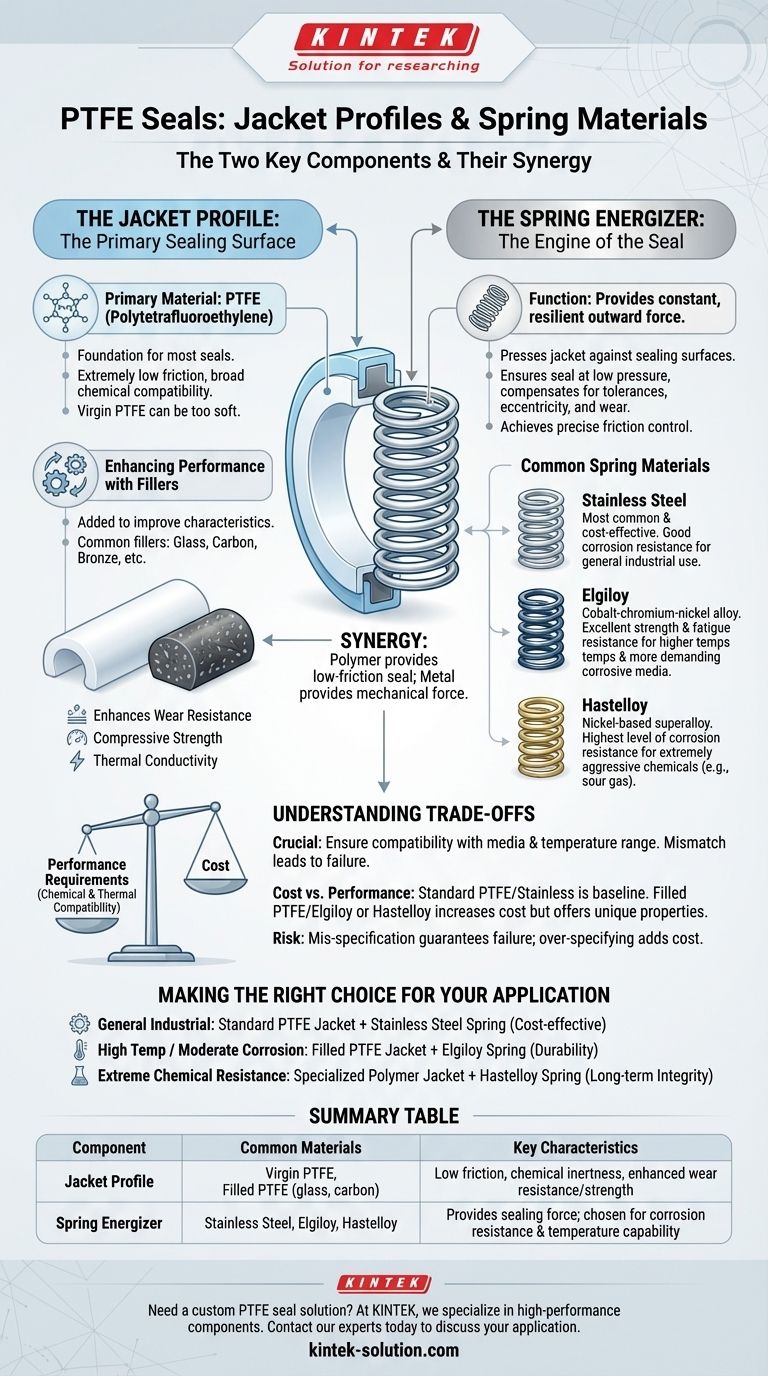
In short, the two key components of a PTFE seal are the jacket and the spring, each made from distinct classes of materials. The seal jacket is typically made from PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) or other high-performance polymers, while the energizing spring is crafted from corrosion-resistant metal alloys, most commonly stainless steel, Elgiloy, or Hastelloy.
The core principle of a spring-energized PTFE seal is the synergy between its two parts. The polymer jacket provides the low-friction, chemically inert sealing surface, while the metal spring provides the constant mechanical force required to maintain a reliable seal across varying pressures and temperatures.
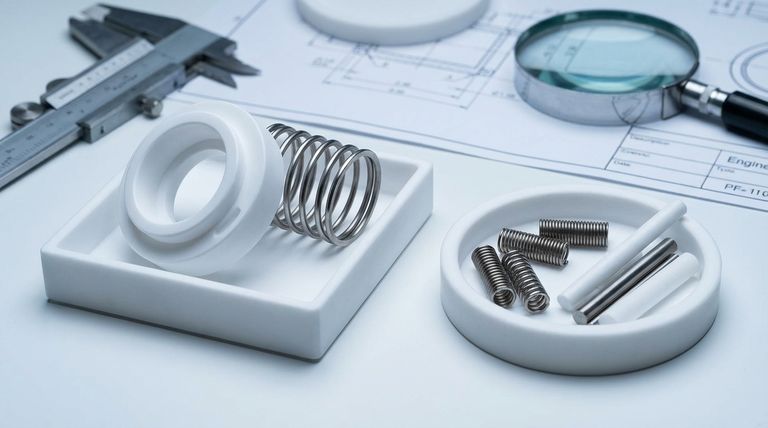

The Role of the Jacket Profile
The jacket is the primary body of the seal that makes contact with the hardware. Its material is chosen for its unique surface properties and its ability to withstand the system's operating environment.
