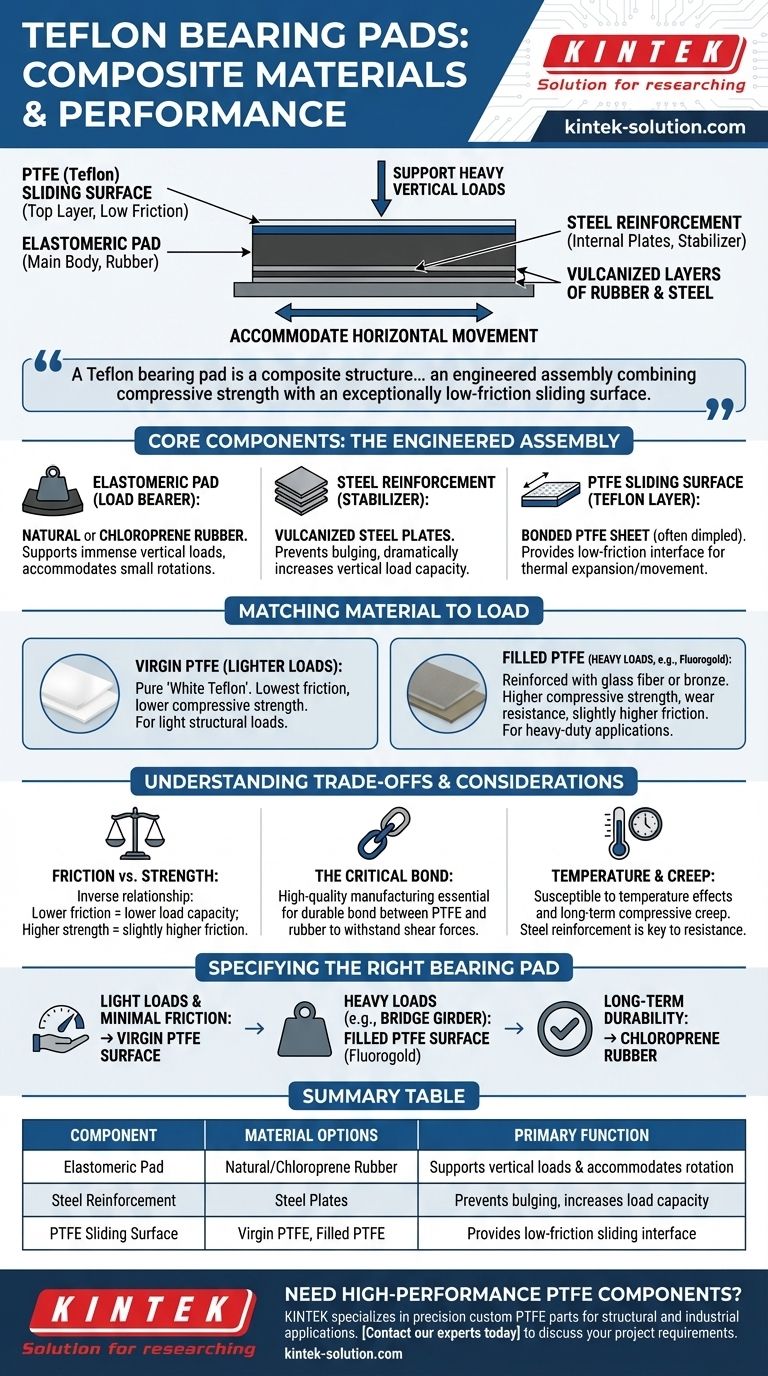
At its core, a Teflon bearing pad is a composite structure, not a single material. It is constructed from a laminated elastomeric pad, which is made of vulcanized layers of rubber and steel, bonded to a specialized Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plate, commonly known by its brand name, Teflon. This design allows it to support heavy vertical loads while permitting low-friction horizontal movement.
A Teflon bearing pad is not simply a piece of Teflon. It is an engineered assembly that combines the compressive strength of a steel-reinforced rubber pad with the exceptionally low-friction sliding surface of a PTFE sheet.
