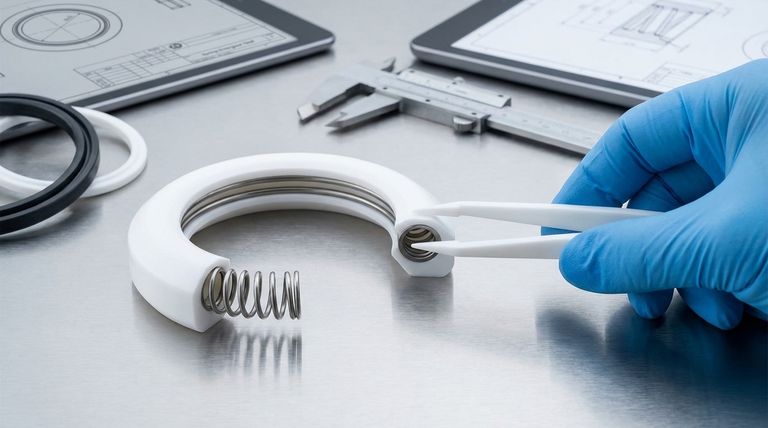
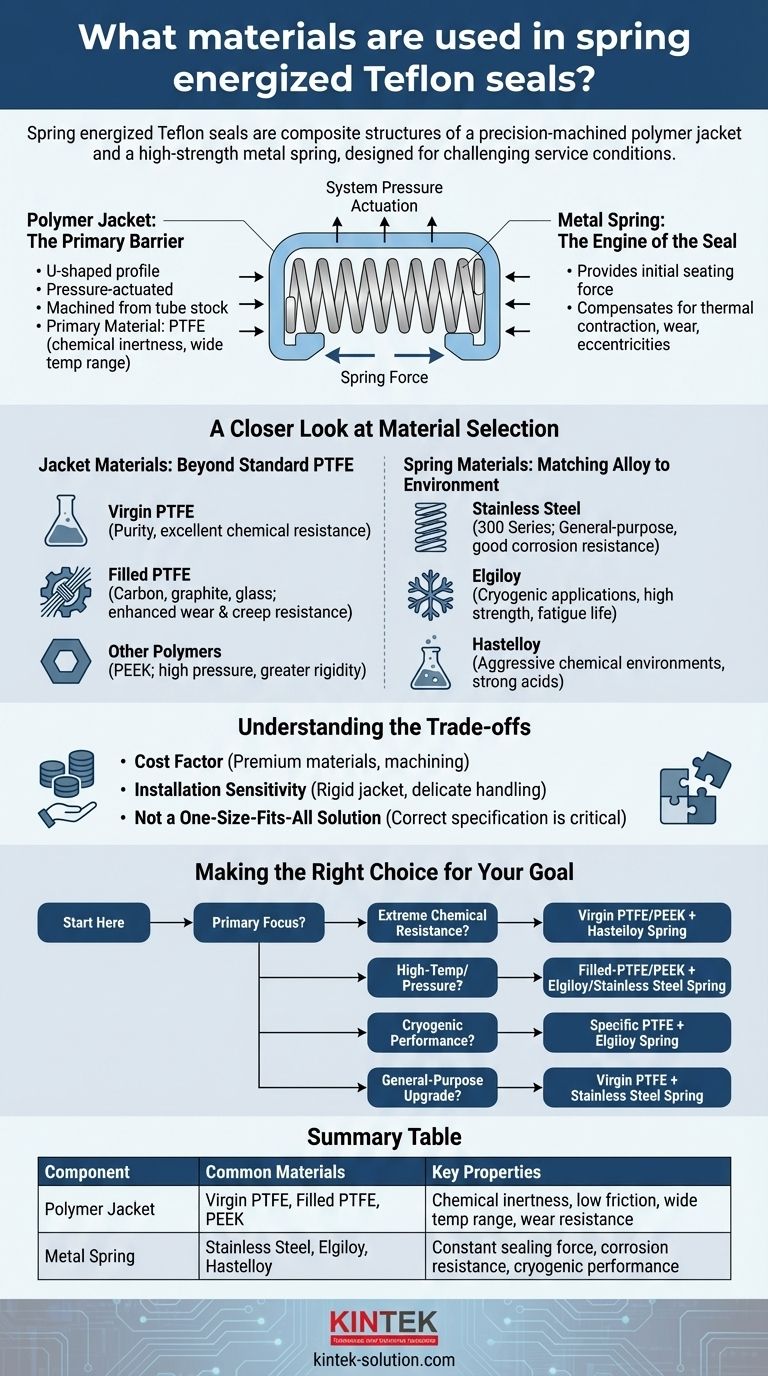
Spring energized Teflon seals are composite structures built from two primary components: a precision-machined polymer jacket and a high-strength metal spring. The jacket is most commonly made from PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene, the generic name for Teflon), while the spring is typically formed from a corrosion-resistant alloy like stainless steel, Elgiloy, or Hastelloy. This dual-material design is engineered to create a robust seal for challenging service conditions.
The core principle of a spring energized seal is the combination of materials. It pairs the low friction and extreme chemical and temperature resistance of a polymer jacket with the constant mechanical force of a metal spring, enabling reliable sealing in environments where traditional elastomeric seals would quickly fail.

The Anatomy of a Spring Energized Seal
To understand why specific materials are chosen, you must first understand the function of each component. The seal works as a system where the jacket provides the barrier and the spring provides the energy.
