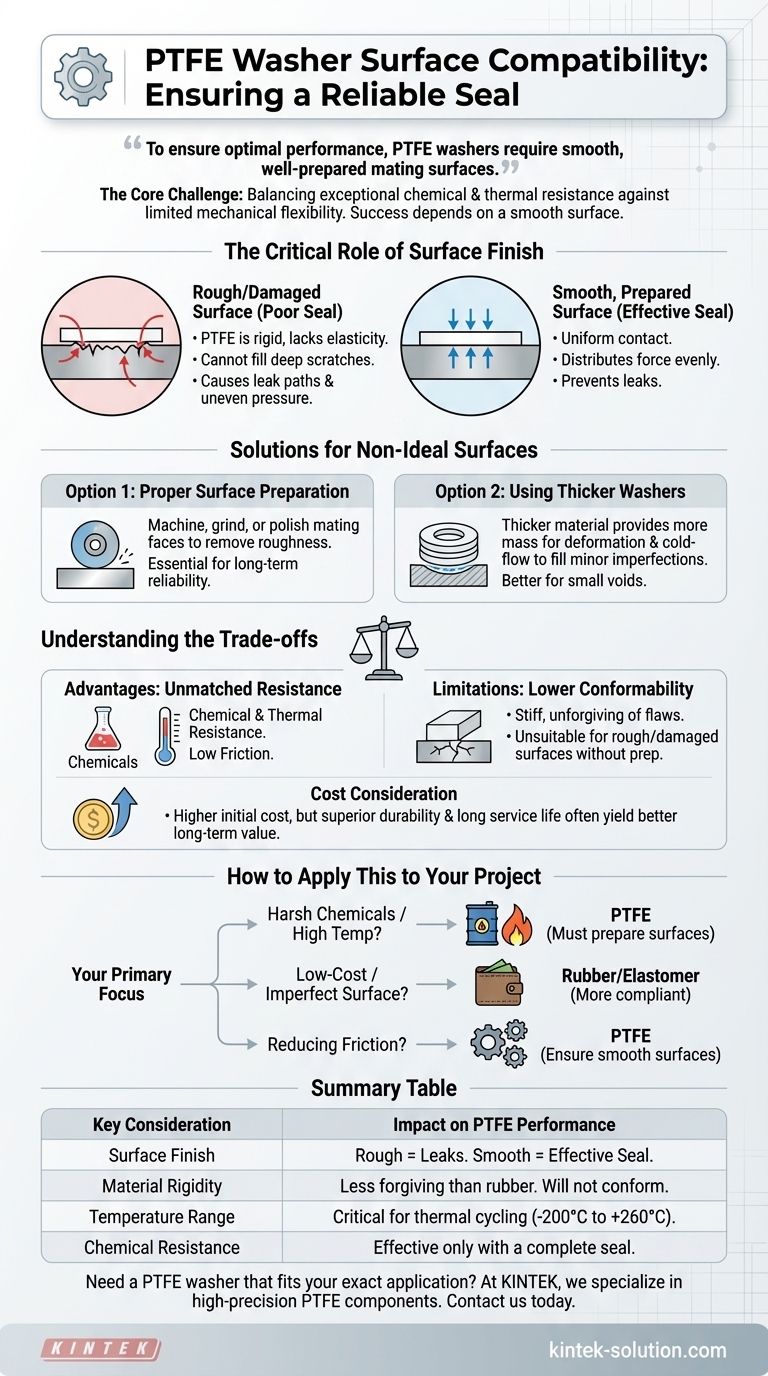
To ensure optimal performance, PTFE washers require smooth, well-prepared mating surfaces. Unlike more forgiving materials like rubber, PTFE is relatively rigid and will not easily conform to surface imperfections, which can compromise its ability to create a reliable seal.
The core challenge of using PTFE washers is balancing their exceptional chemical and thermal resistance against their limited mechanical flexibility. Success depends on ensuring the mating surface is smooth enough for the washer to function as designed.

The Critical Role of Surface Finish
The unique properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) dictate its specific requirements for surface interaction. Understanding this relationship is the key to preventing leaks and component failure.
Why Smoothness is Non-Negotiable
PTFE is a relatively hard plastic material. It lacks the elastic, compliant nature of rubber, meaning it cannot easily flow into and fill deep scratches, grooves, or irregularities on a flange or mating surface.
These imperfections can create microscopic leak paths under the washer, rendering its excellent chemical resistance useless.
The Impact of a Poor Surface
Using a PTFE washer on a rough or damaged surface leads to uneven pressure distribution. The washer will only make contact with the high points of the surface, creating gaps and preventing a consistent, effective seal.
This not only causes immediate leaks but can also lead to premature wear and failure of the washer.
Solutions for Non-Ideal Surfaces
If you are working with surfaces that are not perfectly smooth, you have two primary strategies to ensure a proper seal with PTFE.
Option 1: Proper Surface Preparation
The most reliable solution is to prepare the surface to meet the washer's needs. This involves machining, grinding, or polishing the mating faces to remove any significant radial marks, gouges, or general roughness.
A smooth, flat, and clean surface allows the PTFE washer to distribute the clamping force evenly and create the intended seal.
Option 2: Using Thicker Washers
In situations with minor surface imperfections, a thicker PTFE washer can improve sealing efficiency. A thicker washer provides more material that can deform and cold-flow under compression.
This additional material mass gives it a slightly better ability to fill small voids and conform to the surface than a thinner counterpart.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing PTFE involves acknowledging its distinct advantages and limitations. Its demand for a smooth surface is a direct result of the properties that make it so valuable in other areas.
The Advantage: Unmatched Resistance
PTFE is selected for the most demanding environments. Its primary benefits include exceptional resistance to virtually all industrial chemicals and a massive operating temperature range, from -200°C to +260°C.
It also has an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it ideal for dynamic applications where parts must slide against each other.
The Limitation: Lower Conformability
The key trade-off is its relative stiffness. Compared to a flexible elastomer like rubber, PTFE is far less forgiving of surface flaws. This makes it unsuitable for applications with rough cast surfaces or previously damaged flanges unless they are properly repaired.
The Cost Consideration
PTFE washers are typically more expensive than common rubber or fiber alternatives. However, their superior durability, resistance to wear and corrosion, and long service life often make them a more cost-effective investment over the long term by reducing maintenance and replacement frequency.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice should be dictated by the specific demands of your operating environment and the condition of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is sealing in harsh chemical or high-temperature environments: PTFE is the correct material, but you must invest in preparing the mating surfaces to be smooth and free of defects.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost, general-purpose seal on an imperfect surface: A more compliant material like rubber may be a more practical and forgiving choice, provided it meets your chemical and temperature needs.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction between moving parts: PTFE is an excellent choice, but ensure the surfaces are smooth to maximize its low-friction benefit and prevent abrasive wear.
Matching the unique requirements of PTFE with the right surface conditions is the key to unlocking its unparalleled performance in challenging applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Impact on PTFE Washer Performance |
|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Rough surfaces create leak paths; smooth, flat surfaces are essential for an effective seal. |
| Material Rigidity | PTFE is less forgiving than rubber and will not conform to surface imperfections. |
| Temperature Range | PTFE operates from -200°C to +260°C, making surface preparation critical for thermal cycling. |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior chemical resistance is only effective if the washer can form a complete seal. |
Need a PTFE washer that fits your exact application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your PTFE washers perform flawlessly, even in the most demanding environments. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and let us help you achieve a perfect, reliable seal.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















