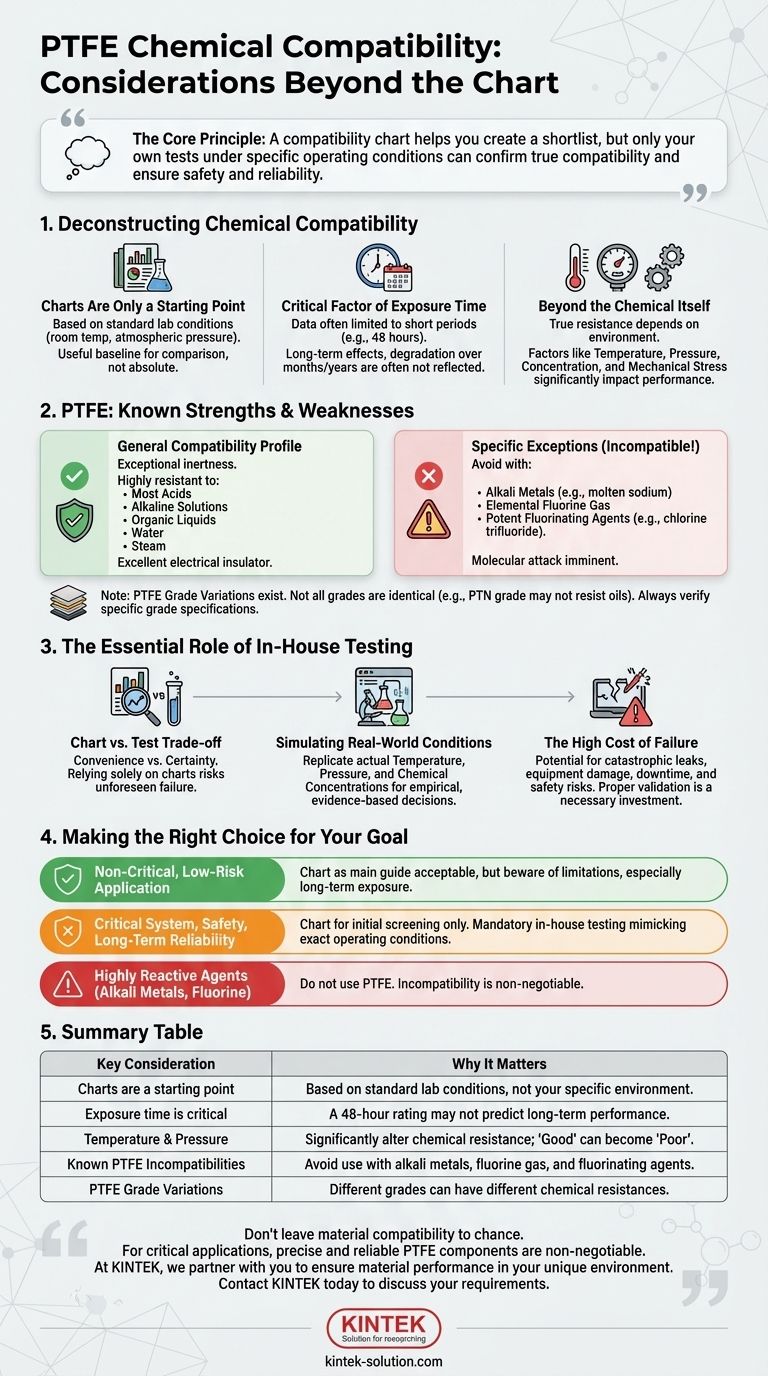
First and foremost, you must treat any chemical compatibility chart for PTFE as a preliminary guide, not as an absolute guarantee of performance. Its ratings are based on standardized conditions that may not reflect your specific operational environment. Factors like temperature, pressure, concentration, and exposure duration can significantly alter the material's resistance, making independent verification essential for any critical application.
The core principle is this: A compatibility chart helps you create a shortlist of materials, but only your own tests, conducted under your specific operating conditions, can confirm true compatibility and ensure the safety and reliability of your equipment.

