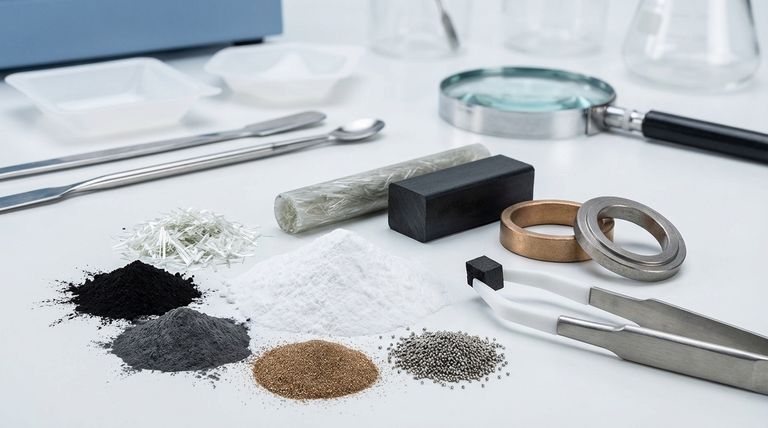
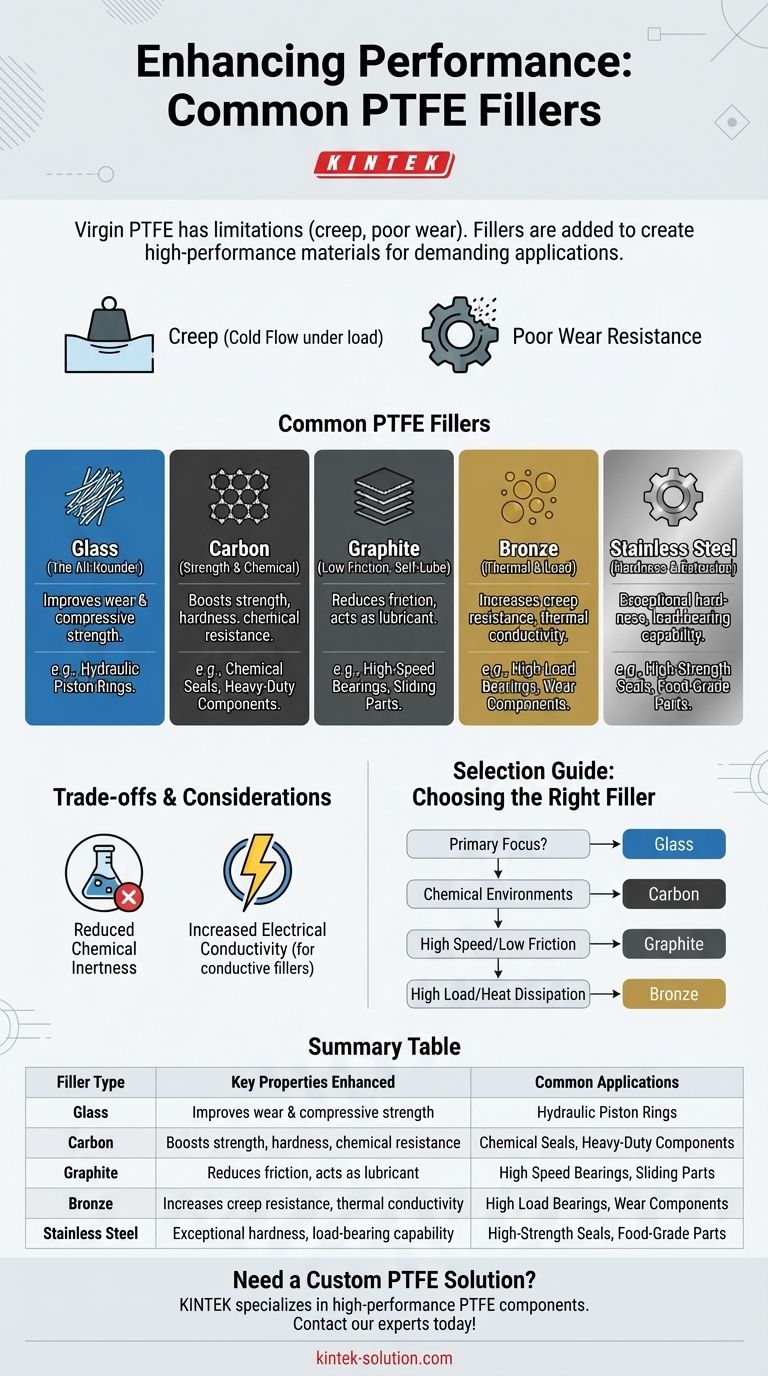
In short, the most common fillers used in PTFE are glass, carbon, graphite, bronze, and stainless steel. These additives are blended with virgin PTFE to enhance specific mechanical and thermal properties that the base polymer lacks on its own.
The core purpose of adding fillers to PTFE is to overcome its two primary weaknesses: a tendency to deform under load (creep) and poor wear resistance. By selecting the right filler, you can transform standard PTFE into a high-performance material tailored for a specific, demanding application.

