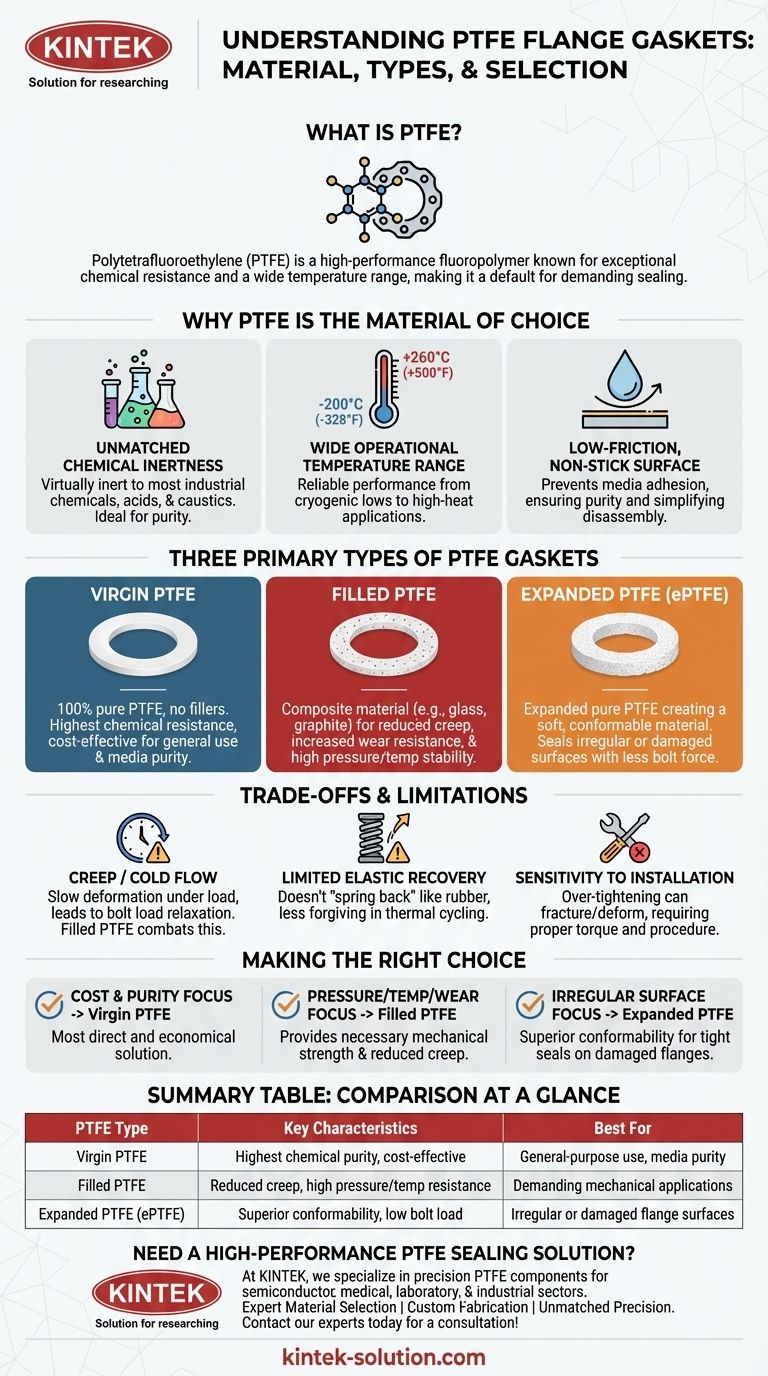
At its core, a PTFE flange gasket is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene, a high-performance fluoropolymer. This synthetic material is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance and its ability to function across a vast temperature range, making it a default choice for demanding industrial sealing applications.
While all PTFE gaskets share a common base material, the critical distinction lies in its form. Understanding the three primary types—Virgin, Filled, and Expanded—is the key to selecting the right gasket for your specific operational pressure, temperature, and surface conditions.

What Makes PTFE the Material of Choice?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not just a single-benefit material. Its selection for critical sealing is based on a combination of powerful properties that work together to create a reliable barrier.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, acids, and caustics. This makes it an essential material for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage, where media purity and gasket longevity are paramount.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
PTFE gaskets perform reliably in extreme temperature conditions, from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat applications of +260°C (+500°F). This versatility allows for standardization across many different plant processes.
Low-Friction, Non-Stick Surface
The material's inherently low coefficient of friction and non-stick nature are highly valuable. This prevents process media from adhering to the gasket surface, ensuring purity, simplifying flange disassembly, and minimizing friction in any dynamic sealing applications.