Deconstructing Chemical Compatibility
Why Charts Are Only a Starting Point
Chemical compatibility charts are typically based on simple immersion tests conducted at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. These standardized conditions provide a useful baseline for comparison.
However, your real-world application likely involves a more complex interplay of factors that can impact how PTFE performs.
The Critical Factor of Exposure Time
The data in these charts is often limited to a specific, and relatively short, exposure period. The provided references, for example, specify a 48-hour test window.
There is often no data available for the effects of continuous, long-term exposure. A chemical that shows no effect after 48 hours could potentially cause degradation or failure over weeks, months, or years.
Beyond the Chemical Itself
True chemical resistance is a function of the entire operating environment. A rating of "Excellent" on a chart can become "Poor" when other variables are introduced.
Key factors to consider that are not reflected in a simple chart include temperature, pressure, chemical concentration, and the presence of mechanical stress on the PTFE component.
Known Strengths and Weaknesses of PTFE
General Compatibility Profile
PTFE is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness. It is highly resistant to a wide range of substances.
This includes most acids, alkaline solutions, organic liquids, water, and steam. It is also an excellent electrical insulator and generally resists oils.
The Specific Exceptions to a Near-Universal Rule
Despite its robustness, PTFE is not invincible. It is known to be incompatible with a small but critical group of highly reactive chemicals.
You must avoid using PTFE with certain alkali metals (like molten sodium), elemental fluorine gas, and other potent fluorinating agents (e.g., chlorine trifluoride). These substances can attack the material at a molecular level.
Variations Between PTFE Grades
It is also important to recognize that not all PTFE is identical. Additives or manufacturing processes can create different grades with slightly different properties.
For instance, the references note that while most PTFE grades have good resistance to oils, a specific grade (PTN) is not compatible with them. Always verify the specifications for the exact grade you intend to use.
The Essential Role of In-House Testing
Why "Good" on the Chart Isn't Good Enough
The primary trade-off you face is between convenience and certainty. Relying solely on a chart is fast and easy, but it carries the risk of unforeseen material failure.
Conducting your own tests requires an investment of time and resources but is the only way to validate performance and mitigate risk in critical systems.
Simulating Real-World Conditions
The goal of in-house testing is to replicate your operational environment as closely as possible. Your tests should simulate the actual service temperature, pressure, and chemical concentrations the material will face.
This process moves you from a theoretical assessment to an empirical, evidence-based decision.
The High Cost of Failure
A material failure can lead to catastrophic outcomes, including hazardous leaks, equipment damage, production downtime, and serious safety risks.
When viewed against these potential consequences, the upfront cost of proper material validation is a necessary and sound investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is a non-critical, low-risk application: Using the chart as your main guide may be acceptable, but be aware of its limitations, especially regarding long-term exposure.
- If your primary focus is a critical system, safety, or long-term reliability: Use the chart for initial screening only. In-house testing that mimics your exact operating conditions is mandatory.
- If you are working with highly reactive agents like alkali metals or fluorine: Do not use PTFE. The known incompatibility is a non-negotiable contraindication.
Ultimately, your goal is to ensure system integrity by prioritizing direct validation over generalized data.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Charts are a starting point | Based on standard lab conditions, not your specific environment. |
| Exposure time is critical | A 48-hour chart rating may not predict long-term performance. |
| Temperature & Pressure | Significantly alter chemical resistance; a 'Good' rating can become 'Poor'. |
| Known PTFE Incompatibilities | Avoid use with alkali metals, fluorine gas, and fluorinating agents. |
| PTFE Grade Variations | Different grades (e.g., PTN) can have different chemical resistances. |
Don't leave material compatibility to chance.
For critical applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, precise and reliable PTFE components are non-negotiable.
At KINTEK, we don't just manufacture high-quality PTFE seals, liners, and labware—we partner with you to ensure material performance in your unique environment. From custom prototypes to high-volume production, our focus on precision manufacturing mitigates risk and enhances the safety and longevity of your equipment.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for PTFE components you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















