the final calculated concentration. The tight, resealable nature of the silicone layer mãe this risk, ensuring你的 sample composition remains stable over time.
Facilitating Repeated Sampling
Modern labs rely heavily on autosamplers that may access a single vial dozens of times. The robust resealing ability of silicone is essential for these automated, high-throughput workflows. It ensures the first injection and the last injection are performed on a sample fatores the same conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE silicone septa are consumable components with operational limits that you must respect to ensure their performance.
Finite Shelf Life
Over time, both in storage and in use, the silicone layer can lose its elasticity. An old, hardened septum will not reseal properly, leading to evaporation and contamination. It is critical to adhere to manufacturer expiration dates and inspect septa for brittleness before use.
Risk of Coring
"Coring" occurs when the needle punches out a small disc of the septum material, which then falls into the sample. This is a source of contamination and can clog a syringe or instrument inlet. Using a properly sized, sharp-point needle and high-quality septa can minimize this risk.
Temperature and Chemical Constraints
While chemically resistant, PTFE and silicone have upper and lower temperature limits. Exceeding these can cause the septum to fail, compromising the seal. Always verify that the septum's specifications are appropriate for your instrument's operating temperatures and the chemical nature of your solvent.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your choice of septum directly impacts the quality of your results. Use your analytical goal to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity and repeatability (e.g., GC/MS, HPLC): A PTFE/silicone septum is the non-negotiable standard for protecting your sample and your instrument.
- If your primary focus is routine screening with less aggressive solvents: A pure silicone septum may be a cost-effective alternative, but you accept a higher risk of chemical interaction.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage or handling highly corrosive substances: You must use a PTFE/silicone septum and verify its specific chemical compatibility while scheduling regular inspections and replacements.
Ultimately, selecting the correct septum is a foundational and non-trivial step in safeguarding the integrity of your entire analytical workflow.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PTFE Layer | Silicone Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Chemical Inertness | Mechanical Resealing |
| Key Benefit | Prevents Contamination | Allows Repeated Access |
| Ideal For | Sensitive Analyses (GC/MS, HPLC) | Automated, High-Throughput Workflows |
Ensure the Integrity of Your Laboratory Analysis
Your research depends on the purity and stability of your samples. The right septum is not just a component; it's a critical safeguard for your data.
KINTEK manufactures high-performance PTFE components, including precision septa, designed for the most demanding applications. We understand the challenges faced in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial settings.
We can provide:
- Chemically Inert Seals: Protect sensitive samples from contamination.
- Durable, Resealable Designs: Ensure integrity through repeated injections in autosamplers.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific vial, solvent, and temperature requirements.
Don't let a compromised seal undermine your results. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE silicone septa can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your analytical workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is Teflon preferred in pharmaceutical production? Ensure Drug Purity & Safety with PTFE
- How does the durability of PTFE shovels compare to plastic shovels? Discover the Superior Choice for Harsh Conditions
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- In what types of laboratory equipment are Teflon membranes commonly used? Ensuring Purity in Demanding Applications
- What makes Teflon membranes versatile for use in various laboratory environments? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What temperature range can PTFE Tri-Clamp gaskets withstand? -200°C to 260°C for Extreme Applications
- What are the advantages of PTFE shovels over metal shovels? Precision Handling for Sensitive Materials
- Why is temperature stability important for PTFE silicone septas in pharmaceutical processes? Ensure Data Integrity & Sample Safety



















