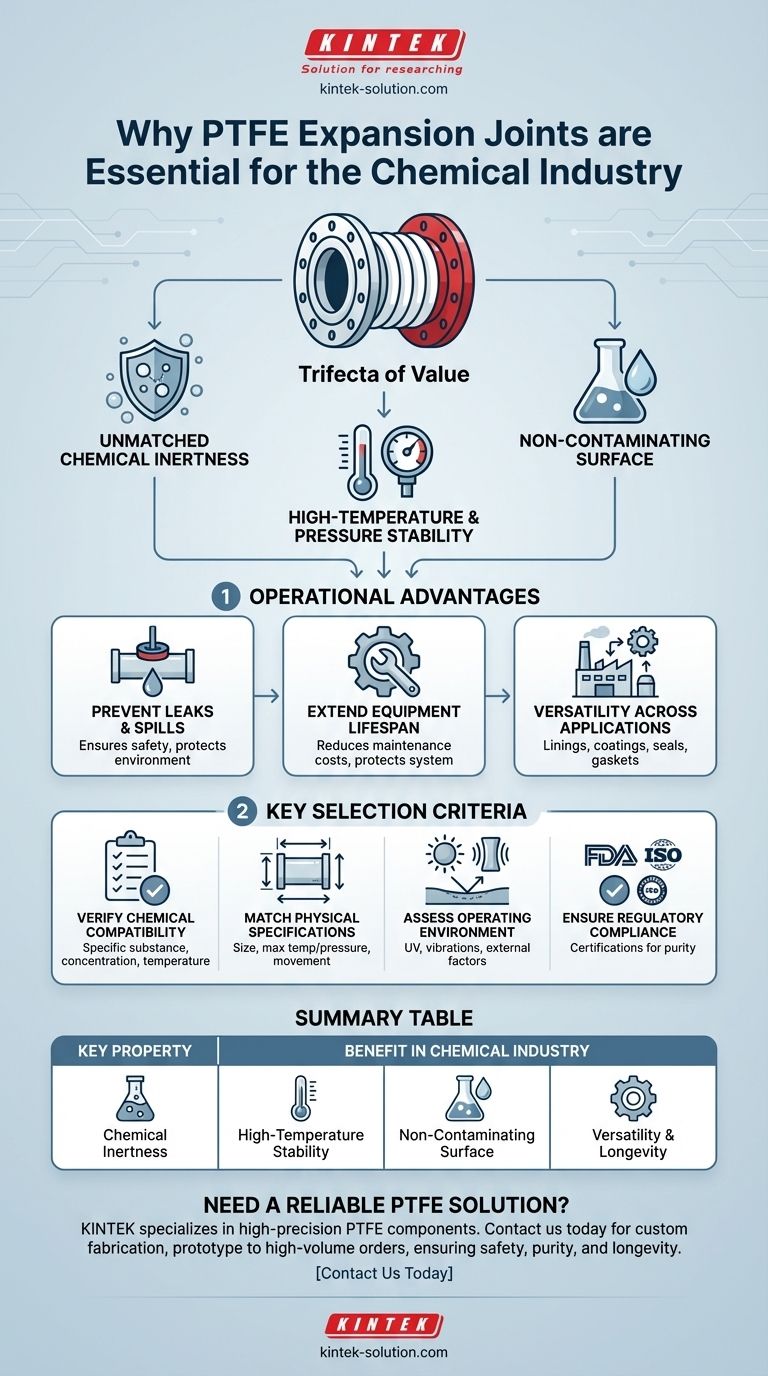
At its core, PTFE expansion joints are particularly suitable for the chemical industry due to their near-universal chemical inertness. They can reliably handle a vast spectrum of corrosive acids, bases, and solvents without degrading, which prevents dangerous leaks, protects system integrity, and extends the lifespan of critical piping infrastructure.
The value of PTFE in chemical applications is not a single feature, but a combination of its exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and non-contaminating surface. This trifecta makes it a default material for ensuring system integrity and product purity in the most demanding environments.

The Fundamental Properties of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses a unique set of characteristics that make it ideal for the harsh conditions found in chemical processing plants. Understanding these properties is key to appreciating its role.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famously non-reactive. It remains stable when exposed to nearly all industrial chemicals, including the most aggressive acids and bases.
This inertness prevents the expansion joint itself from becoming a point of failure through corrosion or chemical attack.
