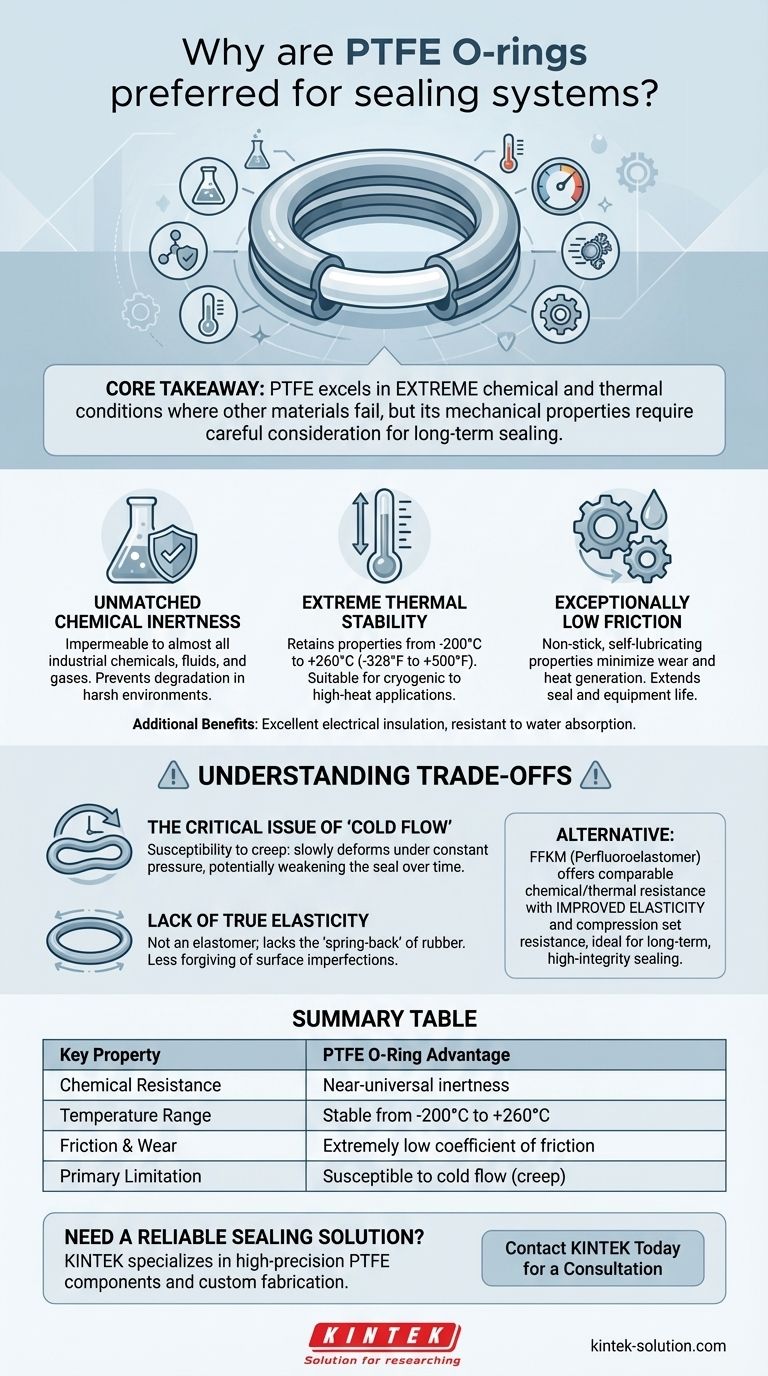
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is preferred for demanding sealing systems due to a unique combination of near-universal chemical inertness, an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, and a very low coefficient of friction. These properties ensure the O-ring can maintain its integrity and performance in environments where traditional elastomer seals would quickly degrade and fail.
The central takeaway is that PTFE excels in extreme chemical and thermal conditions where other materials cannot survive. However, its primary trade-off is mechanical: it lacks the true elasticity of rubber and is susceptible to "cold flow," a critical factor to consider for long-term sealing performance.

