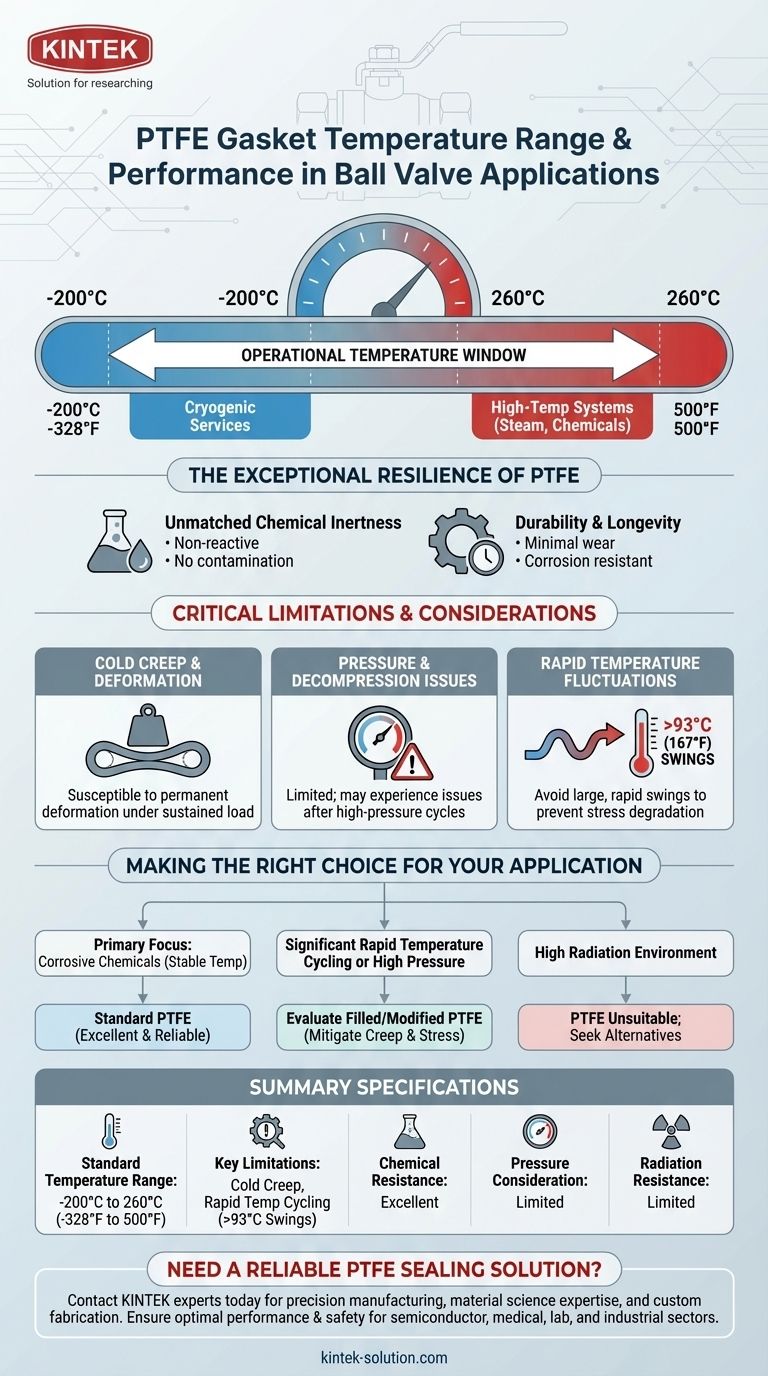
In ball valve applications, a standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gasket can typically withstand a wide temperature range from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This exceptional thermal stability makes it a versatile choice for everything from cryogenic services to high-temperature systems involving steam or aggressive chemicals.
While PTFE's broad temperature range is its most cited feature, its real-world effectiveness depends critically on understanding its limitations regarding pressure, cold creep, and sensitivity to rapid temperature fluctuations.

The Exceptional Resilience of PTFE
PTFE is a go-to material in demanding industrial environments precisely because of its ability to perform reliably under thermal stress. This resilience, combined with its other properties, makes it a uniquely valuable sealing solution.
The Operational Temperature Window
The accepted service temperature range for PTFE gaskets is -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
This wide spectrum means a single material can handle applications from deep cryogenic freezing to processes well above the boiling point of water, such as those found in steam lines and chemical reactors.
Why This Range Matters
This thermal stability allows PTFE-sealed ball valves to be used in industries where temperature variance and aggressive media are common. These include chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food production, and metallurgy.
The gasket maintains its integrity and sealing capability whether the media passing through is extremely cold or hot, ensuring a consistent and reliable seal.
Beyond Temperature: Other Key Properties
Temperature resistance is only part of the story. PTFE's value comes from a combination of powerful characteristics that work together to create a robust seal.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is highly resistant to a vast array of aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents.
It is a non-reactive material, meaning it will not contaminate the process fluid or degrade when exposed to corrosive substances. This ensures both the integrity of the seal and the purity of the media.
Durability and Longevity
These gaskets are engineered for long-lasting performance with minimal wear.
Their inherent resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation means they remain effective over extended periods, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement even in challenging environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use PTFE effectively and safely, it is crucial to understand its operational boundaries and potential failure points. An expert advisor would be remiss not to highlight these critical considerations.
The Challenge of Cold Creep
PTFE is susceptible to cold creep or cold flow, which is the tendency of the material to deform permanently under a sustained load, even at low temperatures. This can eventually lead to a loss of sealing pressure.
Pressure and Decompression Issues
While excellent for temperature, standard PTFE has pressure limitations. It may experience decompression problems after being subjected to high-pressure cycles, potentially compromising the seal.
Sensitivity to Rapid Temperature Fluctuations
This is a critical nuance. While PTFE has a wide static temperature range, some sources warn that it should not be exposed to rapid temperature swings greater than 93°C (167°F).
Extreme and rapid cycling can cause thermal expansion and contraction stress that degrades the seal's integrity over time, a factor that must be considered in dynamic process environments.
Limited Radiation Resistance
PTFE has a limited lifetime when exposed to radiation. This makes it unsuitable for certain applications, such as those in the nuclear industry, where other materials would be specified.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires balancing the benefits against the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive chemicals across a wide, but stable, temperature range: Standard PTFE is an excellent and highly reliable choice due to its inertness and thermal stability.
- If your application involves significant and rapid temperature cycling or high pressure: You must carefully evaluate if standard PTFE is sufficient, or if a filled or modified grade of PTFE is required to mitigate creep and stress.
- If your environment includes high radiation: PTFE is not a suitable material, and you must seek out alternatives specifically designed for radiation resistance.
Understanding these operational boundaries is the key to leveraging PTFE's remarkable strengths while ensuring the safety and reliability of your system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Standard Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Key Limitation: Cold Creep | Susceptible to permanent deformation under sustained load |
| Key Limitation: Rapid Temp Cycling | Avoid swings >93°C (167°F) to prevent stress degradation |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Highly inert to acids, solvents, and corrosive media) |
| Pressure Consideration | Limited; may experience decompression issues after high-pressure cycles |
| Radiation Resistance | Limited; unsuitable for nuclear applications |
Need a reliable PTFE sealing solution tailored to your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware. Whether your application is in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components perform reliably within their operational limits.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and leverage our expertise in material science and precision production for optimal performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability



