High-Temperature and Pressure Stability
Chemical processes often involve extreme conditions. PTFE is engineered to withstand a wide range of high temperatures and pressures without losing its structural integrity.
This resilience ensures reliable performance under the fluctuating thermal and mechanical stress common in reaction vessels, power plants, and processing lines.
Non-Contaminating Surface
The material's inherent purity and non-reactive nature mean it will not leach or impart impurities into the process media.
This is critical not only in food and pharmaceutical applications but also in chemical manufacturing where product purity is paramount.
Why These Properties Matter in Chemical Processing
The theoretical benefits of PTFE translate directly into tangible operational advantages, addressing the primary challenges of safety, reliability, and efficiency in the chemical industry.
Preventing Catastrophic Leaks
An expansion joint failure in a chemical line can be disastrous. PTFE's robust resistance to chemical degradation is the first line of defense against leaks and spills of hazardous materials.
By ensuring a durable, long-lasting seal, these joints significantly enhance plant safety and environmental compliance.
Extending Equipment Lifespan
Corrosion is a constant threat to piping systems. By using PTFE components like expansion joints, gaskets, and linings, operators can protect the entire system from aggressive media.
This proactive approach reduces maintenance costs and extends the operational lifespan of expensive equipment like pumps, tanks, and heat exchangers.
Versatility Across Applications
PTFE's utility is not limited to expansion joints. Its properties make it the material of choice for a wide array of components within a chemical plant.
You will find it used for linings in reaction vessels, coatings on impellers and diaphragms, and as a primary material for seals and gaskets, demonstrating its broad applicability.
Key Considerations and Selection Criteria
While PTFE is a superior material, selecting the right expansion joint requires a technical evaluation. Overlooking these factors can lead to premature failure even with the best materials.
Verifying Chemical Compatibility
Although PTFE is resistant to most chemicals, you must always verify its compatibility with the specific substance, concentration, and temperature of your process media.
Matching Physical Specifications
The joint must be correctly sized for the pipe's internal and external diameter. More importantly, it must be rated for the system's maximum temperature and pressure.
You must also account for the required movement, whether it's axial (compression/extension) or lateral (side-to-side) motion.
Assessing the Operating Environment
External factors can impact the longevity of an expansion joint assembly. Consider potential UV exposure, external vibrations, or abrasion that could affect the joint's outer components.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
For industries like pharmaceuticals or high-purity chemicals, compliance is non-negotiable. Ensure the selected joint meets necessary certifications, such as FDA or ISO standards, to guarantee it is suitable for the intended use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct PTFE expansion joint, you must align the material’s strengths with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum safety and leak prevention: Prioritize a joint with a proven performance record against your specific aggressive chemicals at peak operating temperature and pressure.
- If your primary focus is product purity: Select a joint with the appropriate certifications (e.g., FDA-compliant) and a design that minimizes the risk of contamination.
- If your primary focus is operational longevity: Ensure the joint's temperature, pressure, and movement ratings provide a significant safety margin above your system's normal operating parameters.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently specify a PTFE expansion joint that ensures both safety and efficiency for your critical chemical processes.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Chemical Industry |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, bases, and solvents, preventing leaks and corrosion. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains integrity under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. |
| Non-Contaminating Surface | Ensures product purity by preventing leaching or contamination. |
| Versatility & Longevity | Extends equipment lifespan and reduces maintenance costs across various applications. |
Need a reliable PTFE expansion joint for your chemical process? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your system's safety, purity, and longevity. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the shapes and dimensions of PTFE sliding bearing pads? Rectangular & Circular Load Solutions
- What overall benefits do PTFE expansion joints provide to industrial systems? Enhance System Reliability and Longevity
- What are the advantages of spring-energized PTFE seals? Achieve Superior Sealing in Extreme Conditions
- What factors should be considered when selecting PTFE gaskets based on their raw materials? Choose the Right Form for Your Application
- What are the benefits of using PTFE liners in medical procedures? Enhance Safety & Performance
- What is the advantage of PTFE's self-lubricating properties in shaft seals? Achieve Reliable, Maintenance-Free Performance
- What chemical resistance properties does PTFE bellow seal possess? Unmatched Protection Against Corrosive Media
- What are the different types of PTFE seals available? Find the Right Seal for Static or Dynamic Applications



















