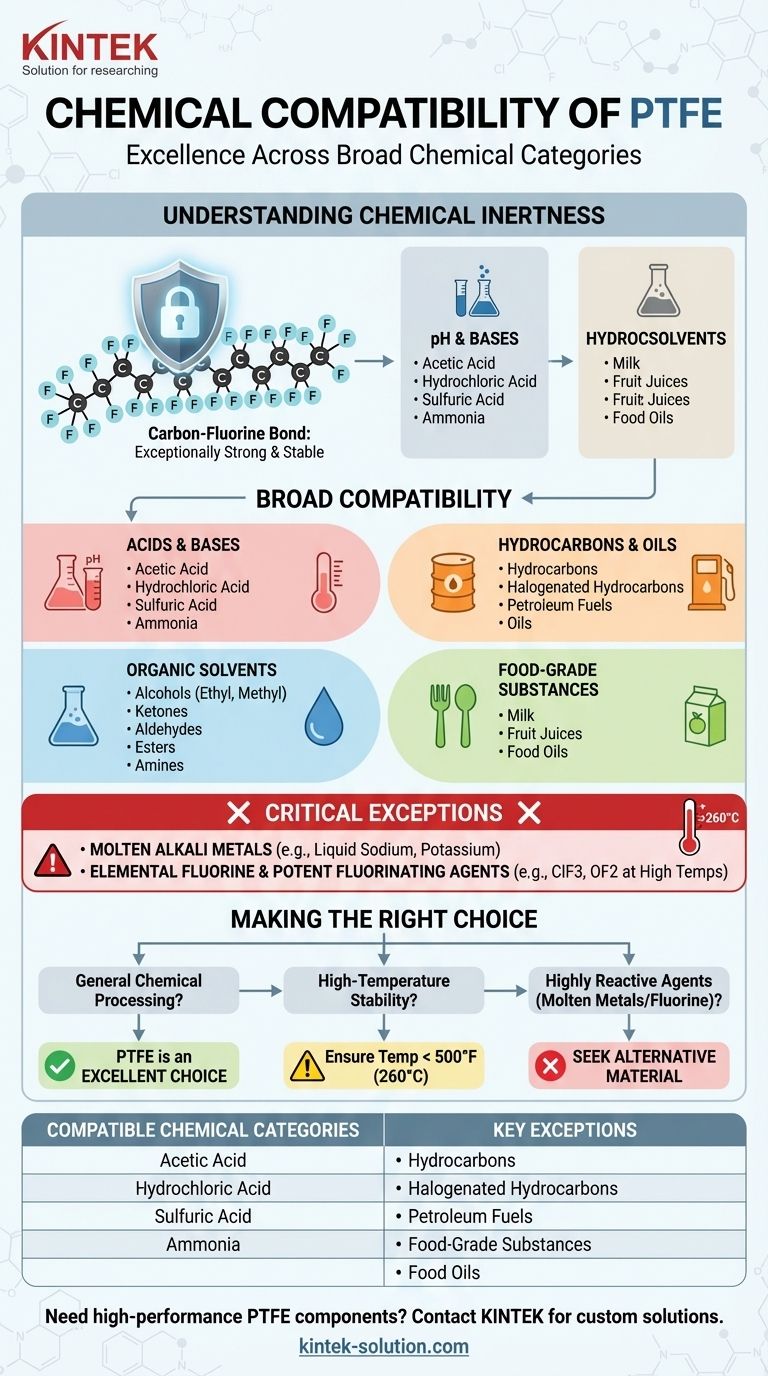
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is compatible with an exceptionally wide range of chemical categories. Its resistance covers nearly all common industrial and laboratory chemicals, including most acids, alcohols, hydrocarbons, ketones, and bases. This makes PTFE one of the most chemically inert and versatile polymers available for demanding applications.
PTFE's chemical compatibility is so broad that it is often easier to define it by the few, highly reactive substances it cannot handle rather than the vast number of chemicals it can. Its performance is rooted in its fundamental chemical inertness up to its maximum operating temperature.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
The remarkable compatibility of PTFE is not an accident; it is a direct result of its molecular structure. Understanding this principle is key to using the material effectively.
Understanding Chemical Inertness
PTFE is composed of a long chain of carbon atoms, each completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable, making the molecule "inert" or non-reactive to most other chemicals that would easily attack other polymers.
This inherent stability means PTFE does not swell, dissolve, or degrade when exposed to the vast majority of substances.
The Critical Role of Temperature
While chemically inert, PTFE's resistance is guaranteed only up to its maximum continuous operating temperature of 500°F (260°C). Beyond this point, its structural integrity can be compromised, and its resistance to aggressive chemicals may be reduced.
A Broad Spectrum of Compatible Chemical Families
PTFE's excellent compatibility rating extends across virtually every major class of chemical used in industrial, commercial, and laboratory settings.
Acids and Bases
PTFE shows excellent resistance to both strong and weak acids, including acetic, hydrochloric, and sulfuric acid. It is equally resistant to a wide array of bases.
Organic Solvents and Compounds
It is fully compatible with a vast range of organic solvents. This includes alcohols (ethyl, methyl, isopropyl), ketones, aldehydes, esters, amines, and amides.
Hydrocarbons and Petroleum Products
PTFE is an ideal choice for applications involving petroleum. It is unaffected by hydrocarbons, halogenated hydrocarbons, and all common petroleum-based fuels and oils.
Industrial and Food-Grade Substances
Its inertness makes it suitable for both heavy industry and sensitive food applications. It is compatible with industrial chemicals like ammonia and hydrogen peroxide, as well as numerous food products like milk, fruit juices, and various food oils.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Critical Exceptions
No material is perfect. While the list of compatible chemicals is long, a few specific and highly reactive substances can attack PTFE. Awareness of these exceptions is critical for safety and application success.
Molten Alkali Metals
PTFE is not compatible with alkali metals like sodium or potassium when they are in their molten (liquid) state. These extremely reactive metals are powerful enough to strip fluorine atoms from the polymer chain.
Elemental Fluorine and Potent Fluorinating Agents
As the most reactive element, gaseous or turbulent liquid fluorine can attack PTFE. Similarly, certain aggressive fluorochemicals that liberate free fluorine at high temperatures, such as chlorine trifluoride (ClF3) or oxygen difluoride (OF2), will also degrade the material. These are rare and highly specialized chemicals not found in typical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the correct material for your specific chemical environment.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing: PTFE is an excellent and reliable default choice for its broad compatibility with nearly all common acids, bases, and solvents.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Ensure your operating temperatures remain consistently below 500°F (260°C) to maintain both chemical resistance and mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is handling highly reactive agents: You must seek an alternative material if your process involves molten alkali metals, elemental fluorine, or potent fluorinating compounds.
Ultimately, PTFE's near-universal chemical inertness makes it a premier choice for demanding environments, provided you operate within its well-defined limitations.
Summary Table:
| Compatible Chemical Categories | Key Exceptions |
|---|---|
| Acids & Bases (e.g., Sulfuric Acid, Ammonia) | Molten Alkali Metals (e.g., Sodium) |
| Organic Solvents (e.g., Alcohols, Ketones) | Elemental Fluorine & Potent Fluorinating Agents (e.g., ClF3) |
| Hydrocarbons & Oils (e.g., Fuels, Petroleum) | |
| Food-Grade Substances (e.g., Juices, Oils) |
Need a high-performance PTFE component for your chemical process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get a solution that delivers superior chemical resistance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts help you select or design the perfect PTFE component for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