The Polymer Jacket: The Primary Barrier
The jacket is the main body of the seal and is in direct contact with the sealed media and the hardware surfaces. Its U-shaped profile is designed to be pressure-actuated, meaning system pressure pushes against the inside of the "U" to increase the sealing force.
Jackets are machined from tube stock, not injection molded. This allows for precise profiles tailored to specific applications and avoids the stresses inherent in molding. The primary material, PTFE, is chosen for its exceptional properties, including a near-universal chemical inertness and a very wide operating temperature range.
The Metal Spring: The Engine of the Seal
The spring is the energizer that provides the initial seating force when the system is not pressurized. It ensures the seal lips are held firmly against the sealing surfaces, preventing leaks at low pressure or in a vacuum.
Crucially, the spring also compensates for material changes. It counteracts the thermal contraction of the PTFE jacket at cryogenic temperatures, makes up for minor material wear over the seal's life, and accommodates any slight eccentricities in the hardware.
A Closer Look at Material Selection
The true performance of the seal is determined by choosing the right polymer and alloy for the specific operating conditions.
Jacket Materials: Beyond Standard PTFE
While virgin PTFE is the baseline, various fillers are blended in to enhance specific properties.
- Virgin PTFE: The standard choice for its excellent chemical resistance and compliance. Best for applications where purity is critical.
- Filled PTFE: Carbon, graphite, or glass fibers are added to PTFE to increase wear resistance, improve creep resistance under load, and enhance performance at high pressures.
- Other Polymers (e.g., PEEK): For applications with extremely high pressure or where greater rigidity and wear resistance are needed beyond what filled PTFE can offer, other high-performance polymers like PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) may be used.
Spring Materials: Matching Alloy to Environment
The spring alloy must resist corrosion from the sealed media and retain its mechanical properties at the service temperature.
- Stainless Steel (300 Series): The general-purpose workhorse. It offers good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties for a wide range of industrial applications.
- Elgiloy: A cobalt-chromium-nickel alloy known for its excellent strength, fatigue life, and resistance to corrosion. It is a superior choice for cryogenic applications as it retains its spring properties at very low temperatures.
- Hastelloy: A nickel-based superalloy with exceptional resistance to highly corrosive media, such as strong acids and chlorine. It is specified for the most aggressive chemical environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, these seals come with considerations that are critical for successful implementation.
The Cost Factor
Due to the premium materials and the machining process required to create custom profiles, spring energized seals are significantly more expensive than molded elastomeric seals like O-rings. Their use is an investment justified by performance requirements that commodity seals cannot meet.
Installation Sensitivity
Compared to soft elastomers, PTFE jackets are relatively rigid. This makes installation more delicate. Improper handling or the lack of correct installation tools can lead to scratching the jacket's sealing lip, creating a leak path from day one.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The seal's success depends entirely on the correct specification. Choosing the wrong spring material, jacket compound, or spring load for the application can lead to premature failure. A detailed analysis of pressure, temperature, media, and hardware dynamics is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection must be driven by your specific operating conditions, as each material combination is engineered to solve a different problem.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: Prioritize a virgin PTFE jacket for purity or a PEEK jacket for strength, paired with a Hastelloy spring for the most aggressive media.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or high-pressure service: Select a filled-PTFE or PEEK jacket for creep resistance and an Elgiloy or stainless steel spring for mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: An Elgiloy spring is the standard choice to prevent loss of sealing force, combined with a specific grade of PTFE jacket designed for low-temperature flexibility.
- If you need a general-purpose upgrade from elastomers: A standard virgin PTFE jacket energized by a 300-series stainless steel spring is the most common starting point for a broad range of applications.
By understanding how these materials work together, you can specify a seal that delivers reliable performance in your most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Component | Common Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer Jacket | Virgin PTFE, Filled PTFE (carbon, glass), PEEK | Chemical inertness, low friction, wide temperature range, wear resistance |
| Metal Spring | Stainless Steel, Elgiloy, Hastelloy | Provides constant sealing force, corrosion resistance, performs at cryogenic temps |
Need a custom spring energized seal for your demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom spring energized seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical relationship between material selection and performance in extreme environments.
We can help you navigate the complexities of jacket material (PTFE, filled PTFE, PEEK) and spring alloy (stainless steel, Elgiloy, Hastelloy) to create a seal that delivers reliable performance under high pressure, extreme temperatures, or aggressive chemicals.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements for prototypes or high-volume orders. Let our expertise in custom fabrication ensure a perfect seal for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between monoaxial and multidirectional expanded PTFE? Choose the Right ePTFE for Your Seal
- What chemical solvents can be used to clean Teflon residue? The Safer, More Effective Alternatives
- What considerations are important when designing Teflon machined parts? Avoid Failure with Smart PTFE Design
- Can Teflon be machined into different shapes? Precision Techniques for Complex PTFE Parts
- How is TFE (tetrafluoroethylene) produced? A Guide to the High-Temperature Synthesis Process
- What temperature range can PTFE-lined butterfly valves withstand? Ensuring Safe & Reliable Operation
- Are PTFE and PEEK backup rings usually pure, or do they contain fillers? Discover the Role of Fillers in High-Performance Seals
- What are PTFE encapsulated O-rings made of? A Hybrid Seal for Extreme Chemical Resistance



