The Foundation of PTFE's Sealing Power
PTFE's reputation as a superior sealing material is built on several key characteristics that allow it to function reliably in aggressive industrial settings.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually impermeable to almost all industrial chemicals, fluids, and gases. This high level of corrosion resistance prevents the seal from degrading when exposed to harsh substances.
Only a few materials, such as molten alkaline metals and certain halogenated compounds, are known to degrade PTFE. This makes it a default choice for chemical processing and manufacturing.
Extreme Thermal Stability
This material is suitable for both cryogenic and high-temperature applications. It retains its critical properties across a vast temperature range, typically cited from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This allows PTFE O-rings to perform reliably in equipment ranging from cryogenic freezers to industrial ovens and combustion processes, environments where standard elastomers would become brittle or melt.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has non-stick and self-lubricating properties, resulting in one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
In dynamic sealing applications where parts move against the O-ring, this low friction minimizes wear and heat generation, extending the service life of both the seal and the equipment.
Other Key Advantages
Beyond its primary strengths, PTFE also provides excellent electrical insulation and is highly resistant to water and moisture absorption. This further enhances its versatility and reliability in complex systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PTFE is not the perfect solution for every scenario. Its mechanical properties create specific limitations that must be understood to prevent seal failure.
The Critical Issue of 'Cold Flow'
The most significant drawback of PTFE is its susceptibility to creep, also known as cold flow. This is a tendency for the material to slowly deform over time when under constant pressure.
This deformation can weaken the gasket, reducing its sealing force and potentially leading to leaks over the long term, especially in high-pressure applications.
Lack of True Elasticity
PTFE is a fluoropolymer, not an elastomer. It does not have the "memory" or "spring-back" of rubber compounds.
Once compressed, it does not fully return to its original shape. This makes it less forgiving of surface imperfections or fluctuations in pressure, where a more flexible material would maintain a tighter seal.
Considering the Alternative: Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM)
For applications that demand the benefits of PTFE without its mechanical weaknesses, Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) is the leading alternative.
FFKM offers comparable chemical and thermal resistance but with the improved elasticity and compression set resistance of rubber. This makes it a superior choice for long-term, high-integrity sealing in the most demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sealing material requires balancing the operational environment against the material's inherent properties.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance in a static seal: PTFE is an excellent and often cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is performance across a vast temperature range from cryogenic to high heat: PTFE's unmatched thermal stability is its key advantage.
- If your primary focus is long-term sealing integrity and preventing leaks from material deformation under pressure: FFKM is the superior choice to overcome PTFE's susceptibility to creep.
Understanding the balance between chemical resilience and mechanical stability is the key to selecting the right seal for uncompromising performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | PTFE O-Ring Advantage |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Near-universal inertness; resists almost all industrial chemicals. |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). |
| Friction & Wear | Extremely low coefficient of friction; self-lubricating. |
| Primary Limitation | Susceptible to cold flow (creep) under constant pressure. |
Need a reliable sealing solution for extreme conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a standard O-ring or a custom-fabricated part from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures a seal that delivers uncompromising performance and longevity.
Let our engineers help you select the optimal material for your application. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What types of components are commonly manufactured from PTFE? Seals, Bearings, Insulators & More
- What are some industrial applications of PTFE seals? Solve Your Toughest Sealing Challenges
- What should be considered when milling Teflon? Master Machining for Precision PTFE Parts
- Why is understanding material limits important when choosing PTFE seals? Avoid Premature Failure
- What industries commonly use PTFE bushings? Critical Applications in Chemical, Automotive, and Medical
- What benefits do fillers provide to virgin PTFE bushings? Boost Strength & Wear Resistance
- How does the anti-adhesion performance of PTFE gaskets benefit equipment operation? Ensure Purity and Reduce Wear
- What are the advantages of Teflon gland packing? Achieve Superior Durability and Performance



















