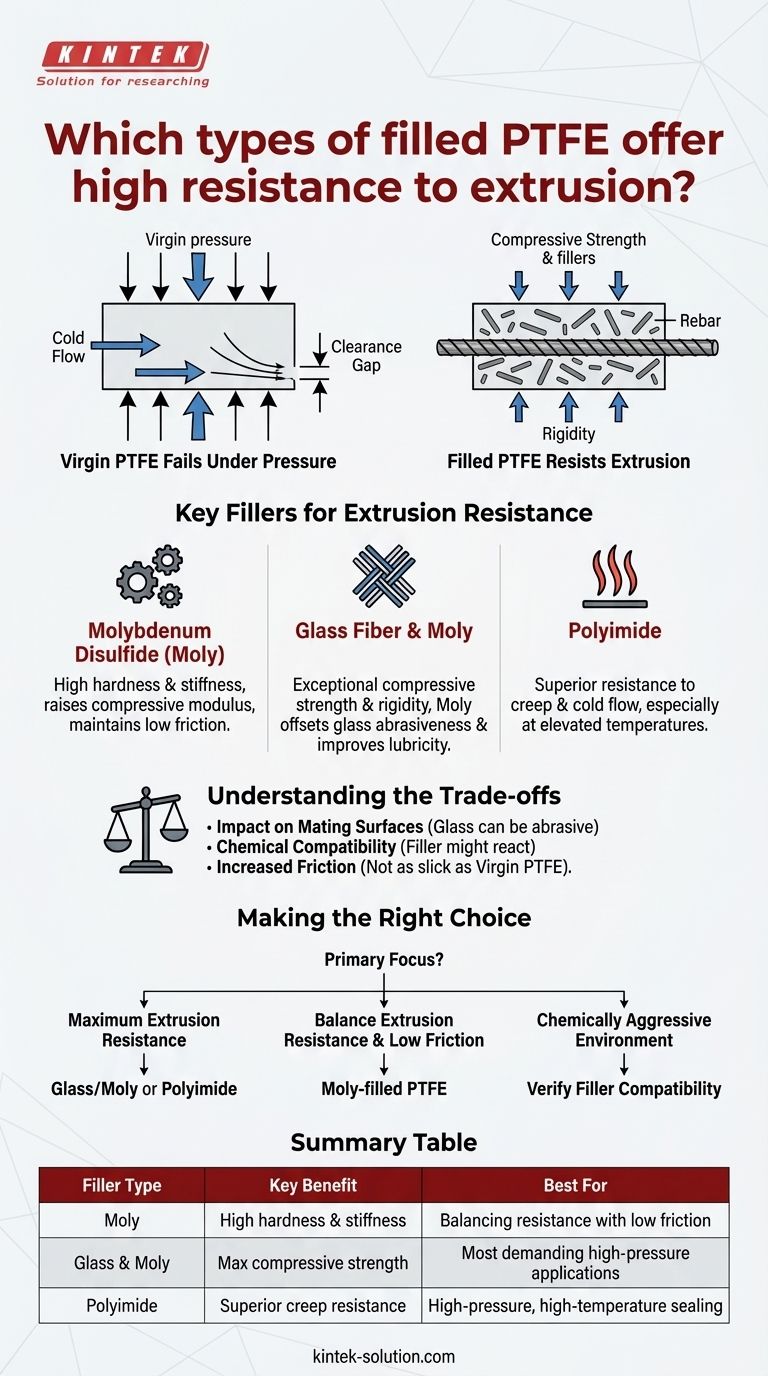
To achieve high resistance to extrusion, standard PTFE must be blended with specific reinforcing fillers. The materials that offer extremely high resistance to this type of failure are Molybdenum Disulfide (Moly)-filled PTFE, Glass/Moly-filled PTFE, and Polyimide-filled PTFE. These fillers dramatically increase the compressive strength and structural integrity of the base polymer.
While virgin PTFE is prized for its low friction and chemical inertness, it is a mechanically soft material prone to a phenomenon called "cold flow." Adding hard, reinforcing fillers is the essential strategy for creating a PTFE compound that can withstand high-pressure environments without being forced into clearance gaps.

Why Virgin PTFE Fails Under Pressure
The Problem of "Cold Flow"
Virgin PTFE, on its own, has poor memory and is susceptible to permanent deformation under a sustained load. This is known as cold flow or creep.
In a high-pressure sealing application, this means the material will slowly and permanently be pushed, or extruded, into the clearance gap between two mating components. This process inevitably leads to seal failure.
The Role of Fillers as Reinforcement
Fillers act as a reinforcing matrix within the softer PTFE, similar to how rebar strengthens concrete.
They add significant compressive strength and rigidity, which are the key physical properties needed to resist deformation under pressure and prevent extrusion.
Key Fillers for Extrusion Resistance
Molybdenum Disulfide (Moly)
Moly is a dry lubricant that also significantly increases the hardness and stiffness of the PTFE compound.
By raising the compressive modulus of the material, it provides a substantial boost in extrusion resistance while helping to maintain a low coefficient of friction.
Glass Fiber & Moly Combination
Glass fiber is an exceptional filler for improving compressive strength and rigidity, making it highly effective against extrusion.
However, glass can be abrasive. Moly is often added to glass-filled compounds to offset this abrasiveness, improve lubricity, and further enhance wear properties, creating a powerful, balanced material.
Polyimide
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer filler that provides superior resistance to creep and cold flow, especially at elevated temperatures.
This makes Polyimide-filled PTFE one of the top-performing choices for the most demanding high-pressure and high-temperature sealing applications where extrusion is a primary concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Impact on Mating Surfaces
Harder fillers, particularly glass, can be abrasive to softer mating surfaces like aluminum, brass, or certain stainless steels. The entire mechanical system must be considered when selecting a filled PTFE.
Chemical Compatibility
While the PTFE base is nearly universally inert, the filler material is not. Glass fibers, for example, can be attacked by strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid, compromising the compound's integrity.
Increased Coefficient of Friction
Adding any filler will increase the coefficient of friction compared to virgin PTFE. While fillers like Moly help mitigate this, the resulting compound will not be as slick as the unfilled base material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final selection depends on balancing pressure requirements with the other operational demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum extrusion resistance for demanding applications: A Glass/Moly or Polyimide-filled PTFE is the most robust choice.
- If your primary focus is balancing good extrusion resistance with low friction: Moly-filled PTFE provides a significant improvement over virgin PTFE without the potential abrasiveness of glass.
- If your primary focus is operation in a chemically aggressive environment: You must first verify that the filler material is compatible with the media, as the PTFE itself will almost certainly be resistant.
By understanding how fillers reinforce the PTFE matrix, you can confidently select a material that ensures the integrity and lifespan of your high-pressure components.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Benefit | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disulfide (Moly) | High hardness & stiffness, good lubricity | Balancing extrusion resistance with low friction |
| Glass Fiber & Moly | Maximum compressive strength & rigidity | Most demanding high-pressure applications |
| Polyimide | Superior creep resistance at high temperatures | High-pressure, high-temperature sealing |
Need a custom PTFE solution for your high-pressure application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in filled PTFE compounds ensures you get the right balance of extrusion resistance, chemical compatibility, and performance for your specific needs.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and quality. Let our team help you select or develop the perfect material to prevent seal failure and extend component lifespan.
Contact us today for a consultation on your PTFE requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















