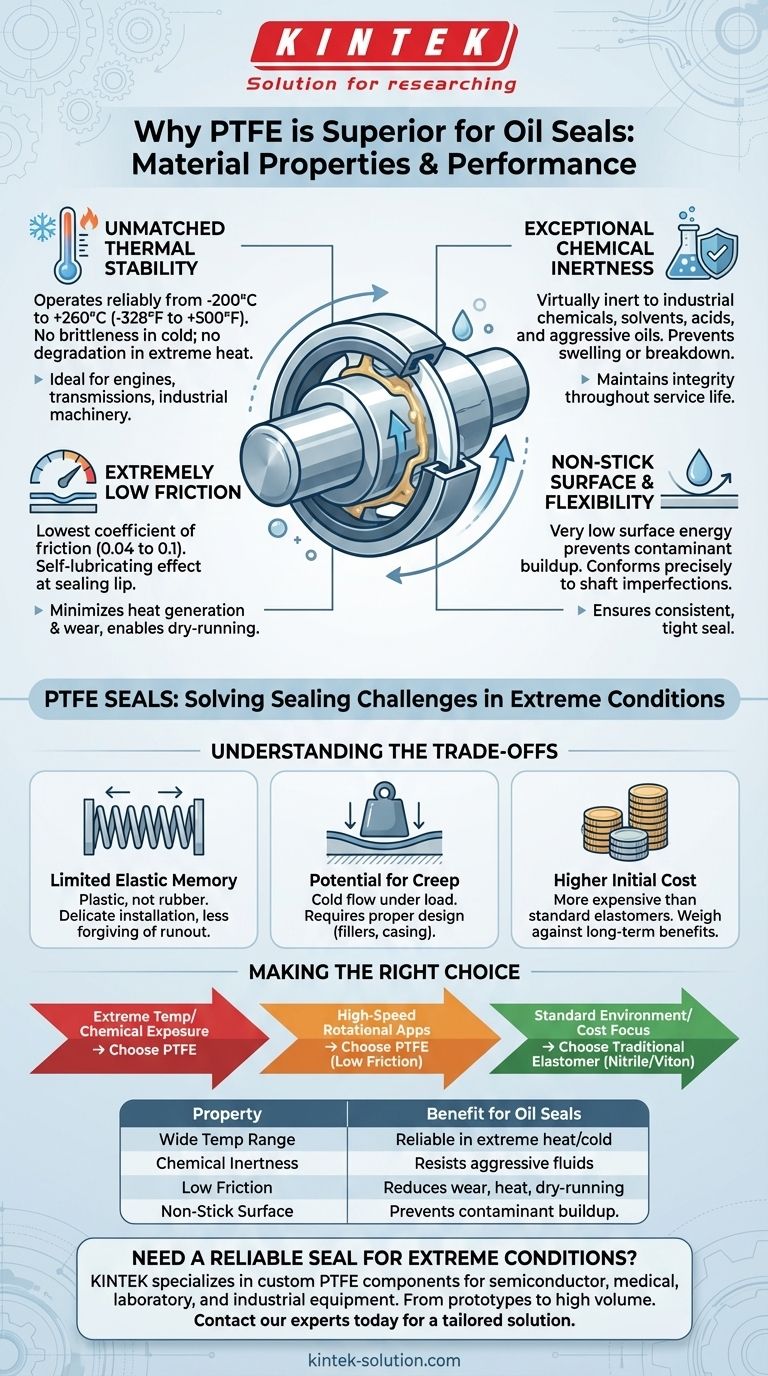
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a superior material for oil seals due to a unique combination of four critical properties: an extremely wide operating temperature range, near-universal chemical resistance, an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, and a non-stick surface. These characteristics allow PTFE to maintain a reliable seal in demanding environments where traditional elastomeric materials would quickly degrade.
While many materials can form a basic seal, PTFE's distinct properties solve the engineering challenge of sealing dynamic systems under extreme conditions. Its ability to withstand high heat, aggressive fluids, and high speeds without significant wear sets it apart as a premier choice for critical applications.