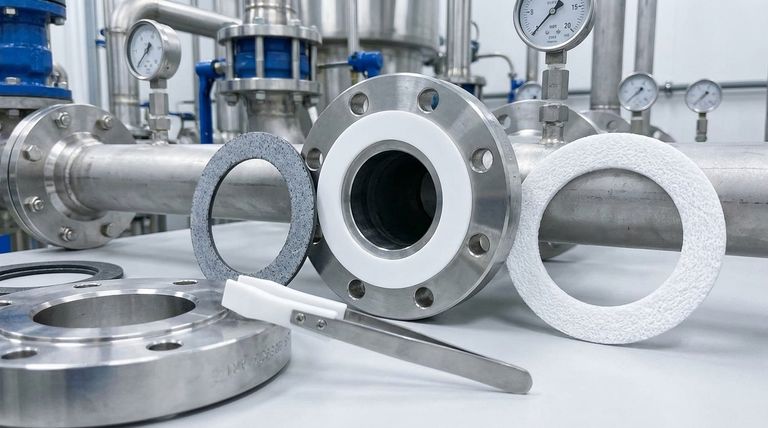
Understanding the Three Primary Types of PTFE Gaskets
The term "PTFE gasket" is a category, not a single product. The performance of the seal is dictated by which of the three main variations you choose.
Virgin PTFE: The Pure Standard
This is 100% pure PTFE, manufactured without any filler materials. It offers the highest chemical resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it a cost-effective choice for general-purpose use, particularly where media purity is the top concern.
Filled PTFE: Enhanced for Performance
Filled PTFE gaskets are composite materials where a substance is added to Virgin PTFE to improve specific mechanical properties. Common fillers like glass, graphite, or carbon are used to significantly reduce creep, increase wear resistance, and improve stability under high pressure and temperature.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE): The Conformable Solution
Expanded PTFE is created by expanding Virgin PTFE, which creates a soft, highly conformable material. Its key advantage is its ability to create a tight seal on irregular, pitted, or damaged flange surfaces with less bolt force, all while retaining the exceptional chemical resistance of pure PTFE.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its inherent limitations is critical for proper application and avoiding premature seal failure.
The Challenge of "Creep" or Cold Flow
PTFE, especially the virgin type, is susceptible to creep—a slow deformation under sustained compressive load. This can cause the bolt load to relax over time, potentially leading to leaks. Filled PTFE grades are specifically designed to combat this weakness.
Limited Elastic Recovery
Unlike rubber elastomers, PTFE does not "spring back" well after being compressed. This means it is less forgiving in systems with significant thermal cycling or pressure fluctuations, as it may not adapt to the changing flange gap.
Sensitivity to Installation
The mechanical properties of PTFE gaskets demand proper installation. Over-tightening is a common mistake that can fracture or permanently deform the gasket, especially with virgin PTFE, leading to an immediate loss of sealing capability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct PTFE gasket type is critical for ensuring a reliable, long-lasting seal in your system. Your decision should be guided by your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and general chemical service: Virgin PTFE is your most direct and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is high pressure, temperature, or wear resistance: A Filled PTFE gasket provides the necessary mechanical strength and reduced creep.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular, old, or damaged flange surfaces: Expanded PTFE offers the superior conformability needed to ensure a tight seal.
By matching the specific type of PTFE to your operational demands, you can leverage its unique properties for a secure and durable sealing solution.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Highest chemical purity, cost-effective | General-purpose use, media purity |
| Filled PTFE | Reduced creep, high pressure/temperature resistance | Demanding mechanical applications |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Superior conformability, low bolt load | Irregular or damaged flange surfaces |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Sealing Solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide the right PTFE material for your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical resistance requirements.
We offer:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance on choosing between Virgin, Filled, and Expanded PTFE for optimal performance.
- Custom Fabrication: From initial prototypes to high-volume production runs.
- Unmatched Precision: Quality components designed for reliability and longevity in your most critical applications.
Let us help you solve your toughest sealing challenges. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PTFE-encapsulated O-rings? Superior Sealing for Harsh Chemical & High-Temp Environments
- How does the compressibility of ePTFE gaskets benefit sealing applications? Achieve Superior, Leak-Free Seals
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of PTFE Lined Plug Valves? Weighing Corrosion Resistance vs. Operational Demands
- Why are PTFE O-Rings considered versatile for low-pressure, static applications? Unlock Superior Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What technical services are provided for PTFE product development? A Guide from Concept to Component
- What are the key properties of Teflon sheets? A Guide to PTFE's Versatility
- What types of working conditions can PTFE seals adapt to? Conquer Extreme Heat, Cold, and Chemicals
- How are Teflon rods applied in the automotive and aerospace industries? Solve Friction, Heat, and Chemical Challenges



