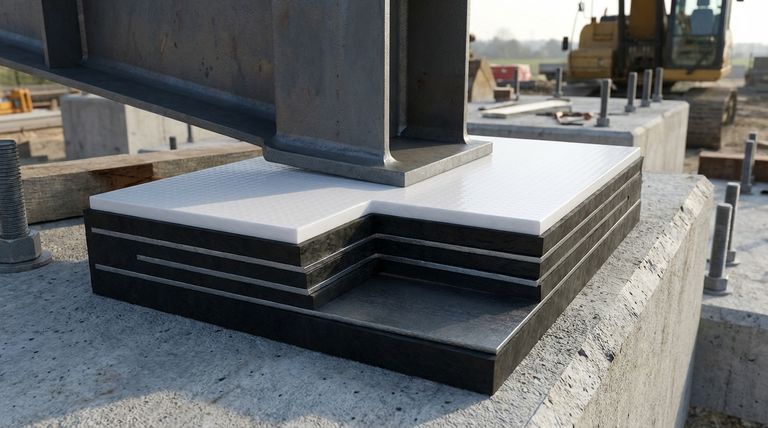

The Core Components of a Teflon Bearing Pad
To understand how these pads function in bridges, buildings, and other large structures, you must first understand the role of each constituent material.
The Elastomeric Pad (The Load Bearer)
The main body of the bearing is an elastomeric pad. This component is typically made from either natural rubber or chloroprene rubber, a synthetic alternative known for its durability. Its primary function is to support immense vertical loads and accommodate small rotational movements of the structure.
The Steel Reinforcement (The Stabilizer)
Thin steel plates are layered within the rubber pad. These plates are vulcanized—bonded during the rubber's curing process—to become an integral part of the pad. This reinforcement is critical; it prevents the rubber from bulging outwards under compression, dramatically increasing the pad's vertical load capacity.
The PTFE Sliding Surface (The "Teflon" Layer)
A sheet of PTFE (Teflon) is bonded to the top surface of the elastomeric pad. This provides the low-friction interface required for thermal expansion and contraction or other sources of horizontal movement. The PTFE is often dimpled to create pockets that retain lubricant, further reducing the coefficient of friction.
Matching the Material to the Load
The specific formulation of the PTFE layer is a critical design choice that directly impacts the bearing's performance under different load conditions.
Virgin PTFE for Lighter Loads
For applications with relatively light structural loads, a standard, unfilled "white Teflon" is often sufficient. This pure PTFE offers the lowest coefficient of friction but has lower compressive strength compared to its reinforced counterparts.
Filled PTFE (Fluorogold) for Heavy Loads
For heavy-duty applications, the PTFE is reinforced with filler materials to enhance its mechanical properties. Formulations like Fluorogold, which is a type of filled PTFE, are used. These fillers, such as glass fiber or bronze, significantly increase the material's compressive strength and resistance to wear under extreme pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specifying a Teflon bearing pad involves balancing competing performance characteristics. The choice is never without consequence.
Friction vs. Compressive Strength
There is an inverse relationship between friction and strength. Virgin PTFE offers the lowest friction but also the lowest load capacity. Filled PTFE can handle much higher pressures but at the cost of a slightly higher coefficient of friction.
The Criticality of the Bond
The adhesive bond between the PTFE sheet and the elastomeric pad is a potential point of failure. A high-quality manufacturing process is essential to ensure a durable, long-lasting bond that can withstand the shear forces generated during movement.
Temperature and Creep
Like all polymers, PTFE's performance is affected by temperature. More importantly, it is susceptible to creep—a slow, permanent deformation under sustained load. The steel-reinforced elastomeric backing provides the primary resistance to long-term compressive creep, making the composite design essential for structural integrity.
Specifying the Right Bearing Pad
Understanding these components allows you to make an informed decision based on your project's specific engineering demands.
- If your primary focus is accommodating light structural loads with minimal friction: A standard bearing with a virgin PTFE surface is the most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is supporting heavy loads like a major bridge girder: You must specify a bearing with a filled PTFE surface (such as Fluorogold) to handle the high compressive stress.
- If your primary focus is long-term environmental durability: Selecting a pad made with chloroprene rubber will provide superior resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering compared to natural rubber.
By understanding the distinct roles of the rubber, steel, and specific grade of PTFE, you can ensure the structural bearing you choose is precisely matched to its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Options | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Elastomeric Pad | Natural Rubber, Chloroprene Rubber | Supports vertical loads & accommodates rotation |
| Steel Reinforcement | Steel Plates | Prevents bulging, increases load capacity |
| PTFE Sliding Surface | Virgin PTFE, Filled PTFE (e.g., Fluorogold) | Provides low-friction sliding interface |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your structural or industrial applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware. Our expertise in material science and custom fabrication ensures you get parts that meet exact specifications for compressive strength, friction, and durability—whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















