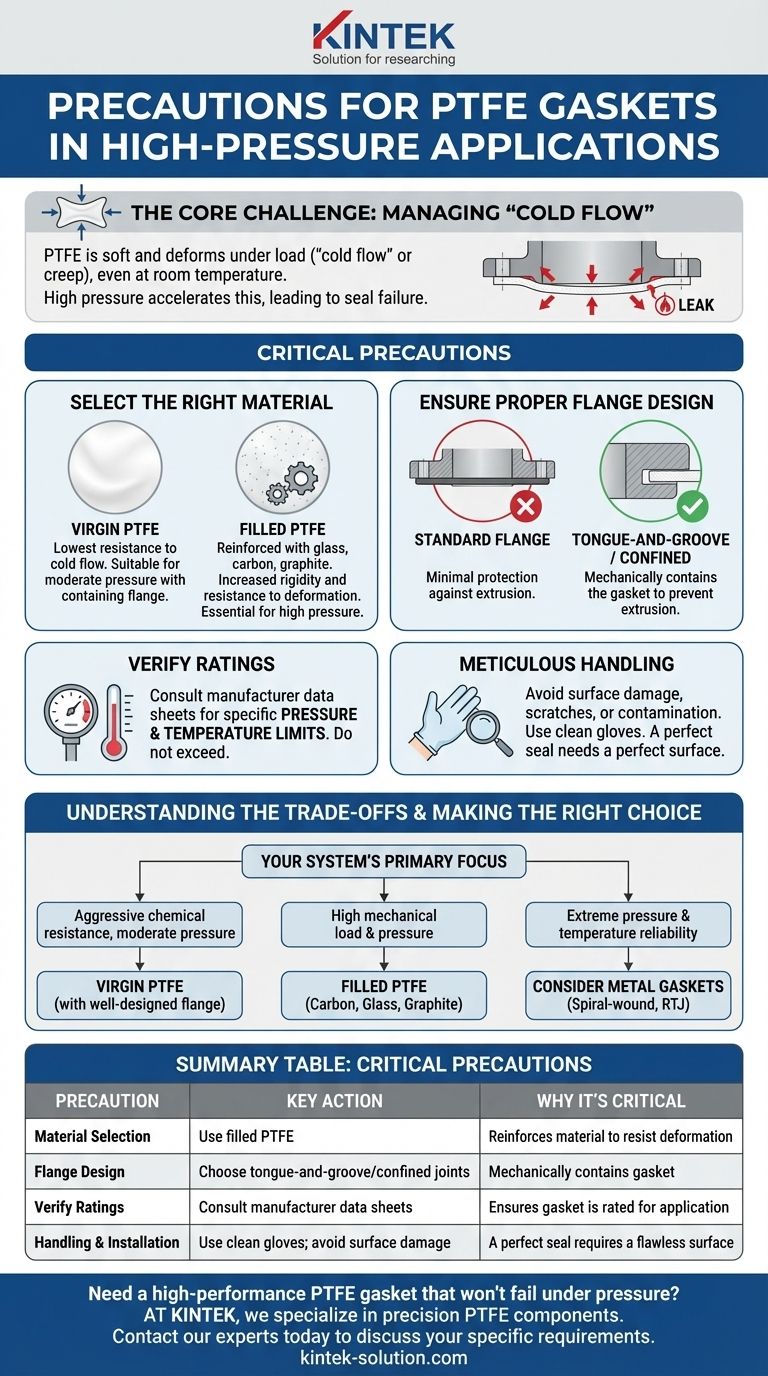
When using PTFE gaskets in high-pressure applications, the most critical precautions are to select an appropriate grade of filled PTFE and ensure the flange or joint is designed to mechanically contain the gasket. Because standard PTFE is soft and deforms under load, these engineering controls are essential to prevent the gasket from extruding and causing the seal to fail.
The fundamental challenge with PTFE is its inherent tendency to deform, or "cold flow," under pressure. Success in high-pressure applications depends less on installation technique and more on choosing a reinforced material and a system design that physically prevents the gasket from being squeezed out of the joint.
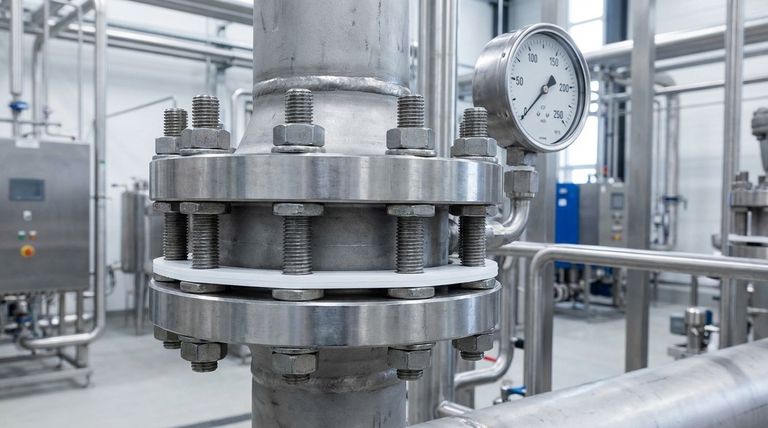

The Core Challenge: Managing "Cold Flow"
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is an exceptionally useful polymer, but its primary weakness in mechanical applications is its softness. Understanding this characteristic is key to using it effectively under pressure.