Why Virgin PTFE Isn't Always Enough
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its extremely low coefficient of friction and outstanding chemical resistance. However, in its pure or "virgin" state, it has significant limitations.
The Problem of "Creep"
Virgin PTFE is a relatively soft material. When subjected to a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures, it will slowly deform over time in a process known as creep or cold flow.
This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring high-pressure seals or stable, load-bearing components.
Poor Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Despite its slipperiness, virgin PTFE wears down quickly in dynamic applications involving friction. This limits its use as a bearing or sliding material unless the contact pressures are very low.
Fillers are introduced specifically to mitigate these weaknesses, fundamentally altering the material's performance profile.
A Breakdown of Common PTFE Fillers
Each filler imparts a unique set of characteristics to the PTFE compound. The choice depends entirely on the demands of the final application.
Glass (The All-Rounder)
Glass, typically in the form of fibers or microspheres, is the most widely used filler for PTFE.
It significantly improves wear resistance and compressive strength, reducing deformation under load. This makes it a common choice for components like hydraulic piston rings.
Carbon (For Strength and Chemical Environments)
Carbon, often added as a powder or fiber, dramatically increases compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
It provides better chemical resistance than glass-filled compounds, making it suitable for applications with harsh chemicals. Carbon also enhances thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in dynamic applications.
Graphite (For Low Friction and High Speeds)
Graphite is often combined with other fillers like carbon or glass. Its primary contribution is reducing the coefficient of friction and acting as a superb lubricant.
This makes graphite-filled PTFE ideal for high-speed, dynamic applications where low friction and good wear properties are critical.
Bronze (For Thermal Conductivity and Heavy Loads)
Bronze powder significantly increases hardness, creep resistance, and thermal conductivity. It creates a very durable compound capable of handling heavy loads.
Its excellent ability to conduct heat away from surfaces makes it a top choice for high-speed bearings and wear components. However, bronze has poor chemical resistance compared to other fillers.
Stainless Steel (For Hardness and Extrusion Resistance)
Stainless steel powder creates a compound with exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and load-bearing capability.
It is frequently used in applications requiring high mechanical strength and resistance to being pushed out of place (extrusion). Certain grades are also suitable for food-grade applications.
Other Specialized Fillers
Less common but important fillers are used for specific needs. Molybdenum Disulphide improves hardness and reduces friction, while Aromatic Polyester (Ekonol) is used for high-temperature service.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not a free lunch. While they enhance certain properties, they can also detract from some of PTFE's most valued inherent characteristics.
The Impact on Chemical Resistance
The most significant trade-off is a reduction in chemical inertness. Virgin PTFE is resistant to nearly all chemicals, but fillers like glass and bronze can be attacked by certain aggressive media, compromising the material.
Changes in Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. Adding conductive fillers like carbon, graphite, or metal powders will increase the electrical conductivity of the compound, which can be either a benefit or a drawback depending on the goal.
Manufacturing Considerations
Any filler used must be able to withstand the high temperatures (around 360-380°C) of the PTFE sintering process. This limits the types of materials that can be successfully blended.
How to Select the Right Filled PTFE
Your choice of filler should be driven directly by the primary challenge of your application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose wear resistance: Glass-filled PTFE is the most common and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is performance in chemical or water-based systems: Carbon-filled PTFE offers superior strength and better chemical compatibility than glass.
- If your primary focus is high-speed sliding or self-lubrication: Graphite-filled PTFE provides the lowest friction and excellent wear properties.
- If your primary focus is high compressive loads and heat dissipation: Bronze-filled PTFE delivers the best creep resistance and thermal conductivity.
Ultimately, selecting the correct filler transforms PTFE from a unique polymer into a versatile engineering solution for complex problems.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Properties Enhanced | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | Wear resistance, compressive strength | Hydraulic piston rings, general seals |
| Carbon | Compressive strength, hardness, chemical resistance | Chemical seals, heavy-duty components |
| Graphite | Low friction, self-lubrication | High-speed bearings, sliding parts |
| Bronze | Creep resistance, thermal conductivity | High-load bearings, wear components |
| Stainless Steel | Hardness, extrusion resistance | High-strength seals, food-grade parts |
Need a Custom PTFE Solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components with precisely engineered fillers to meet your specific requirements. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure optimal material performance for your application.
Let us help you overcome PTFE's limitations and achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of Teflon (PTFE) used in custom parts? | Achieve Peak Performance
- How is Teflon sheet utilized in the healthcare industry? Enhancing Patient Safety and Device Performance
- Are PTFE and PEEK backup rings usually pure, or do they contain fillers? Discover the Role of Fillers in High-Performance Seals
- Why are PTFE rotary shaft lip seals ideal for chemical processing plants? Ensure Reliability in Corrosive Environments
- What are the primary advantages of expanded PTFE? Achieve Superior Sealing and Performance
- How are Teflon-encapsulated O-Rings utilized in heavy equipment and hydraulics? Achieve Superior Sealing and Reduce Downtime
- What are the limitations of PTFE oil seals, and how are they addressed? Overcome Material Challenges with Engineered Solutions
- What makes PTFE gaskets resistant to heat and chemicals? The Molecular Secret to Unmatched Performance



















