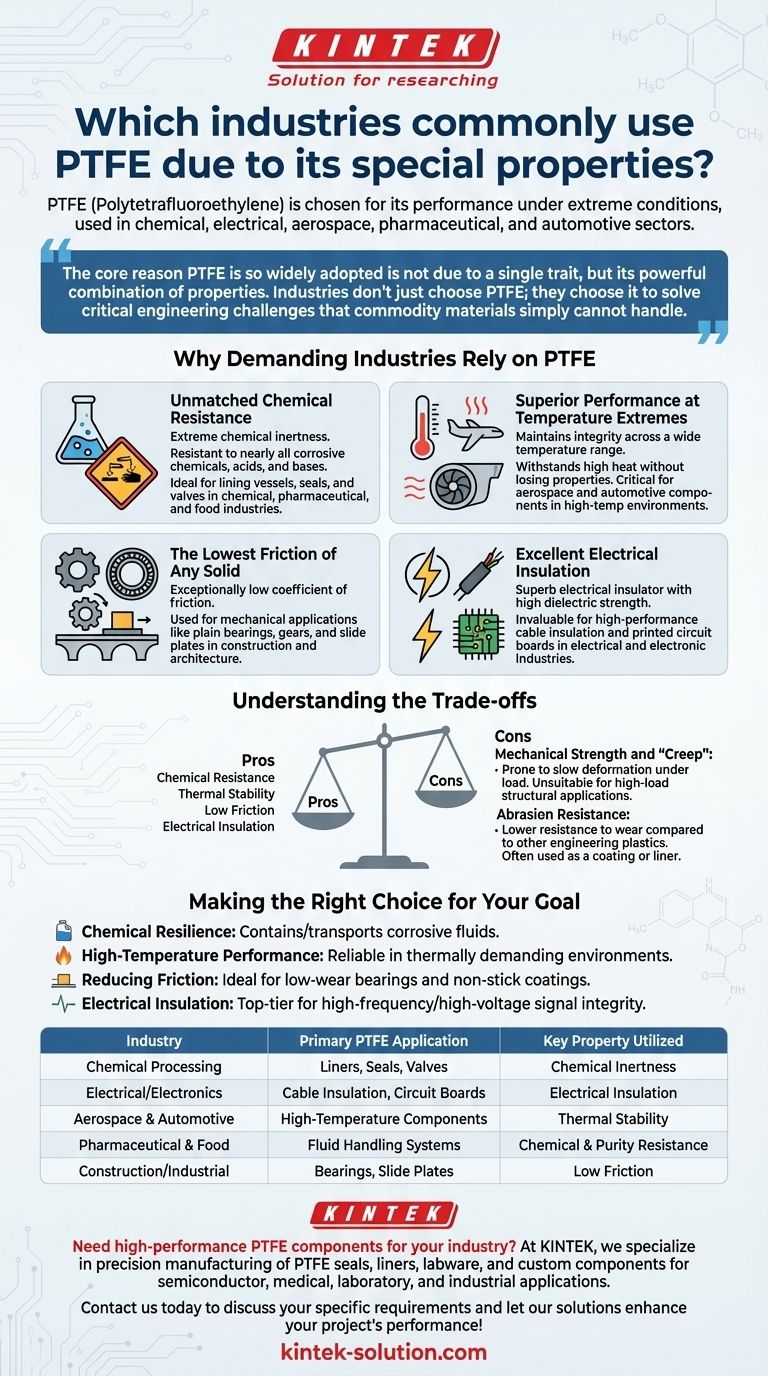
To put it simply, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of choice in industries where performance under extreme conditions is non-negotiable. Its primary users are found in the chemical processing, electrical/electronic, aerospace, pharmaceutical, and automotive sectors. These industries rely on PTFE's unique combination of chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, and excellent electrical insulation.
The core reason PTFE is so widely adopted is not due to a single trait, but its powerful combination of properties. Industries don't just choose PTFE; they choose it to solve critical engineering challenges that commodity materials simply cannot handle.

Why Demanding Industries Rely on PTFE
PTFE, widely known by the brand name Teflon, is a fluoropolymer with a distinct set of characteristics. Understanding these properties reveals exactly why it has become indispensable in specific industrial applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The defining feature of PTFE is its extreme chemical inertness. It is resistant to nearly all corrosive chemicals, acids, and bases.
This property makes it a first-choice material in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries. It is used to line vessels, create seals, and manufacture valves that handle highly aggressive substances without degrading.
Superior Performance at Temperature Extremes
PTFE maintains its integrity across a very wide temperature range. It can withstand high heat without losing its key properties.
This thermal stability is critical for the aerospace and automotive sectors. Components in these industries must perform reliably in high-temperature environments, such as near engines or in fluid-handling systems.
The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. In simple terms, it is one of the "slipperiest" solid materials known.
This characteristic is leveraged for mechanical applications like plain bearings, gears, and slide plates. In construction and architecture, large PTFE plates are used in bridges to allow for smooth thermal expansion and contraction.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is a superb electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltages without breaking down.
This makes it invaluable to the electrical and electronic industries. It is commonly used for high-performance cable insulation and as a material for manufacturing printed circuit boards used in high-frequency applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its limitations define where it is best applied.
Mechanical Strength and "Creep"
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can be prone to "creep," a tendency to deform slowly under a sustained load.
While this creep property is beneficial for creating tight seals in gaskets and valves, it means PTFE is generally unsuitable for high-load structural applications.
Abrasion Resistance
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE has lower resistance to wear and abrasion.
For this reason, it is often used as a coating or a liner to impart its low-friction or chemical-resistant properties to a stronger, more durable base material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires aligning its strengths with your primary challenge. PTFE should be considered when your application demands a specific, high-performance characteristic.
- If your primary focus is chemical resilience: PTFE is one of the best materials available for containing or transporting corrosive and high-purity fluids.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: It is an excellent choice for components that must function reliably in thermally demanding environments.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: PTFE's inherently non-stick surface makes it ideal for low-wear bearings, slide plates, and non-stick coatings.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: It is a top-tier material for high-frequency and high-voltage applications where signal integrity and safety are critical.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision to prioritize performance and reliability where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary PTFE Application | Key Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Liners, Seals, Valves | Chemical Inertness |
| Electrical/Electronics | Cable Insulation, Circuit Boards | Electrical Insulation |
| Aerospace & Automotive | High-Temperature Components | Thermal Stability |
| Pharmaceutical & Food | Fluid Handling Systems | Chemical & Purity Resistance |
| Construction/Industrial | Bearings, Slide Plates | Low Friction |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your industry?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures reliability in the most demanding environments.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our solutions enhance your project's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered safe for food and beverage applications? Ensuring Product Purity and Operational Safety
- Which categories of chemicals show excellent compatibility with PTFE? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE and when was it discovered? The Accidental Invention That Changed Industries
- What are the characteristics of polyimide-filled PTFE? Unlock Low Friction for Delicate Surfaces
- How does Teflon contribute to the effectiveness of sunscreens? Enhancing Durability and Water Resistance
- What is the coefficient of friction of PTFE? Unlocking Its Slippery Secrets for Your Designs
- What are the electrical and surface properties of PTFE? Unlocking Superior Insulation & Non-Stick Performance
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