Primary Material: PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the foundation for most seal jackets due to its exceptional properties. It offers an extremely low coefficient of friction and broad chemical compatibility.
However, pure, or "virgin," PTFE can be too soft for demanding applications. To enhance its mechanical properties, it is often blended with fillers.
Enhancing Performance with Fillers
Fillers are added to the base PTFE resin to improve specific characteristics like wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity. The choice of filler depends entirely on the application's demands.
The Function of the Spring Energizer
The internal spring is the engine of the seal. It provides a constant, resilient outward force that presses the jacket lips against the sealing surfaces.
Providing the Initial Sealing Load
The spring is critical for providing the necessary force to create a seal when system pressure is low or absent. This ensures a tight seal from zero pressure up to the system's maximum operating pressure.
Compensating for System Variables
A key function of the spring is to compensate for gland tolerance variations, eccentricity, and normal seal wear over the lifetime of the component. This adaptability ensures consistent performance where a simple O-ring might fail.
Achieving Precise Friction Control
Unlike elastomeric seals, whose sealing force can vary significantly with pressure changes, a spring-energized seal provides a more constant and predictable load. This results in more accurate and stable friction control.
Common Spring Materials
The spring's material must be selected to resist corrosion from the system media and to function reliably at the operating temperature.
Stainless Steel
This is the most common and cost-effective choice for spring energizers. It offers good corrosion resistance in a wide range of general industrial applications.
Elgiloy
For applications involving higher temperatures or more demanding corrosive media, Elgiloy is a superior choice. This cobalt-chromium-nickel alloy provides excellent strength and fatigue resistance.
Hastelloy
When a seal must operate in extremely aggressive chemical environments, such as sour gas or concentrated acids, Hastelloy is the material of choice. This nickel-based superalloy offers the highest level of corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right material combination is a balance between performance requirements and cost.
Chemical and Thermal Compatibility
The most critical factor is ensuring that both the jacket polymer and the spring alloy are fully compatible with the system's chemical media and temperature range. A mismatch will lead to rapid seal failure.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a clear cost progression in these materials. A standard PTFE seal with a stainless steel spring is a baseline. Moving to a filled PTFE and an Elgiloy or Hastelloy spring significantly increases the cost but is non-negotiable for applications that demand their unique properties.
The Risk of Mis-Specification
Choosing a material that is insufficient for the application (e.g., stainless steel in a highly corrosive fluid) guarantees failure. Conversely, over-specifying (e.g., using Hastelloy for a simple hydraulic application) adds unnecessary cost to the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is general industrial use: A standard PTFE jacket with a stainless steel spring offers a reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high temperature or moderate corrosion: A filled-PTFE jacket paired with an Elgiloy spring provides the necessary durability and resistance.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: A specialized polymer jacket with a Hastelloy spring is the only choice to ensure long-term seal integrity.
Ultimately, engineering a reliable seal is about a precise match between the material system and the application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Component | Common Materials | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Jacket Profile | Virgin PTFE, Filled PTFE (e.g., with glass, carbon) | Low friction, chemical inertness, enhanced wear resistance/strength with fillers |
| Spring Energizer | Stainless Steel, Elgiloy, Hastelloy | Provides sealing force; chosen for corrosion resistance and temperature capability |
Need a custom PTFE seal solution for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including precision spring-energized seals. We understand that material selection is critical for reliability in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial environments.
We can help you navigate the trade-offs between cost and performance, ensuring the jacket and spring materials are perfectly matched to your specific chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a seal engineered for peak performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of PTFE oil seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How do PTFE O-rings compare to Teflon O-rings? The Real Difference Between Solid and Encapsulated Designs
- Do PTFE gaskets require lubrication? Trust the Material for a Reliable Seal
- What are the temperature limits for PTFE packing performance? Withstand -200°C to 260°C for Reliable Sealing
- What cost advantages do PTFE lined butterfly valves offer? Achieve Superior Corrosion Resistance at Lower Costs
- What are the key design features of PTFE bushings? Achieve Maintenance-Free, High-Performance Bearing Solutions
- How do PTFE and NBR oil seals compare in terms of chemical resistance? A Guide to Superior Seal Performance
- What is Teflon AF and what are its optical properties? Achieve Superior Optical Clarity with UV Resistance



















