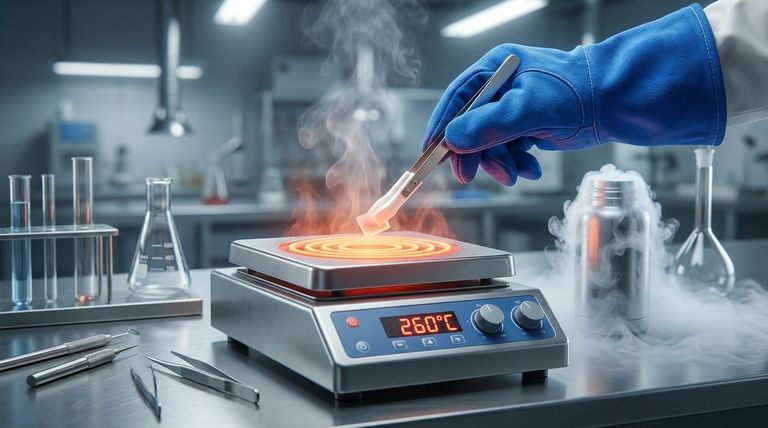
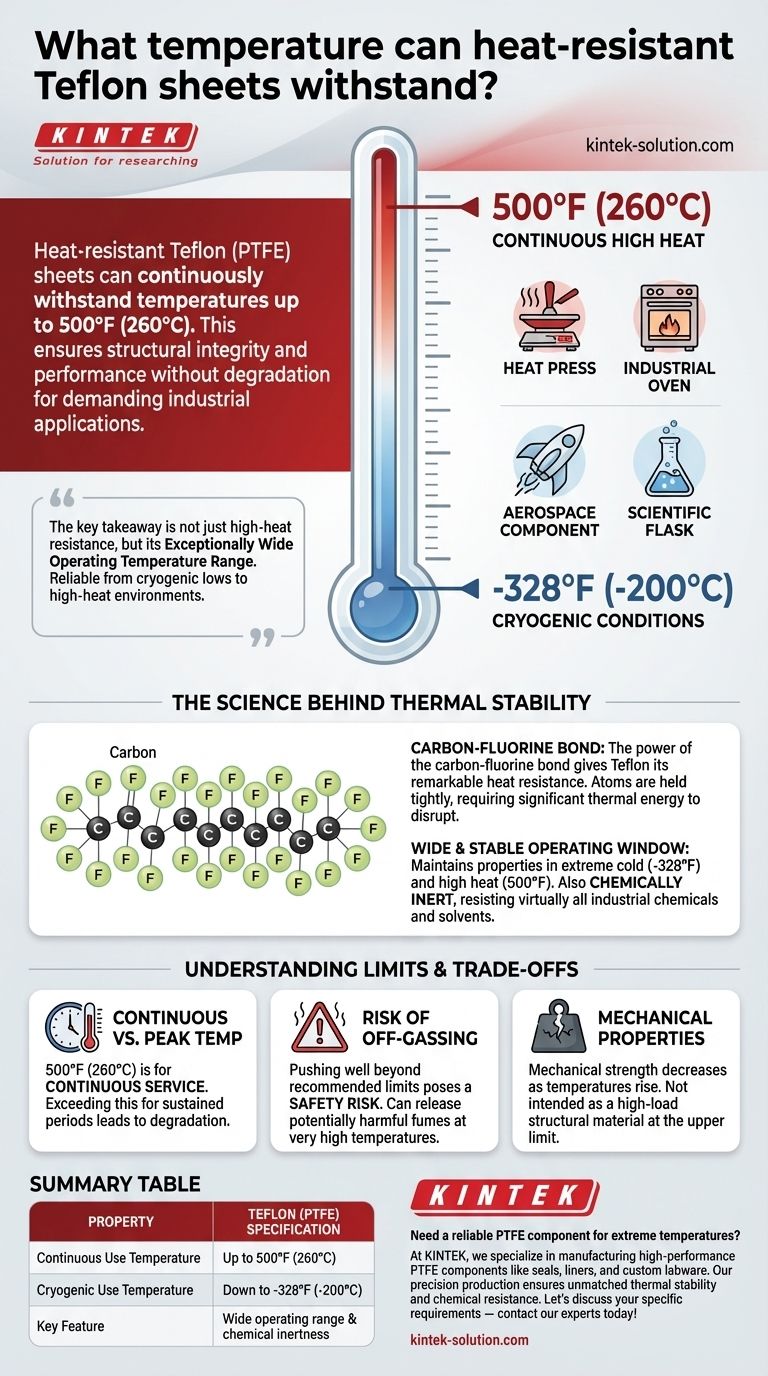
In short, heat-resistant Teflon (PTFE) sheets can continuously withstand temperatures up to 500°F (260°C). This high-heat tolerance ensures the material maintains its structural integrity and performance characteristics without degrading, making it a reliable choice for demanding industrial and commercial applications.