What is Cold Flow?
Cold flow, also known as creep, is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under persistent mechanical stress.
For PTFE, this means that when compressed in a flange, the material will slowly flow outwards from the point of highest pressure. This process happens even at room temperature.
The Impact on Sealing Performance
As the gasket material flows, the initial bolt torque and sealing stress on the gasket are reduced. This loss of stress can eventually lead to a leak path, causing the seal to fail over time.
High pressure dramatically accelerates this process, making standard PTFE unsuitable for such applications without specific countermeasures.
Critical Precautions for High-Pressure Sealing
To ensure a reliable seal, you must address PTFE's tendency to deform through both material selection and mechanical design.
Select the Right Material: Virgin vs. Filled PTFE
Virgin PTFE is the pure, unfilled polymer. While it offers the highest chemical resistance, it is also the softest and most susceptible to cold flow.
Filled PTFE incorporates materials like glass, carbon, or graphite into the PTFE matrix. These fillers act as a reinforcing structure, significantly increasing the gasket's rigidity and resistance to deformation and wear. For high-pressure service, a filled grade of PTFE is almost always necessary.
Ensure Proper Flange and Enclosure Design
The most effective way to combat cold flow is to use a flange design that fully contains the gasket, giving the material nowhere to flow.
Designs like tongue-and-groove or fully confined channels are ideal. Standard raised-face flanges offer minimal protection against extrusion and are not recommended for high-pressure applications with PTFE gaskets.
Verify Manufacturer Pressure/Temperature Ratings
The terms "high pressure" and "high temperature" are relative. Always consult the specific manufacturer's data sheets for the gasket material you are considering.
These specifications will provide clear pressure and temperature limits that must not be exceeded. A gasket's performance in a valve or specific assembly is determined by the total system design.
Meticulous Handling and Installation
PTFE surfaces are soft and can be easily damaged. Any scratch, gouge, or contamination can create a potential leak path.
Always handle gaskets with clean gloves and avoid contact with sharp tools, oils, or dust. A perfect seal requires a perfect surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While an excellent problem-solver, PTFE is not a universal solution. Knowing its limitations is critical for system reliability and safety.
The Limit of "High Pressure"
For applications involving extreme mechanical stress or very high pressures, PTFE may not be the appropriate choice, even in its filled forms.
In these cases, metal gaskets, such as spiral-wound or solid ring-type-joint (RTJ) gaskets, offer superior strength and will maintain a seal under conditions that would cause any polymer to fail.
The Risk of High Temperatures
High pressure is often accompanied by high temperature. While PTFE has a wide operating temperature range (typically up to 260°C or 500°F), it can degrade or burn if its upper limit is exceeded for prolonged periods.
Always ensure your system's operating temperature remains safely within the gasket's specified range.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the system's demands.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical resistance at moderate pressure: Virgin PTFE may be sufficient, provided you use a well-designed, containing flange.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a seal under high mechanical load and pressure: A filled PTFE gasket (carbon, glass, or graphite) is the correct choice to resist deformation.
- If your primary focus is extreme pressure and temperature reliability: You must consider alternatives like spiral-wound or solid metal gaskets for maximum safety and performance.
Ultimately, successful high-pressure sealing with PTFE is achieved through deliberate material selection and sound engineering design.
Summary Table:
| Precaution | Key Action | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Use filled PTFE (glass, carbon, graphite) | Reinforces material to resist deformation and cold flow |
| Flange Design | Choose tongue-and-groove or fully confined joints | Mechanically contains the gasket to prevent extrusion |
| Verify Ratings | Consult manufacturer data sheets | Ensures gasket is rated for your specific pressure/temperature |
| Handling & Installation | Use clean gloves; avoid surface damage | A perfect seal requires a flawless gasket surface |
Need a high-performance PTFE gasket that won't fail under pressure?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom gaskets and seals for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between chemical resistance and mechanical strength.
We can help you select the right filled PTFE material and design for your high-pressure system, ensuring a reliable, long-lasting seal. From prototypes to high-volume orders, our custom fabrication prioritizes precision and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution engineered for reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How often should torque settings on bolts be checked in PTFE butterfly valves? Prevent Leaks with Proper PTFE Maintenance
- What industries commonly use Teflon CNC machined parts? Critical Solutions for Aerospace, Medical & More
- What is the purpose of PTFE gasket sealing material in mechanical equipment? Enhance Reliability and Efficiency
- What makes PTFE versatile in medical applications? Unlock the Power of Biocompatible Polymers
- What are PTFE valve seat rings used for? Achieve a Leak-Proof Seal in Demanding Applications
- What processing methods are typically used for PTFE? Mastering the Unique Path from Powder to Precision Part
- Why are PTFE flange gaskets suitable for chemical processing industries? Unlock Superior Safety & Reliability
- What are the key material characteristics of PTFE that affect its CNC machining? Master Precision for Soft, Slippery Materials



