The Core Properties That Define PTFE Seals
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at how each of its core material properties translates into a direct performance advantage in an oil seal application.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
PTFE operates reliably across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
This stability means the seal will not become brittle at low temperatures or soften and degrade at the high temperatures found in engines, transmissions, and industrial machinery.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
The strength of the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond gives PTFE its renowned chemical resistance. It is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and oils.
This property ensures the seal will not swell, harden, or break down when exposed to aggressive fluids, maintaining its integrity and sealing performance over its entire service life.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often cited as 0.04 to 0.1. This creates a self-lubricating effect at the sealing lip.
This low friction minimizes heat generation from the rotating shaft, reduces wear on both the seal and the shaft, and lowers the energy required to turn the shaft. It also allows PTFE seals to perform well in applications with minimal lubrication or even in dry-running conditions.
Non-Stick Surface and Flexibility
PTFE's very low surface energy gives it a non-stick quality, which prevents contaminants or system media from adhering to the seal lip and causing wear.
Combined with its inherent flexibility, this allows the seal to conform precisely to the shaft's surface, ensuring a tight and reliable seal even on shafts with minor imperfections.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE
No material is perfect for every situation. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging the limitations and design considerations associated with PTFE.
Limited Elastic Memory
Unlike traditional rubber elastomers, PTFE has poor "elastic memory." It is a plastic, not a rubber, meaning it does not spring back to its original shape as effectively after being stretched.
This can make installation more delicate and means it may be less forgiving of high levels of shaft runout or misalignment compared to a highly elastic material like nitrile.
Potential for Creep
Under sustained load and temperature, PTFE can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow. This is a slow, permanent deformation of the material.
Proper seal design, often involving the use of fillers (like carbon or glass fiber) and stainless steel casing, is critical to manage this property and ensure long-term sealing pressure.
Higher Initial Cost
As a high-performance polymer, PTFE and PTFE-filled compounds are generally more expensive than common commodity elastomers like Nitrile (Buna-N).
The higher upfront cost must be weighed against the benefits of longer service life, reduced maintenance, and superior performance in harsh conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal material depends entirely on the demands of your specific operating environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature or chemical exposure: PTFE is the definitive choice, providing reliability where standard elastomers would experience catastrophic failure.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotational applications: PTFE's low-friction nature is ideal, as it minimizes heat buildup and abrasive wear on the shaft.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a standard environment: A traditional elastomeric seal, such as Nitrile or Viton, is likely the more economical and suitable option.
By understanding these core properties and their practical trade-offs, you can confidently select the right sealing material for even the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Oil Seals |
|---|---|
| Wide Temp Range (-200°C to 260°C) | Reliable performance in extreme heat or cold without degrading. |
| Exceptional Chemical Inertness | Resists swelling or breakdown from aggressive oils, acids, and solvents. |
| Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction (0.04-0.1) | Reduces wear, minimizes heat, and allows for dry-running capability. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents contaminant buildup for a consistent, reliable seal. |
Need a reliable seal for extreme conditions?
PTFE's unique properties solve the toughest sealing challenges in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial equipment. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensuring your application performs reliably under pressure, heat, and chemical exposure.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does Reinforced PTFE differ from Virgin PTFE? Unlock the Right Material for Your Application
- In which industries are PTFE O-Rings commonly used? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What makes Teflon suitable for use in bearings and similar applications? Discover Its Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Advantages
- How do PTFE oil seals compensate for the material's low elasticity? Achieve Superior Sealing in Harsh Environments
- What are some common applications of Teflon? From Cookware to Aerospace Components
- How should PTFE-lined valves be maintained for optimal performance? Ensure Long-Term Reliability & Prevent Costly Downtime
- What configurations are available for PTFE rotary shaft seals? Optimize Performance with Lip, Shell & Material Options
- What are the limitations of machining Teflon (PTFE)? Overcome Challenges for Precision Parts



















