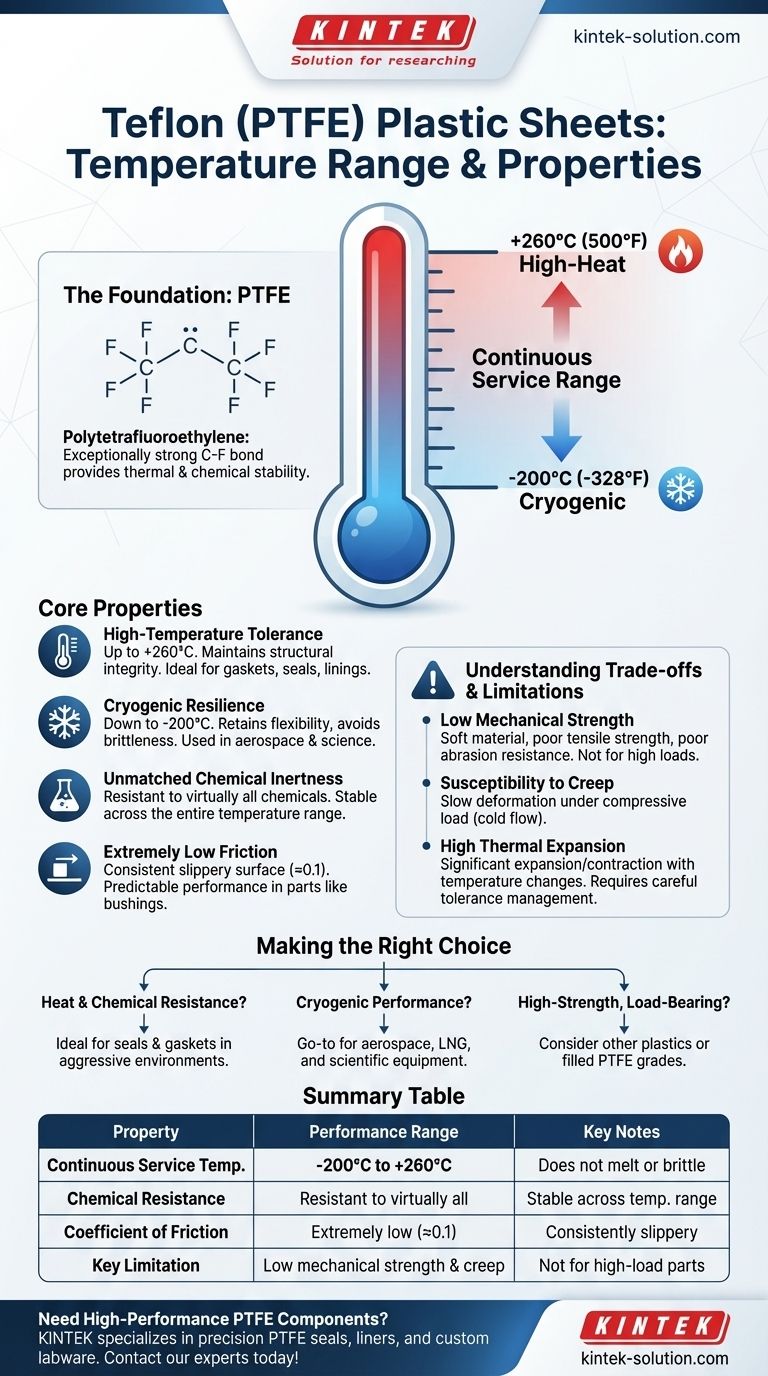
In short, Teflon (PTFE) plastic sheets can operate continuously in a remarkably wide temperature range, from as low as -200°C (-328°F) to as high as +260°C (500°F). This stability allows the material to maintain its core performance characteristics in both cryogenic conditions and high-heat industrial applications without degradation.
Teflon's value is not just its wide temperature range, but its ability to maintain its other key properties—unmatched chemical inertness and an extremely low friction coefficient—consistently across that entire range.

The Foundation of Teflon's Thermal Stability
The properties commonly associated with "Teflon" sheets originate from the material they are made of: PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene). Teflon is simply a well-known brand name for PTFE.
PTFE's molecular structure is composed of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. This carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable, which is the direct source of its remarkable resistance to both thermal and chemical attack.
Deconstructing Teflon's Core Properties
Understanding how temperature affects Teflon requires looking beyond a single number. Its performance is a combination of three interconnected traits that remain stable across its operational temperature range.
Exceptional High-Temperature Tolerance
Teflon sheets can withstand continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
Up to this point, the material does not melt or lose its fundamental structural integrity, making it highly reliable for applications like gaskets, seals, and linings in high-heat systems.
Resilience in Cryogenic Conditions
On the other end of the spectrum, Teflon maintains its usefulness in extreme cold, down to approximately -200°C (-328°F).
Unlike many plastics that become extremely brittle and fail at low temperatures, PTFE retains a degree of flexibility and strength, making it a critical material for aerospace and scientific applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Teflon's resistance to virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents is legendary.
Critically, this property is not compromised by temperature. It can handle highly corrosive substances even at elevated temperatures, a scenario where many other materials would quickly fail.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
Known as one of the most slippery materials in existence, Teflon's low-friction surface remains consistent across its temperature range.
This ensures that mechanical parts like bushings or slide bearings made from Teflon perform predictably, whether in a frozen environment or a hot processing plant.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal and chemical properties are elite, Teflon is not the right choice for every application. Its limitations are primarily mechanical.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has poor tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to other engineering plastics like PEEK or Nylon. It is not suitable for high-load structural components.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under sustained compressive load, Teflon can be subject to "creep" or "cold flow," meaning it will slowly deform over time. This must be accounted for in the design of seals and gaskets.
High Thermal Expansion
Teflon expands and contracts more than most metals when heated and cooled. In designs with tight tolerances, this high coefficient of thermal expansion must be carefully managed to avoid part failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its complete profile to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is combined heat and chemical resistance: Teflon is an ideal choice for seals, linings, and gaskets in chemically aggressive and high-temperature environments where mechanical stress is low.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: Teflon's ability to avoid brittleness at extreme cold makes it a go-to material for components in aerospace, liquefied natural gas (LNG), and scientific equipment.
- If your primary focus is a high-strength, load-bearing part: You should evaluate other engineering plastics or consider "filled" grades of PTFE, which incorporate additives to improve mechanical strength and reduce creep.
Ultimately, understanding Teflon's full profile—both its incredible strengths and its clear limitations—is the key to successful material selection.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance Range | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temperature | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Does not melt or become brittle within this range. |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to virtually all chemicals | Property is stable across the entire temperature range. |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely low (≈0.1) | Remains consistently slippery from cryogenic to high heat. |
| Key Limitation | Low mechanical strength & creep | Not ideal for high-load structural parts. |
Need high-performance PTFE components that excel in extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our custom fabrication ensures your parts perform reliably from cryogenic conditions to high-heat environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the mechanical properties of Teflon? A Guide to Its Unique Strengths and Limitations
- What makes PTFE unique compared to other engineering plastics? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How does PTFE's low friction property benefit mechanical engineering applications? Achieve Efficiency and Reliability
- What distinguishes Virgin PTFE from Reprocessed PTFE? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- Why is Teflon suitable for waterproof makeup products? Unlock the Secret to Smudge-Proof Wear
- What is Teflon/PTFE and what are its key properties? Discover the Premier High-Performance Polymer
- What are the uses of PTFE in the automotive industry? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the different grades of PTFE and their uses? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material



















