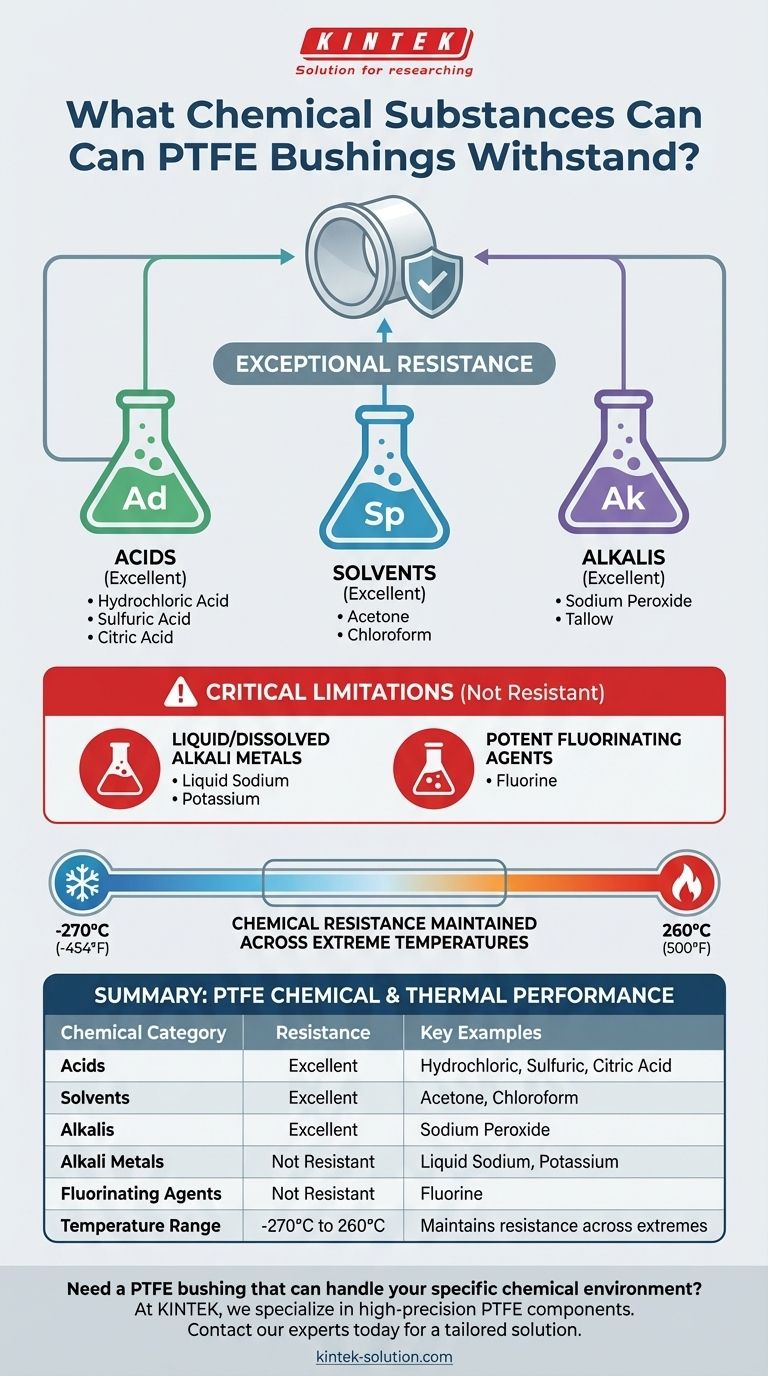
To put it simply, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) bushings demonstrate exceptional resistance to a vast range of chemical substances. They are highly inert and can reliably withstand exposure to most common acids, solvents, and alkalis, making them a default choice for aggressive chemical environments.
PTFE's near-universal chemical resistance is its defining characteristic. However, this material is not entirely invincible; it has specific, well-documented vulnerabilities to alkali metals and certain potent oxidizing agents like fluorine.

The Scope of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
PTFE's resilience is not accidental. It is a fundamental property of its molecular structure, which results in a material that does not readily react with other substances. This makes it stable in most corrosive and aggressive media.
Broad Categories of Resistance
PTFE bushings are engineered to handle prolonged contact with major chemical classes. This includes strong acids, aggressive solvents, and powerful alkalis.
Specific Chemical Examples
The material has been proven to be stable when exposed to a wide variety of specific chemicals. These include substances like acetone, chloroform, citric acid, hydrochloric acid, and sulfuric acid.
It also holds up against materials like tallow and sodium peroxide, showcasing its versatility in both industrial and processing applications.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
No material is perfect for every application. Understanding PTFE's specific vulnerabilities is crucial for ensuring system safety and longevity. Ignoring these limitations can lead to material degradation and component failure.
What PTFE Cannot Withstand
The primary exceptions to PTFE's chemical inertness are very specific. It is not resistant to attack from liquid or dissolved alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium.
Additionally, it is vulnerable to fluorines and other extremely potent oxidizing agents. These substances are aggressive enough to break down PTFE's stable structure.
The Overlooked Factor: Thermal Stability
A key reason PTFE is so valued is its ability to maintain chemical resistance across an enormous temperature range. Its properties remain consistent under conditions where other plastics would fail.
PTFE can operate reliably in temperatures from cryogenic lows of -270°C (-454°F) up to high-heat environments of 260°C (500°F). This ensures that its chemical resistance is not compromised by thermal cycling or extreme operating conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating PTFE bushings, you must consider both the chemical and thermal demands of your specific environment.
- If your primary focus is resistance to common acids, solvents, or alkalis: PTFE is an exceptionally safe and reliable choice for your application.
- If your primary focus is performance across extreme temperature shifts: PTFE's wide operating range ensures its mechanical and chemical properties will not degrade.
- If your primary focus involves alkali metals or potent fluorinating agents: You must seek an alternative material, as PTFE is known to be vulnerable to these specific substances.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision for reliability in nearly all but the most specialized and aggressive chemical scenarios.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | Resistance | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Acids | Excellent | Hydrochloric Acid, Sulfuric Acid, Citric Acid |
| Solvents | Excellent | Acetone, Chloroform |
| Alkalis | Excellent | Sodium Peroxide |
| Alkali Metals | Not Resistant | Liquid Sodium, Potassium |
| Fluorinating Agents | Not Resistant | Fluorine |
| Temperature Range | -270°C to 260°C | Maintains chemical resistance across extremes |
Need a PTFE bushing that can handle your specific chemical environment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and bushings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components will deliver unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing a perfect fit for your application's demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a solution tailored for reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