The key takeaway isn't just Teflon's high-heat resistance, but its exceptionally wide operating temperature range. It performs reliably from cryogenic lows to high-heat environments, which is a rare and valuable trait for any material.

The Science Behind Teflon's Thermal Stability
Understanding why Teflon, or Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), can handle such extreme temperatures helps clarify its best use cases. Its unique properties are rooted in its molecular structure.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE is composed of long chains of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable.
This powerful chemical bond is what gives Teflon its remarkable resistance to heat. The atoms are held together so tightly that it takes a significant amount of thermal energy to disrupt them.
A Wide and Stable Operating Window
While its high-heat capability is impressive, its performance at the other end of the spectrum is equally notable. PTFE maintains its properties in cryogenic conditions, remaining functional at temperatures as low as -328°F (-200°C).
This makes it one of the few materials suitable for applications that span extreme cold and high heat, from aerospace components to industrial processing equipment.
More Than Just Heat Resistance
The same molecular structure that provides thermal stability also makes Teflon chemically inert. It resists virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents, ensuring it won't corrode or break down in harsh environments where both heat and chemicals are present.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limits
While 500°F (260°C) is the established continuous operating temperature, it's critical to understand the material's absolute limits to ensure safety and performance.
Continuous vs. Peak Temperature
The 500°F (260°C) rating is for continuous service. The material can handle this temperature indefinitely without losing its core properties. Exceeding this temperature for sustained periods will lead to degradation.
The Risk of Off-Gassing
Pushing Teflon well beyond its recommended temperature limit poses a significant safety risk. At very high temperatures, it can begin to decompose and release potentially harmful fumes. Always operate within the specified temperature range.
Mechanical Properties Under Load
While Teflon maintains its structural integrity up to its limit, its mechanical strength (like compressive resistance) decreases as temperatures rise. It is not intended to be a high-load structural material at the upper end of its temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the operational demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-heat processing: For applications like heat presses, industrial ovens, or food processing, Teflon's 500°F (260°C) limit provides a reliable and safe operating margin.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: For aerospace, scientific, or specialized industrial uses, Teflon's stability at temperatures down to -328°F (-200°C) is its most critical feature.
- If your primary focus is combined chemical and thermal stress: In environments with corrosive chemicals and high heat, Teflon's chemical inertness and thermal stability make it an ideal choice for seals, liners, and bushings.
Ultimately, choosing Teflon is a decision for unmatched reliability across an extreme range of operating conditions.
Summary Table:
| Property | Teflon (PTFE) Specification |
|---|---|
| Continuous Use Temperature | Up to 500°F (260°C) |
| Cryogenic Use Temperature | Down to -328°F (-200°C) |
| Key Feature | Wide operating range & chemical inertness |
Need a reliable PTFE component for extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components like seals, liners, and custom labware. Our precision production ensures your parts deliver unmatched thermal stability and chemical resistance, whether for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial applications.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let's discuss your specific temperature and chemical resistance requirements — contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is chemical resistance an important feature of PTFE reducing flanges? Ensure Safety and Purity
- Why are FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings used in the food and pharmaceutical industries? Ensure Purity and Compliance
- What are the limitations of PTFE gaskets in high-temperature environments? Understanding Thermal Degradation and Creep
- What are the key properties that make Teflon sheets stand out? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE heat press sheets? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results
- In which industries are Teflon bearings commonly used? Solve Critical Bearing Challenges Across Industries
- What general maintenance practices can extend the lifespan of PTFE gaskets? Optimize Selection, Installation, and Monitoring
- What are the available size options for PTFE envelope gaskets? Find Your Perfect Fit from DN15 to DN2000



















