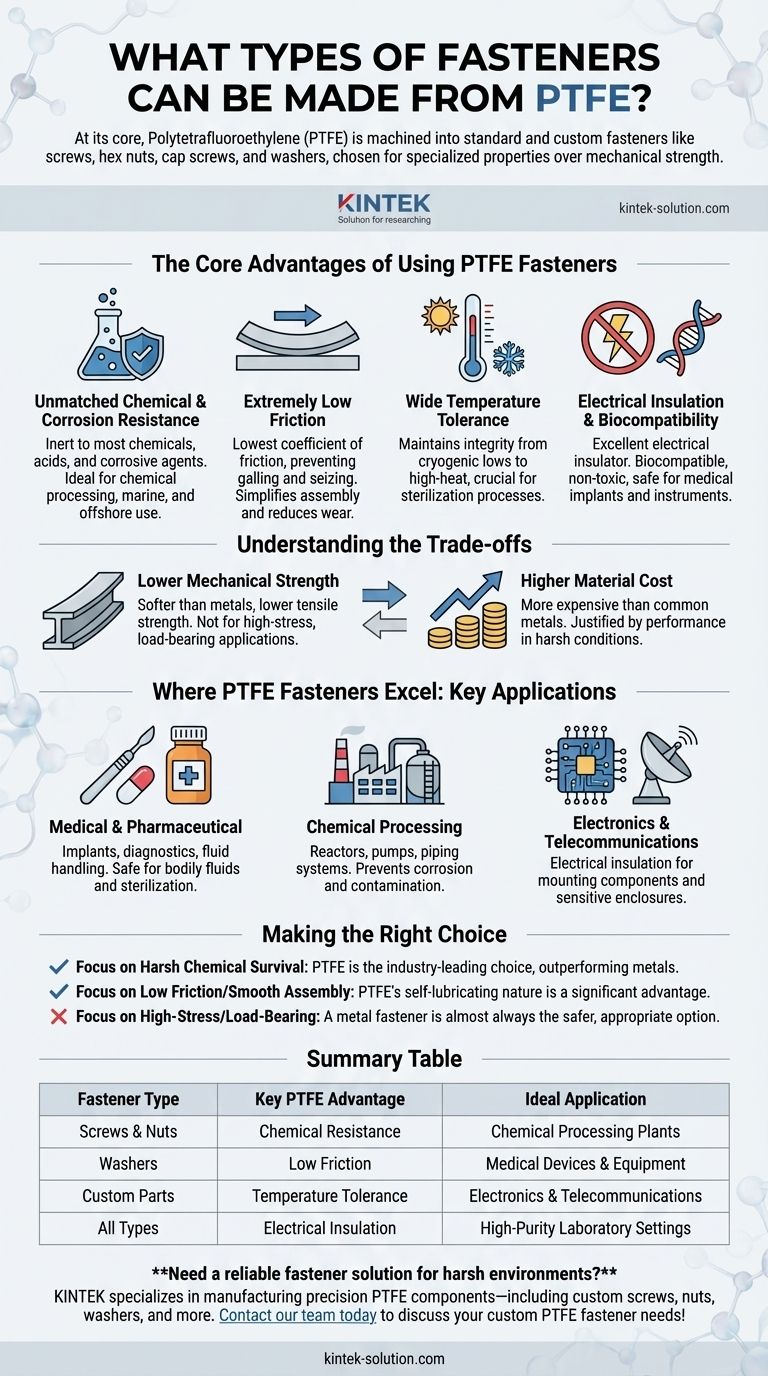
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) can be machined into a variety of standard and custom fasteners. The most common types include screws, hex nuts, hex head cap screws, and flat washers, but the material's versatility allows for the fabrication of nearly any custom-designed part.
The decision to use PTFE for fasteners is rarely about mechanical strength. Instead, it is a strategic choice for specialized applications where its unparalleled chemical resistance, extremely low friction, and wide temperature tolerance are critical operational requirements.

The Core Advantages of Using PTFE Fasteners
Understanding why PTFE is selected requires looking beyond its basic function as a fastener and focusing on its unique material properties.
Unmatched Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
PTFE is almost completely inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of chemicals, acids, or corrosive agents. This makes it an ideal choice for equipment used in chemical processing, marine, and offshore industries where metal fasteners would rapidly degrade.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This property prevents galling and seizing, which simplifies assembly and disassembly and reduces wear in applications that require frequent adjustments.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
These fasteners maintain their structural integrity across an extreme temperature range, from cryogenic lows to high-heat environments. This is particularly valuable for medical devices that must undergo high-temperature sterilization processes like autoclaving.
Electrical Insulation and Biocompatibility
As an excellent electrical insulator, PTFE is used in electronics and telecommunications to prevent electrical conductivity. Furthermore, its biocompatibility means it is non-toxic and safe for direct contact with human tissues, making it a staple in medical implants and surgical instruments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is crucial for proper application.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals like steel or titanium, PTFE is a much softer material with lower tensile strength. This limits its use in high-stress, load-bearing applications where mechanical integrity is the primary concern.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE fasteners are typically more expensive than those made from common metals or other plastics. Their use is justified when the cost of failure due to corrosion, chemical attack, or friction outweighs the initial component price.
Where PTFE Fasteners Excel: Key Applications
The unique combination of properties makes PTFE the superior choice in several demanding fields.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
Used in implants, diagnostic equipment, and fluid handling systems, PTFE's biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization ensure safety and reliability in environments exposed to bodily fluids and harsh cleaning chemicals.
Chemical Processing
In reactors, pumps, and piping systems that handle aggressive chemicals, PTFE fasteners prevent corrosion that would compromise the entire system, ensuring longevity and preventing contamination.
Electronics and Telecommunications
PTFE's role as an electrical insulator is critical for mounting components on circuit boards or assembling sensitive electronic enclosures where conductivity must be avoided.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct fastener material depends entirely on the primary demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is survival in harsh chemical or corrosive environments: PTFE is an industry-leading choice that will outperform most metals.
- If your primary focus is low friction for smooth assembly or preventing seizure: The self-lubricating nature of PTFE is a significant operational advantage.
- If your primary focus is high-stress, load-bearing capability: A metal fastener is almost certainly the more appropriate and safer option.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE fastener is an engineering decision to solve specific challenges that conventional materials cannot.
Summary Table:
| Fastener Type | Key PTFE Advantage | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Screws & Nuts | Chemical Resistance | Chemical Processing Plants |
| Washers | Low Friction | Medical Devices & Equipment |
| Custom Parts | Temperature Tolerance | Electronics & Telecommunications |
| All Types | Electrical Insulation | High-Purity Laboratory Settings |
Need a reliable fastener solution for harsh environments? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom screws, nuts, washers, and more—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures components that resist chemicals, reduce friction, and perform under extreme temperatures. Contact our team today to discuss your custom PTFE fastener needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using Teflon sheets with a heat press? Achieve Flawless, Professional Transfers
- What are the key features of PTFE reducing flanges? Superior Chemical Resistance and Leak-Proof Performance
- How are PTFE rotary shaft lip seals utilized in the automotive industry? Essential for High-Performance & EV Systems
- Why are Teflon seals ideal for harsh chemical environments? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Reliability
- What makes Teflon (PTFE) suitable for food handling equipment? Discover its Safety & Efficiency Benefits
- What key offerings are associated with Teflon-encapsulated O-Rings? Beyond the Part to Full-System Support
- What industries benefit from PTFE's non-stick properties? Boost Efficiency and Purity
- Are fragments of PTFE harmful if they come loose during medical procedures? The Truth About PTFE Safety



















